Recognizing and Treating Mouth Problems: A Parent’s Guide
Mouth lesions are common medical disorders that can range from minor abrasions to more serious chronic conditions. They can be caused by a variety of factors, such as physical trauma, viral or bacterial infections, systemic diseases, and certain medications. Depending on the cause and severity of the condition, mouth lesions may appear as ulcers, blistering sores, lumps or bumps on the tongue, gums or inner lining of the mouth. Patients may experience persistent pain and discomfort in the affected area along with additional symptoms like bleeding when brushing teeth or eating. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
How to take care of the mouth at home
How to address mouth lesions
When to seek urgent medical care
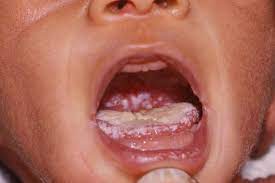
MOUTH PROBLEMS
These are common types of mouth problems and their potential causes:
- Lesions as a result of fever: Fever can weaken the immune system, making the mouth more susceptible to infections and leading to the development of lesions.
- Dry lips and mouth as a result of dehydration: Dehydration reduces saliva production, leading to dry lips and a dry mouth, which can result in discomfort and increased susceptibility to mouth issues.
- Cracks to the lips as a result of inadequate nutrition: Poor nutrition can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, causing the lips to become dry, cracked, and prone to irritation.
- Fungal infection as a result of dental issues: Poor oral hygiene or underlying dental problems can create an environment conducive to fungal growth, leading to infections such as oral thrush.
- Swelling to the tongue as a result of food accumulating between the teeth: Food particles trapped between teeth can cause irritation and inflammation of the surrounding tissues, including the tongue, leading to swelling and discomfort.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth: Various factors, including oral infections, poor oral hygiene, certain medications, or systemic conditions, can result in an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
-
Stinky breath: Also known as halitosis, bad breath can be caused by poor oral hygiene, oral infections, gum disease, dry mouth, certain foods, or underlying health conditions.
HOW TO TAKE CARE OF THE MOUTH AT HOME
Taking care of the mouth at home involves several key practices to maintain oral health:
- Regular brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and food particles.
- Flossing: Use dental floss or interdental brushes daily to clean between teeth and along the gumline where a toothbrush can’t reach.
- Rinsing: Rinse your mouth with an antimicrobial mouthwash to help reduce bacteria and prevent plaque buildup.
- Healthy diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks, which can contribute to tooth decay.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your mouth moist and help flush away food particles and bacteria.
- Avoid tobacco: Avoid smoking or using tobacco products, which can contribute to gum disease, oral cancer, and other health problems.
- Limit alcohol: Drink alcohol in moderation, as excessive consumption can dry out the mouth and increase the risk of oral health issues.
-
Regular dental check-ups: Visit your dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings to detect any oral health problems early and receive professional care and advice.
HOW TO ADDRESS MOUTH LESIONS
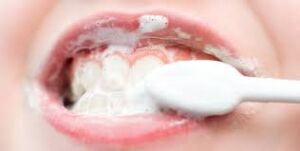
Addressing mouth lesions involves several steps to alleviate discomfort and promote healing:
- Consult a healthcare professional: If you notice any unusual lesions or sores in your mouth that don’t heal within a week or two, it’s important to see a dentist or doctor for proper evaluation and diagnosis. If your healthcare provider prescribes medication or other treatments for underlying conditions causing the lesions, follow their instructions carefully and complete the full course of treatment.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Continue brushing your teeth gently twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Avoid irritating the lesions while brushing.
- Avoid irritants: Refrain from consuming spicy, acidic, or rough-textured foods that may further irritate the lesions. Sharing lip products can spread infection and worsen mouth lesions. Try to minimize touching or rubbing the lesions to prevent further irritation. Also, avoid tobacco and alcohol, which can delay healing and worsen symptoms.
- Maintain hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your mouth moist and prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate mouth lesions.
