Guiding You Through the Journey of Premature Baby Care
Premature babies are born before the end of a full-term pregnancy, often referred to as preemies. Premature birth is defined as any birth taking place after a baby has spent less than 8 months or 37 weeks in the mother’s womb. Preterm birth is a major public health concern worldwide, contributing to more than one million infant deaths every year. Premature babies face many risks due to their underdeveloped organs and immune systems, including increased risk of breathing problems, developmental delays, vision and hearing problems, feeding difficulties, jaundice and infections. They often require special care in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). With careful monitoring and treatment, however, most premature babies go on to lead healthy lives. Please keep reading for details on premature baby care:
Breastfeeding of a premature baby
What is skin to skin contact
Benefits of skin-to-skin contact for a baby
Premature infant (preemie)
Causes of premature birth
How a premature baby is taken care of
When can the premature baby be discharged from the hospital
Complications of a premature baby
Risks for preterm birth
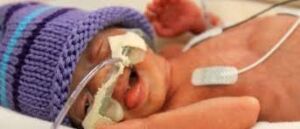
BREASTFEEDING OF A PREMATURE BABY
Breastfeeding a premature baby can be a challenging but rewarding experience. While it may not always be possible due to medical complications, there are various techniques and resources available to help moms who wish to continue breastfeeding their premature baby. From understanding the different stages of breastfeeding and what to expect, to learning how to provide optimal nutrition for your baby, to finding the necessary support, there are many ways to make breastfeeding a premature baby successful.
Premature babies use a lot of energy to breastfeed
If the baby is ill or too small, the woman can express the milk to feed baby, until baby is able to breastfeed
WHAT IS SKIN-TO-SKIN CONTACT

Skin to skin contact is defined as direct contact between two people, typically involving some form of physical contact such as touching, hugging, or cuddling. This type of contact is thought to have many health benefits, such as releasing oxytocin in the brain and reducing stress levels in both parties involved. Skin to skin contact can also help to promote feelings of safety, comfort, and connection. It is especially important for newborn babies as it helps with bonding and supports healthy growth and development.
BENEFITS OF SKIN-TO-SKIN CONTACT FOR A BABY
Decreases pain
Makes it easier for baby to begin breastfeeding
Improves baby’s sleep
Improves baby’s breathing and pulse
BENEFITS OF SKIN-TO- SKIN CONTACT TO THE PARENTS
Helps reduce the risk postpartum depression
Boosts their confidence
Improves breastfeeding
Helps establish a bond with baby

PREMATURE INFANT (PREEMIE)
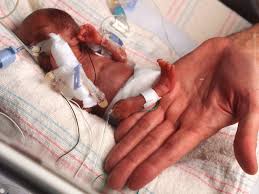
The delivery of a premature baby can be a difficult and emotional time for parents and families. Premature babies are born before 37 weeks of pregnancy and may have a variety of health issues due to their underdeveloped organs and systems. Premature babies often need special medical care and monitoring to help them reach full term, and parents and families should be aware of the long-term implications associated with preterm birth. Understanding the risks and potential complications of preterm birth is essential in helping to ensure the best care for the baby and their family.
A baby born more than 3 weeks before the due date
Due to their weight, they spend lots of energy to perform basic body functions such as breathe and feed
They require lots of warmth, comfort and skin to skin contact
Provide breast milk for baby to help with growth and to boost immunity
The sleep for short periods of time but very often
They are oversensitive and easily aroused by excessive light, touch and noise
Avoid swaddling baby too tightly to avoid problems with the hips
Placing the baby on the back decreases the risk of sudden death
Breast feed baby on demand and avoid leaving baby more that 3 to 4 hours without feeding
Minimize exposure to smoke and sick persons
CAUSES OF PREMATURE BIRTH
Multiple pregnancy
Maternal infection
Abnormality of the cervix or uterus
Use of alcohol, tobacco or illegal drugs in the pregnancy
HOW A PREMATURE BABY IS TAKEN CARE OF
Caring for a premature baby can be an incredibly difficult and challenging experience. Parents may find themselves faced with a range of emotions, from fear and anxiety to joy and hope. It is important for parents of premature babies to be aware of the extra support and resources that are available to them during this difficult time. This guide will provide an overview of the special care and considerations that should be taken when caring for a premature baby. It will discuss topics such as providing the best nutrition, proper sleep and rest, and how to create a safe and nurturing home environment.
Long stay at the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) until the baby can breathe on his/her own and maintain body heat
The baby will be placed in an incubator for warmth
Feeding will be done through a tube or vein (intravenously), until the baby is able to feed with no challenges
Close monitoring for signs of infection and trouble breathing will be conducted
If the lungs are underdeveloped, baby may need the help of breathing ventilators (breathing machine) or other oxygen devices
The temperature will be monitored closely
The baby will be attached to a heart monitor where the oxygen levels, breathing and heart rate will be constantly monitored
Fluids and medication will be administered through the vein in the umbilicus
Various diagnostic exams will be performed such as X rays, ultrasounds, heart tests to detect abnormalities so that they can be treated in a timely manner
Hearing and vision tests will be conducted for early correction
WHEN CAN THE PREMATURE BABY BE DISCHARGED FROM THE HOSPITAL
When the baby is able to feed properly
The baby breathes well
The baby has achieved an acceptable of weight gain
Baby can maintain warmth
The breathing and heart rate are normal
COMPLICATIONS OF A PREMATURE BABY
Premature labor is a serious complication that can have a lasting impact on a baby’s health and development. It occurs when labor begins before the 37th week of pregnancy and can be caused by a variety of biological and environmental factors. Complications of premature labor may include increased risk of infection, breathing problems, low birth weight, developmental delays, and long-term physical and mental health issues. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of premature labor and to seek medical attention immediately if they occur. With proper care, many babies born prematurely can lead healthy and normal lives. However, these babies can acquire the following a premature birth:
Bleeding in the brain
Chronic lung disease
RISKS FOR PRETERM BIRTH
Premature labor can have serious consequences for both mother and baby, and the risk factors associated with it can be wide-ranging. Everything from gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and genetic conditions to lifestyle habits such as smoking or drug use can increase the chances of a premature delivery. Other potential risks include a short inter-pregnancy interval or having a mother or baby that has a history of preterm labor. Understanding the potential risks can help you take the steps needed to reduce your risk of premature labor. Below is a list of risk factors for premature birth.
Maternal infection
Short or incompetent cervix
The woman had previous preterm births
Previous surgery on the cervix
Age less than 18 years
Smoking during pregnancy
Use of illegal drugs in the pregnancy
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

