Understanding Causes, Symptoms &Treatments of VAGINAL INFECTIONS
vaginal infections
Vaginal infections are a common issue among women and can be caused by a variety of factors. These infections can be mild or severe and can range from uncomfortable to even painful. Knowing the symptoms, causes, and treatments of vaginal infections can help you identify and manage the issue if you experience it. We will provide an overview of the most common types of vaginal infections and how to treat them. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
The vagina
Causes of vaginal infections
Types of vaginal infections
Symptoms of vaginal infections
How vaginal infections are diagnosed
Yeast infection
Bacterial vaginosis
Viral vaginosis
Trichomoniasis
Clamydia
Gonorrhea
Vaginitis
Preventing vaginal infections
Best foods to eat
Foods to avoid
Vaginal infections in pregnancy
Overview of the vagina
Welcome to the world of the vagina! This amazing organ is both complex and versatile, and its role in the human body is essential and far-reaching. The vagina is one of the most important and fascinating parts of the female anatomy. It is a muscular, elastic canal connecting the cervix to the outer vulva, providing a path for menstrual flow and sexual intercourse. The vagina is made up of several layers of tissue that protect and lubricate the area, making it an ideal environment for sexual activities. The walls of the vagina also contain numerous nerve endings that can provide intense pleasure during sexual stimulation. The vagina is an incredibly complex and important part of the female body, and understanding its anatomy and function is key to understanding a woman’s health and wellbeing. We will now explore the anatomy of the vagina, its functions, and the impact it has on a person’s physical, mental, and emotional wellbeing.
Causes of vaginal infections
Sexually transmitted infection (STIs): Certain STIs, such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and genital herpes, can cause vaginal infections. These infections are typically transmitted through sexual contact and can lead to inflammation and discomfort in the vaginal area.
Douching, or rinsing the vagina with water or other liquid: Douching involves rinsing the vagina with water or other solutions. While some people may do this for hygiene purposes, it can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and pH levels in the vagina, making it more susceptible to infections. Douching can wash away the beneficial bacteria that help maintain vaginal health, leading to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria or yeast.
Changes in the level of hormones in the woman: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those that occur during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, menopause, or while taking hormonal contraceptives, can impact the vaginal environment. Changes in hormone levels can alter the pH balance of the vagina, making it more prone to infections.
Antibiotic Use: Antibiotics are medications used to treat bacterial infections. However, they can also kill off the beneficial bacteria in the vagina, disrupting its natural balance. This disruption can allow harmful bacteria or yeast to overgrow, leading to a vaginal infection such as bacterial vaginosis or a yeast infection.
Vaginal Penetration: Sexual activity, particularly vaginal penetration, can introduce bacteria or other microorganisms into the vagina. If these microorganisms are pathogenic or if the vagina’s natural defenses are compromised, it can result in an infection.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy causes various hormonal changes in the body, which can affect the vaginal environment. Increased levels of estrogen during pregnancy can lead to changes in vaginal pH and increased vaginal discharge, making pregnant individuals more susceptible to vaginal infections.
Frequent Elevation of blood sugar: High blood sugar levels, such as those seen in individuals with poorly controlled diabetes, can create an environment conducive to yeast overgrowth. Yeast infections, particularly caused by the fungus Candida, are more common in individuals with diabetes due to the excess sugar in their bodily fluids, providing an ideal environment for yeast to thrive.
Symptoms of vaginal infections
Here is a list of symptoms and a breakdown of what each symptom might indicate. It’s essential for individuals experiencing any of these symptoms to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Many vaginal infections or conditions can be effectively treated with medication or other interventions, but accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management.
Burning sensation to the vagina: A burning sensation in the vagina can be caused by several factors, including yeast infections (caused by Candida overgrowth), bacterial vaginosis (resulting from an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina), or sexually transmitted infections (such as trichomoniasis or genital herpes). It can also occur due to irritation from soaps, perfumes, or other products applied to the genital area.
Vaginal itching: Itching in the vaginal area is often associated with yeast infections, which can cause intense itching and discomfort. However, it can also be a symptom of other conditions such as bacterial vaginosis or sexually transmitted infections. Additionally, allergic reactions to certain products or materials can lead to vaginal itching.
Unpleasant odor to the vagina: A foul or unpleasant odor emanating from the vagina can be a sign of bacterial vaginosis, particularly if the odor is fishy or stronger after sexual intercourse. It can also be caused by a sexually transmitted infection or poor hygiene practices. In some cases, changes in vaginal odor can occur due to hormonal fluctuations.
