understanding Vaginal Discharge: Normal vs. Abnormal – Tips for Women
Vaginal discharge is a natural occurrence for all women and an important part of a healthy reproductive system. This discharge is composed of secretions from the cervix, vagina and other glands in the reproductive system. The color, consistency and amount of discharge can indicate different things about your reproductive health. It is important to understand the different types of vaginal discharge and what they mean to ensure that your reproductive system is functioning properly. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
Overview of vaginal discharge
Normal vaginal discharge
Abnormal vaginal discharge
How to assess the vaginal discharge
Causes of abnormal vaginal discharge
Types of abnormal discharge
Ways to keep the vagina healthy
When to seek urgent medical care
VAGINAL DISCHARGE
The housekeeper of the reproductive system, which plays a crucial role in maintaining vaginal health.
The discharge produced by the cervix, serves as a natural cleanser, helping to remove bacteria and dead cells from the vagina.
By carrying away these potentially harmful substances, the discharge helps prevent infections and maintains the pH balance of the vaginal environment, contributing to overall reproductive health.
HOW TO CHECK THE VAGINAL DISCHARGE
-
Wash and dry the hands: Begin by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water, then dry them completely.
- Use tissue to wipe the vagina: Use clean tissue to gently wipe the vaginal area, removing any external discharge.
- Assess the color, smell, and characteristics: Observe the color, smell, and consistency of the discharge. Note any unusual or abnormal characteristics.
- Assess the discharge on the underwear: Check the underwear for any visible discharge, noting its color and quantity.
- Collect some discharge from inside the vagina with the finger: Insert a clean finger into the vagina to collect a small sample of discharge for closer examination.
-
Rub and pull the secretion between the fingers to assess the color and discharge: Rub the collected discharge between your fingers to assess its color, texture, and consistency. This can help identify any abnormalities or changes in the discharge.
NORMAL VAGINAL DISCHARGE
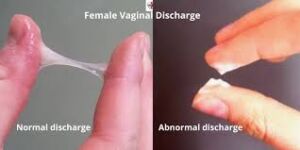
- Colorless and watery: This type of discharge is typically clear and fluid-like. It can occur at any time during the menstrual cycle and is considered normal. It serves to keep the vagina moist and clean.
- Stretchy, resembling egg white: This type of discharge is often observed during ovulation, which typically occurs around the middle of the menstrual cycle. It has a consistency similar to raw egg whites and is stretchy. This type of discharge indicates increased fertility and is associated with the release of an egg from the ovary.
- Brownish: Discharge that appears brownish in color often occurs towards the end of the menstrual period. It may be a result of older blood mixing with vaginal discharge. It is considered normal and usually not a cause for concern.
-
Spotting: Spotting refers to the occurrence of light bleeding or discharge between menstrual periods. It can appear as small amounts of blood mixed with vaginal discharge. Spotting can have various causes, including hormonal fluctuations, ovulation, or minor vaginal trauma. In some cases, it may indicate an underlying health issue and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional if it persists or is accompanied by other symptoms.
ABNORMAL VAGINAL DISCHARGE
- Has unpleasant smell: Abnormal vaginal discharge may have a foul or unpleasant odor, which can indicate an underlying infection or imbalance in the vaginal flora. A strong, fishy odor, for example, may be a sign of bacterial vaginosis.
- Discomfort such as burning and itching: Abnormal discharge may be accompanied by symptoms such as burning, itching, irritation, or discomfort in the vaginal area. These symptoms can be indicative of various infections, such as yeast infections or sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
-
Creamy – pregnancy: During pregnancy, some women may experience creamy or milky white vaginal discharge, which is considered normal. This discharge, known as leukorrhea, is caused by increased estrogen levels and increased blood flow to the pelvic area. It helps to maintain the cleanliness of the vagina and prevent infections. However, if the discharge is accompanied by itching, burning, or unusual odor, it may indicate an infection and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
CAUSES OF ABNORMAL DISCHARGE
-
Medication (antibiotics, steroids, contraceptives): Certain medications, such as antibiotics, steroids, and hormonal contraceptives, can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the vagina, leading to changes in vaginal discharge. Antibiotics, for example, can kill both harmful and beneficial bacteria, allowing yeast to overgrow and cause a yeast infection. Similarly, hormonal contraceptives can alter hormone levels, affecting vaginal pH and increasing the risk of infections.
- Infection (STI, bacteria, yeast): Infections, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis, as well as bacterial and yeast infections, can cause abnormal discharge. These infections often result in changes in the color, consistency, and odor of vaginal discharge, along with symptoms such as itching, burning, and irritation.
- Menopause: During menopause, hormonal changes can lead to thinning and drying of the vaginal tissues, known as vaginal atrophy. This can result in changes including decreased lubrication and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Douching: Douching, or the practice of rinsing or cleaning the vagina with water or a mixture of fluids, can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and irritate the vaginal tissues. This can lead to changes and an increased risk of infections.
-
Health conditions (diabetes, cancer of the cervix): Certain underlying health conditions, such as diabetes and cervical cancer, can affect vaginal health and contribute to abnormal discharge. Diabetes, for example, can increase the risk of vaginal yeast infections due to elevated blood sugar levels. Cervical cancer may cause abnormal vaginal bleeding and discharge, especially as the cancer progresses.
TYPES OF ABNORMAL DISCHARGE

Bloody or brown — problem with the reproductive system
Yellow —sexually transmitted disease
Yellow or greenish with a bad smell — sexually transmitted disease
Thick, white, cheesy, lumpy — yeast infection
Milky white discharge– pregnancy
White, gray, yellow, or greenish with a fishy smell —bacterial infection
Pink– the uterus sheds its lining after childbirth
Orange– Vaginal infection
HOW TO KEEP THE VAGINA HEALTHY
- Daily washing: Regularly wash the external genital area with water to keep it clean.
- Avoid feminine products: Refrain from using perfumes or deodorants in the vagina, as they can disrupt the natural pH balance and cause irritation.
- Practice safe sex: Use latex condoms during intercourse, especially with new partners, to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Wear cotton underwear: Opt for breathable and absorbent cotton underwear to help keep the genital area dry and prevent moisture-related issues like yeast infections.
- Avoid synthetic materials: Synthetic fabrics like polyester can trap moisture, promoting the growth of yeast. Stick to cotton underwear instead.
- Avoid douching: Douching can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and increase the risk of infections. It’s best to avoid this practice.
- Avoid tight clothing: Tight-fitting clothing can create a warm, moist environment that encourages the growth of yeast and bacteria. Choose loose, breathable clothing whenever possible.
- Clean from front to back: Always wipe from the vagina towards the anus to prevent the spread of bacteria from the anus to the vagina.
- Keep the vaginal area dry: Moist environments provide a breeding ground for yeast. Keep the genital area dry to discourage yeast growth.
- Change out of damp clothing promptly: Wet or damp clothing, such as underwear or swimsuits, can contribute to yeast infections. Change into dry clothing as soon as possible after swimming or sweating.
-
Consider probiotics: Foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, may help maintain healthy vaginal flora by replenishing beneficial bacteria. Incorporating these foods into your diet may support vaginal health.
WHEN TO SEEK MEDICAL CARE
It is important to know when to seek urgent medical care, as delaying appropriate treatment can lead to further health complications. If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should seek medical help immediately. If you have any doubts about whether you should seek medical care, it is always better to err on the side of caution and consult with your doctor.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

