Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms: Abdominal Pain, Bleeding, and Other Warning Signs
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition in which a fertilized egg implants in a place other than the uterus, most often in the fallopian tube. This type of pregnancy can be life-threatening and requires medical attention. Symptoms include abdominal pain and/or cramping, nausea and vomiting, light vaginal bleeding, and a sharp pain in the lower abdomen, often on one side. If any of these symptoms are present, it is important to seek medical care right away. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent serious complications.
Factors that increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy
Manifestation of an ectopic pregnancy
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
Complications of an ectopic pregnancy
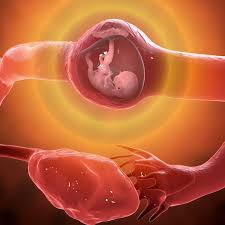
OVERVIEW OF AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
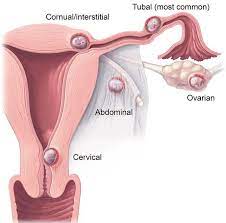
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs where a fertilized egg attaches and develops outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes
This condition can pose severe risks to the woman’s health, potentially leading to life-threatening complications.
Symptoms may include severe abdominal pain concentrated on one side, which might extend to the shoulder, along with symptoms like fainting, weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and heavy vaginal bleeding. These signs necessitate immediate medical attention to prevent further complications or mortality.
FACTORS THAT INCREASE THE RISK OF ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
- Smoking can have adverse effects on reproductive health, including increasing the likelihood of fallopian tube damage and impairing the movement of the fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes. Additionally, smoking may also contribute to hormonal imbalances, which can affect the implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterus and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Pelvic infections particularly those affecting the fallopian tubes, can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. Infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can cause inflammation and scarring in the fallopian tubes, which can interfere with the normal movement of the fertilized egg from the fallopian tubes to the uterus. This can result in the fertilized egg implanting and growing outside the uterus, leading to an ectopic pregnancy.
- Certain medications: particularly those that affect hormone levels or fertility, may increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. These medications can include fertility drugs used during assisted reproductive techniques like in vitro fertilization (IVF), as well as medications that alter hormonal balance.
- Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. While it’s primarily associated with pelvic pain and infertility, it can also increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. The presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, particularly in the fallopian tubes, can disrupt the normal movement of a fertilized egg, leading to its implantation and growth outside the uterus.
- Previous surgeries, especially those involving the fallopian tubes or reproductive organs. Surgical procedures in these areas may cause scarring or damage to the fallopian tubes, which can interfere with the normal movement of the fertilized egg. As a result, the egg may implant and grow outside the uterus, leading to an ectopic pregnancy.
- A history of infertility or previous ectopic pregnancies. In cases of infertility, underlying factors such as fallopian tube abnormalities or pelvic inflammatory disease may contribute to the risk. Additionally, having had a previous ectopic pregnancy indicates a predisposition to the condition, as scarring or damage to the fallopian tubes from the previous ectopic pregnancy may increase the likelihood of future occurrences.
- Fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF). IVF treatments often involve the transfer of fertilized embryos into the uterus, but occasionally, an embryo may implant in the fallopian tubes or elsewhere outside the uterus, resulting in an ectopic pregnancy.
- Other risk factors include the use of intrauterine devices, and exposure to certain chemicals. Intrauterine devices are a form of contraception that are inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. While they are highly effective at preventing pregnancy, there is a small risk that they may increase the likelihood of ectopic pregnancy if pregnancy does occur. Additionally, exposure to certain chemicals, such as those found in tobacco smoke or environmental pollutants, may also contribute to an increased risk of the condition.
MANIFESTATIONS OF AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
While this is relatively rare, occurring in 1 in 50 pregnancies, it can be a serious and life-threatening condition. If not treated in a timely manner, the fallopian tube can rupture and cause serious internal bleeding. Symptoms of include:
- Abdominal pain: Often severe and localized to one side of the abdomen.
- Missed period: In some cases, the menstrual period may be delayed or missed.
- Severe pain in the abdomen that worsens with movement: The pain may be sharp or stabbing.
- Heavy bleeding from the vagina: This may be accompanied by vaginal spotting or bleeding, sometimes accompanied by clots.
- Dizziness or feeling faint and lightheadedness: Due to internal bleeding or shock.
- Manifestations of shock: Rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, and pale or clammy skin.
- Pain in the shoulder: Caused by internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm and nerves.
These symptoms can indicate a medical emergency, and immediate medical attention should be sought if they occur, especially in women who suspect they may be pregnant or have risk factors for ectopic pregnancy.
HOW AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY IS DIAGNOSED
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. Diagnosis requires a medical evaluation, which typically includes a physical exam, ultrasound, and blood tests. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent serious complications, including infertility and in rare cases, death. If you are experiencing any symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, it is important to contact your healthcare provider immediately. Diagnosis typically involves the following:
-
Urine Test: This may be the first step to check for pregnancy hormones.
- Blood Test: A blood test can confirm pregnancy and measure the levels of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which should increase during early pregnancy.
- Pelvic Examination: A physical examination of the pelvic area can help detect any abnormalities, such as tenderness or masses.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: An ultrasound scan can visualize the reproductive organs to locate the pregnancy. Transvaginal ultrasound is often used for better visualization.
-
Surgery: In some cases, particularly if there’s a high suspicion of ectopic pregnancy or if other tests are inconclusive, surgery may be necessary to diagnose and treat the condition. This may involve laparoscopy to directly visualize the fallopian tubes and other pelvic structures.
TREATMENT OF ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
This is a medical emergency that needs to be treated immediately. It occurs when a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. In some cases, treatment involves the removal of the pregnancy tissue, but other treatments such as medication or laparoscopic surgery may also be used. In either case, it is important to seek medical help as soon as possible to minimize any risks.
-
Medication: In cases where the ectopic pregnancy is detected early and hasn’t yet caused significant complications, medication may be used to stop the growth of the embryo and allow the body to absorb it naturally. It’s typically used when the ectopic pregnancy is detected early and the fallopian tube has not ruptured. This medication is typically a type of chemotherapy drug called methotrexate.
-
Surgery: Surgical intervention may be necessary, especially if the ectopic pregnancy has ruptured or is at risk of rupturing to remove the embryo and repair any damage to the fallopian tube or other affected tissues. This can be done through laparoscopic surgery (minimally invasive) or, in more severe cases, through traditional open surgery. The surgery may involve removing the affected fallopian tube (salpingectomy) or attempting to remove the embryo while preserving the tube (salpingostomy).
COMPLICATIONS OF AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
This can lead to serious health risks and, in some cases, can be life-threatening. It is important to understand the potential complications of ectopic pregnancy and to be aware of the signs and symptoms of this medical condition. Complications include:
-
Heavy bleeding: The rupture of the fallopian tube can lead to severe internal bleeding, which may be life-threatening if not promptly treated.
- Injury to the fallopian tube: Surgical intervention to remove the ectopic pregnancy or repair the fallopian tube may result in damage to the tube, which can affect future fertility.
- Increased challenges for future pregnancies: Ectopic pregnancy and its treatment can increase the risk of future ectopic pregnancies and may impact fertility.
- Rupture of the fallopian tube: If not detected and treated promptly, an ectopic pregnancy can cause the fallopian tube to rupture, leading to severe pain, internal bleeding, and shock.
-
Removal of fallopian tube: In cases where the fallopian tube is severely damaged or ruptured, surgical removal (salpingectomy) may be necessary, which can affect future fertility.
WHEN TO SEEK URGENT MEDICAL CARE
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, do not delay seeking medical help. Ectopic pregnancy is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