Abnormal vaginal discharge:Changes in vaginal discharge can indicate various vaginal infections or conditions. A thick, white, cottage cheese-like discharge is often a sign of a yeast infection. Grayish or greenish discharge with a foul odor may indicate bacterial vaginosis or a sexually transmitted infection. Watery discharge can be a symptom of trichomoniasis. Changes in discharge consistency, color, or odor should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Pain to the vagina: Pain in the vaginal area can have multiple causes, including infections (such as yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, or sexually transmitted infections), vaginal dryness (often associated with hormonal changes or menopause), vaginal tears or trauma (from sexual intercourse or other activities), or conditions such as vulvodynia or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Persistent or severe vaginal pain should be assessed by a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
How vaginal infections are diagnosed
A thorough medical history will be obtained
A physical examination will be conducted
A vaginal exam will be conducted
A smooth, tube-shaped tool (speculum) will be inserted into the vagina to hold it open so they can see inside
A special swab will be used to collect a sample of secretions from the vagina
The specimen collected from the vagina will be sent to the lab for testing
A urine test will be done
It is wise to abstain from intercourse at least 24 hours before the exam
Types of Vaginal Infections
Trichomoniasis
Sexually transmitted infection
VAGINOSIS
Vaginosis is a common and often uncomfortable medical condition that affects millions of women around the world. It occurs when the balance of bacteria in the vagina is disrupted, causing an overgrowth of certain types of bacteria. Symptoms of vaginosis can include a grayish-white discharge, a strong fish-like odor, burning, itching and irritation. Vaginosis can be treated with antibiotics, but it is important to understand the causes and risk factors of this condition in order to prevent recurrence. There are two types of vaginosis: bacterial vaginosis and viral vaginosis.
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) is a common condition among women, caused by an imbalance (overgrowth) of the bacteria in the vagina. It can cause a range of symptoms, such as a strong, fishy odor, itching, irritation, and burning. BV is usually easily treated with antibiotics, but it is important to note that it can recur. Taking preventative measures such as avoiding douching or using scented products can help to reduce the likelihood of recurring BV.
Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis
Thick or whitish vaginal discharge
Slippery and clear vaginal discharge
Fishy odor to the vagina
Viral vaginosis
Vaginal Vaginosis (VV) is a common health issue that affects many women. It is caused by an overgrowth of bacteria in the vagina, leading to odor, discharge and itchiness. If left untreated, it can cause further health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility. Fortunately, VV can be successfully treated with a variety of medications and lifestyle changes. With the right medical care and advice, it is possible to manage VV and live a healthy and fulfilling life.
Vaginitis
Vaginitis is a common condition that affects women of all ages. It is characterized by inflammation in the vaginal area, which can result in symptoms such as itching, discharge, burning sensation, and odor. In some cases, vaginitis can be caused by bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections, while in other cases it may be a result of an allergic reaction or an underlying health condition. Treatment options vary depending on the cause of the vaginitis, so it is important to consult a doctor if your symptoms persist. Other causes of vaginitis include:
An allergic reaction or irritation to skin around the vagina caused by
- Scented tampons
- Perfumed soaps
- Fabric softeners
- Sprays or other chemicals
- Clothing
- Latex
There are several types of vaginitis, each with its own causes and characteristics:
- Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): BV occurs when there is an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina, leading to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria. Symptoms may include a thin, grayish-white vaginal discharge with a fishy odor, itching, and irritation. BV is not typically associated with significant vaginal redness or swelling.
- Yeast Infection (Candidiasis): Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of Candida, a type of fungus that naturally resides in the vagina. Symptoms often include a thick, white vaginal discharge resembling cottage cheese, itching, redness, and swelling of the vulva and vagina. Yeast infections can also cause a burning sensation, especially during urination or sexual intercourse.
- Trichomoniasis: Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. Symptoms may include a frothy, yellow-green vaginal discharge with a foul odor, itching, redness, and swelling of the vulva and vagina. Trichomoniasis is typically associated with significant vaginal irritation and discomfort.
- Atrophic Vaginitis: Atrophic vaginitis occurs when there is thinning, drying, and inflammation of the vaginal walls, often due to decreased estrogen levels, particularly during menopause. Symptoms may include vaginal dryness, itching, burning, and pain during sexual intercourse.
- Non-Infectious Vaginitis: Non-infectious vaginitis can result from various factors such as allergic reactions to certain products (e.g., soaps, detergents, latex), irritants (e.g., perfumes, douches), or hormonal changes. Symptoms may include vaginal itching, redness, swelling, and discomfort.
