How to Measure Vital Signs: A Guide to Heart Rate, Temperature, and More
Measure the most basic functions of the body to help detect or monitor medical problems. Vital signs is an innovative medical monitoring system that helps keep track of vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. The system allows users to track their vital signs over time, compare them to averages, and get an overall picture of their health. Vital signs also offers personalized feedback, helping users to better understand their health and make informed decisions. With vital signs, users can easily and effectively monitor their health and stay in control. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
Body temperature Blood pressure Heart rate Breathing rate
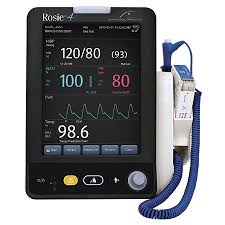
VITAL SIGNS include the following:
-
Body temperature
-
Heart rate (pulse)
-
Breathing rate (respiration)
BODY TEMPERATURE
Body temperature is an important indicator of our overall health. It is important to know what is considered a normal temperature range and what signs to look out for if something seems off. In this article, we will discuss the basics of body temperature, including what is considered a normal range and what signs may indicate a potential issue.
Normal body temperature can range from 97.8° F (36.5°C) to 99°F (37.2°C) in adults
HEART RATE
Heart rate is a measure of the number of times your heart beats in a minute and is one of the best indicators of a person’s health. It is affected by factors such as age, physical activity, anxiety, and stress. An optimal heart rate, or target heart rate, is determined based on individual factors like age and activity levels and is used to help guide and monitor physical activity. Knowing your heart rate can help you track your progress in workouts, prevent injury, and improve overall health.
The number of times the heart beats each minute is called the pulse rate
· The normal pulse ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute in adults
BREATHING RATE
Breathing rate is an innovative approach to improving your breathing and overall health. This program uses a combination of breathing exercises, mindfulness techniques, and lifestyle modifications to help you learn to breathe more efficiently and effectively. By understanding the principles of proper breathing, you can restore balance to your body and mind, leading to improved wellbeing. Through this program, you will learn the science behind breathing and how it can be used to optimize your health and wellness.
The number of breaths one takes each minute is called the Respiratory rate
· The normal respiratory rate ranges from 12 to 20 breaths per minute in an adult
BLOOD PRESSURE
Blood pressure, or BP, is a measurement of the force of your blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. It is one of the most important vital signs for monitoring your health. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a major risk factor for heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. Knowing your blood pressure and understanding what it means can help you take the necessary steps to keep your heart healthy.
The force of the blood pushing against the artery walls during contraction and relaxation of the heart is called the Blood Pressure
· Normal blood pressure is systolic of less than 120 and diastolic of less than 80 (120/80)
· Elevated blood pressure is systolic of 120 to 129 and diastolic less than 80
· Stage 1 high blood pressure is systolic is 130 to 139 or diastolic between 80 to 89
· Stage 2 high blood pressure is when systolic is 140 or higher or the diastolic is 90 or higher
WHAT TO DO BEFORE TAKING THE BLOOD PRESSURE
Check that the device is working correctly. Make sure the tubing is not twisted when storing it and keep it away from heat to prevent cracks and leaks
Don’t smoke, have caffeinated drinks, or exercise for 30 minutes before taking the blood pressure
It is wise to urinate before taking the test
Relax for 5 minutes before taking the measurement
Sit with the back supported
Keep feet on the floor uncrossed
Place the arm on a solid flat surface (like a table) with the upper part of the arm at heart level
Place the middle of the cuff directly above the bend of the elbow
Take the blood pressure at the same time every day
Record the date, time, and blood pressure reading
Take the record to the next medical appointment
Call the doctor if several high readings have been recorded
If the blood pressure reaches a systolic (top number) of 180 or higher OR diastolic (bottom number) of 110 or higher, seek emergency medical treatment
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