- Use over-the-counter remedies: Apply topical oral gels or ointments recommended by your healthcare provider to help relieve pain and promote healing. These may contain ingredients such as benzocaine or lidocaine to numb the area temporarily.
- Practice proper nutrition: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support immune function and aid in the healing process. Avoid foods that are difficult to chew or may further irritate the lesions. Choose foods that are easy to swallow and won’t further irritate the lesions. Making food easier to swallow can reduce discomfort while eating.
- Manage stress: Stress can weaken the immune system and exacerbate mouth lesions. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to help reduce stress levels.
- Monitor for changes: Keep an eye on the lesions and note any changes in size, color, or appearance. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience worsening symptoms or if the lesions don’t improve with home care measures.
- Drink cold beverages: Cold drinks can help soothe discomfort associated with mouth lesions.
- Use a spoon or straw: Drinking through a spoon or straw can help minimize direct contact with the lesions, reducing discomfort.
- Apply petroleum jelly: Applying petroleum jelly to the lips can help soothe and protect lesions from further irritation.
- Chew gum or suck on sweets: Chewing gum or sucking on sweets can stimulate saliva production, which may help alleviate dry mouth and aid in healing.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol: Smoking and alcohol can irritate mouth lesions and contribute to bad breath. Avoiding them can promote healing and improve oral health.
HERBAL REMEDIES
Here are some herbal remedies that may help alleviate symptoms associated with mouth lesions:
- Aloe vera: Aloe vera gel has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties that can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with mouth lesions. Apply a small amount of aloe vera gel directly to the affected area several times a day.
- Chamomile tea: Chamomile tea has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that can help reduce pain and promote healing. Rinse your mouth with cooled chamomile tea several times a day or apply a chamomile tea bag directly to the lesions for a few minutes.
- Calendula: Calendula, also known as marigold, has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that can help soothe and heal mouth lesions. Apply calendula ointment or gel directly to the affected area several times a day.
- Licorice root: Licorice root has anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties that can help reduce pain and promote healing of mouth lesions. Chew on a small piece of licorice root or apply licorice root extract directly to the lesions.
- Sage: Sage has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with mouth lesions. Rinse your mouth with cooled sage tea several times a day or apply sage tea directly to the lesions.
- Tea tree oil: Tea tree oil has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with mouth lesions. Dilute tea tree oil with water and apply it to the affected area with a cotton swab.
- Peppermint oil: Peppermint oil has analgesic and antimicrobial properties that can help reduce pain and discomfort associated with mouth lesions. Dilute peppermint oil with water and apply it to the affected area with a cotton swab or rinse your mouth with peppermint tea.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before using herbal remedies, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications. Some herbal remedies may interact with medications or cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Additionally, if your symptoms persist or worsen despite using herbal remedies, seek medical attention.
WHEN TO SEEK URGENT MEDICAL CARE FOR MOUTH LESIONS
Seek urgent medical care if you experience any of the following symptoms or conditions related to mouth lesions:
- Severe pain: If you have intense or persistent pain that is not relieved by over-the-counter pain medications.
- High fever: A fever accompanied by mouth lesions could indicate a serious infection that requires prompt medical attention.
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing: If mouth lesions cause difficulty breathing or swallowing, seek immediate medical help.
- Bleeding: If the lesions are bleeding heavily or if bleeding persists despite applying pressure.
- Signs of infection: Such as increased redness, warmth, swelling, or pus around the lesions.
- Swelling: Severe swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat can be a sign of an allergic reaction or other serious condition.
- Persistent symptoms: If the lesions do not improve or if they worsen despite home care measures and treatment.
- Systemic symptoms: Such as fatigue, weakness, dizziness, or confusion, which could indicate a more serious underlying condition.
If you are unsure whether your symptoms require urgent medical care, it’s best to err on the side of caution and seek advice from a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance based on your specific situation and recommend appropriate treatment.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