The treatment for vaginitis depends on the underlying cause. Bacterial vaginosis is typically treated with antibiotics, yeast infections with antifungal medications, and trichomoniasis with antibiotics. Atrophic vaginitis may be managed with hormone therapy or vaginal moisturizers. Non-infectious vaginitis may require avoiding irritants or allergens and practicing good hygiene.
Yeast Infection
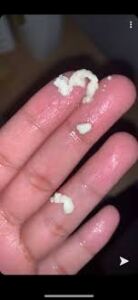
Yeast infections are a common and uncomfortable problem that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. Generally caused by an overgrowth of a type of fungus known as Candida, yeast infections are caused when the fungus overgrows in the body, leading to symptoms such as itching, burning, and soreness. They can be uncomfortable and difficult to treat, but there are a variety of medications, creams, and natural remedies available to help alleviate the symptoms.
Symptoms yeast infection
-
Thick, White Vaginal Discharge Resembling Cottage Cheese: Yeast infections often cause a characteristic discharge that is thick, white, and has a texture resembling cottage cheese. This discharge is typically odorless but may be accompanied by other symptoms.
- Itching to the Vagina: One of the hallmark symptoms of a yeast infection is vaginal itching. The itching can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by irritation or a burning sensation.
- Redness and Swelling of the Vulva and Vagina: Yeast infections can cause inflammation of the vulva and vaginal tissues, leading to redness, swelling, and discomfort in the affected area. The skin may appear irritated or inflamed.
- Burning Sensation to the Vagina When Urinating: Some individuals with yeast infections may experience a burning sensation or discomfort when urinating. This symptom can occur due to irritation of the inflamed vaginal tissues or contact with urine.
It’s important to note that while these symptoms are characteristic of a yeast infection, they can also indicate other vaginal infections or conditions. Therefore, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment for yeast infections typically involves antifungal medications, which may be available over-the-counter or prescribed by a healthcare provider, depending on the severity of the infection. In addition to medication, practicing good hygiene, wearing breathable underwear, and avoiding irritants can help alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrent infections.
How to prevent vaginal infections
Here are some excellent preventive measures to maintain vaginal health and reduce the risk of vaginal infections.
-
Choose Breathable Underwear: Opt for cotton underwear over synthetic materials to allow better airflow and reduce moisture buildup, which can create an environment conducive to bacterial or yeast overgrowth.
- Avoid Damp Clothing: Change out of wet or sweaty clothing promptly to prevent moisture from lingering in the vaginal area, as excess moisture can promote the growth of bacteria or fungi.
- Moderate Sugar Intake and Consume Probiotics: Limiting sugary foods and incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt into your diet can help maintain a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria in the vagina.
- Avoid Irritants: Refrain from using perfumed products or harsh cleansers on the vagina, as these can disrupt the natural pH and irritate the delicate vaginal tissue.
- Don’t Douche: Douching can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and increase the risk of infections. It’s best to avoid douching altogether.
- Practice Safe Sex: Use condoms to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which can lead to vaginal infections. Limiting sexual partners can also lower the risk of exposure to STIs.
- Avoid Bath Products: Steer clear of bubble baths, bath oils, and talcum powder in the genital area, as these products can irritate the vagina and disrupt its natural balance.
- Proper Wiping Technique: After using the restroom, wipe from front to back to prevent bacteria from the anus from entering the vagina and causing infections.
- Regular Changing of Menstrual Products: Change tampons and sanitary napkins frequently to prevent the buildup of bacteria and reduce the risk of infections.
- Don’t Leave Tampons In Overnight: Leaving tampons in for extended periods can increase the risk of toxic shock syndrome and other infections. Change tampons every few hours, even overnight.
- Avoid Scratching: Refrain from scratching the genital area to minimize irritation and reduce the risk of introducing bacteria from the nails into the vagina.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Clean the external genital area with water and mild, unscented soap, and pat dry thoroughly to maintain cleanliness and prevent infections.
- Choose Comfortable Clothing: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing made from natural fibers like cotton to allow air circulation and prevent moisture buildup.
- Use Lubrication: During sexual activity, use lubrication to reduce friction and prevent irritation of the vaginal tissue.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health, including vaginal health.
-
Avoid Rough Fabrics: Avoid using rough fabrics or vigorous rubbing on the vaginal area, as this can cause irritation and discomfort.
Best foods to eat
Best foods and natural remedies can potentially help support vaginal health and prevent infections. Here’s an overview:
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil contains lauric acid, which has antimicrobial properties that may help prevent and treat vaginal infections. Lauric acid can disrupt the cell membranes of pathogens, including bacteria and fungi, potentially reducing their ability to grow and cause infections. Incorporating coconut oil into your diet or using it topically may help maintain vaginal health.
- Foods Containing Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in the body, including the vagina. Yogurt is a well-known source of probiotics, particularly strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus, which are beneficial for vaginal health. Similarly, cranberry products, such as unsweetened cranberry juice or supplements, may help promote urinary tract health and prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Herbs and Spices: Certain herbs and spices, such as garlic and curcumin (the active compound in turmeric), possess antimicrobial and antifungal properties that may help combat vaginal infections. Garlic contains allicin, a compound with potent antimicrobial properties that can help fight off infections. Curcumin has been shown to have antifungal effects against Candida species, which are commonly associated with yeast infections.
Incorporating these foods and remedies into your diet may help support vaginal health and reduce the risk of infections. However, it’s essential to remember that individual responses may vary, and these remedies should not replace medical treatment for existing infections. If you have a vaginal infection or persistent symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, maintaining good hygiene practices and avoiding irritants can further support vaginal health.
Foods to avoid eating
The listed foods can potentially contribute to yeast overgrowth or exacerbate existing yeast infections due to their impact on blood sugar levels, immune function, or gut health. Here’s an explanation of how each category of food may affect yeast infections:
- Foods containing Sugar: Yeast, particularly Candida, feeds on sugar. Consuming foods high in sugar can promote yeast overgrowth, worsening symptoms of yeast infections. This includes sugary snacks, desserts, sweetened beverages, and processed foods with added sugars.
- White and Refined Flour: Refined carbohydrates, such as white flour, are quickly converted into sugar in the body. Like sugar, they can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels, which may fuel yeast growth. Foods made with white flour, such as white bread, pasta, and pastries, should be limited if you have a yeast infection.
- Gluten-rich Food Items: Some individuals with yeast infections find that gluten-containing foods exacerbate their symptoms. While research on the relationship between gluten and yeast infections is limited, some people report symptom improvement after reducing gluten intake. Gluten is found in wheat, barley, rye, and their derivatives.
- Dairy Products Including Milk: Dairy products, particularly milk, may contain lactose, a type of sugar. Consuming dairy products high in lactose can contribute to increased sugar intake, potentially promoting yeast overgrowth. Some individuals with yeast infections find that reducing dairy intake helps alleviate symptoms, although this may vary from person to person.
- Alcohol: Alcohol can disrupt gut health and weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to yeast infections. Additionally, many alcoholic beverages contain sugar, which can further promote yeast overgrowth. Beer, in particular, may contain yeast and carbohydrates that can exacerbate yeast infections.
- Caffeine: While caffeine itself may not directly promote yeast overgrowth, some caffeinated beverages, such as coffee and certain teas, may contain sugar or artificial sweeteners that can contribute to yeast infections. Additionally, caffeine can disrupt sleep patterns and stress the body, potentially weakening the immune system’s ability to fight off infections.
-
Fermented Foods Such as Beer: Fermented foods like beer may contain yeast and carbohydrates that can exacerbate yeast infections. While some fermented foods, such as yogurt with live cultures, can be beneficial for gut health, others may contain yeasts or sugars that could worsen yeast infection symptoms.
Vaginal infections and pregnancy
Vaginal infections can be a common issue during pregnancy, but they don’t have to be. With the right precautions, you can reduce the risk of vaginal infections and make sure that your pregnancy is a healthy and safe one. In this article, we’ll take a look at the different types of vaginal infections that can occur during pregnancy, the symptoms to look out for, and how to reduce your risk of developing an infection.
-
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): Bacterial vaginosis is linked to an increased risk of preterm delivery. It can cause inflammation in the cervix and increase the likelihood of premature rupture of membranes, leading to preterm labor.
- Chlamydia: Chlamydia infection during pregnancy can raise the risk of preterm delivery. Additionally, if left untreated, it can be transmitted from the mother to the baby during childbirth, leading to eye infections (conjunctivitis) and pneumonia in the newborn.
- Gonorrhea: Gonorrhea infection during pregnancy can increase the risk of miscarriage, preterm delivery, and low birth weight. If passed to the baby during childbirth, it can cause serious complications such as eye infections (ophthalmia neonatorum) and even blindness.
- Genital Herpes: Genital herpes infection can be transmitted to the baby during vaginal delivery if the mother is experiencing an active outbreak. This can lead to neonatal herpes, a serious and potentially life-threatening condition in newborns.
- Trichomoniasis: Trichomoniasis in pregnant individuals has been associated with an increased risk of preterm delivery and low birth weight. The infection can cause inflammation of the cervix and the fetal membranes, potentially triggering preterm labor.
Pregnant individuals are typically screened for these infections during prenatal care to detect and treat them promptly. Treatment aims to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes for both the mother and the baby. It’s essential for pregnant individuals to attend regular prenatal check-ups and promptly report any symptoms or concerns to their healthcare provider to ensure timely diagnosis and management of vaginal infections during pregnancy.
Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
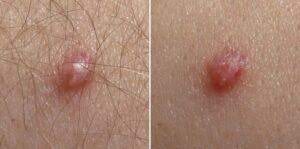
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the United States. HSV is responsible for causing both oral and genital herpes, two highly contagious and uncomfortable skin conditions. HSV is caused by contact with an infected person, usually through sexual contact. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of HSV and to take the necessary steps to reduce your risk of infection.
This virus is uncurable
Symptoms disappear after 19 days but the person still remains infectious
Manifestations of HSV
Pain to the vagina
Painful sores or lesions to the vagina or vulva which can spread through oral sex
Lesions can be seen during a vaginal examination by the healthcare provider
Burning or pain while urinating
Swollen lymph nodes
Swelling of the vulva
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
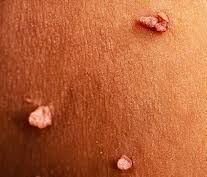
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a highly contagious virus that is spread through skin-to-skin contact. It is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) and affects both men and women. Most commonly, HPV is transmitted through sexual activity, but it can also be spread through any direct skin-to-skin contact. HPV can cause a range of health problems, including genital warts and certain types of cancers. It is uncurable and can also cause cell changes that may lead to cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancers in women, and penile and anal cancer in men. Vaccines are available to help protect against some types of HPV. The virus is detected during a Pap smear. It is important to get tested for HPV regularly and to practice safe sex to reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
Manifestations of HPV
Growth of a painful condyloma or wart on the genital area (rectum, groin, vulva or vagina)
The warts are usually white to gray, pink or purple in color
Warts are not usually visible
Trichomoniasis
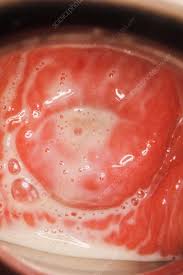
Trichomoniasis, also known as “trich”, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a parasite. It is one of the most common STIs, and it can be spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Symptoms of trichomoniasis can include genital itching, burning, and redness, as well as a foul-smelling discharge. In some cases, trichomoniasis may not cause any symptoms at all. If left untreated, trichomoniasis can increase the risk of HIV transmission and other STIs. Treatment with antibiotics can help cure trichomoniasis and prevent it from spreading to others.
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis
Burning sensation to the vagina
Irritation to the vagina
Redness of the vulva
Swelling of the vulva
Yellow-gray or greenish vaginal discharge
Foul or fishy odor to the vagina
Pain to the vagina during urination and intercourse
Itching and soreness to the vagina and vulva
Discomfort to the lower abdomen
Chlamydia Vaginitis
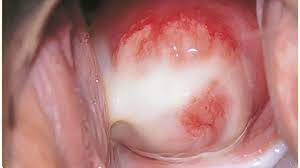
Chlamydia Vaginitis is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that affects the vagina and can cause painful, uncomfortable symptoms. It is caused by a bacteria called Chlamydia trachomatis and can be spread from person to person through unprotected sexual activity. Symptoms of Chlamydia Vaginitis can include itching and burning in the vaginal area, pain during urination, and abnormal discharge from the vagina. It is important to get tested for the infection if you have any symptoms and to practice safe sex with all partners to reduce the risk of infection. Treatment for Chlamydia Vaginitis usually involves a course of antibiotics.
Manifestations of Chlamydia
Inflammation of the vagina
Abnormal vaginal discharge
Spotting between periods or after intercourse
The woman may not present any symptoms
Pain to the lower abdomen and pelvic region
Can lead to fertility problems
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is an extremely common infection, affecting millions of people worldwide each year. It is spread through contact with an infected person’s genitals, anus, or mouth. If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to serious health complications including pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and life-threatening ectopic pregnancies. It is important to get tested and treated as soon as possible if you think you may have been exposed.
It is highly contagious
Woman with gonorrhea may also have chlamydia
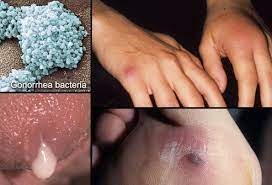
Symptoms of gonorrhea
Abnormal vaginal discharge
Vaginal pain during urination
Vaginal pain during intercourse
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

