Placenta Previa: Understanding the Condition and Its Risks During Pregnancy
Placenta Previa is a serious medical condition that affects pregnant women and their unborn children. During pregnancy, the placenta forms a temporary organ for the baby to receive nutrients and oxygen from the mother’s blood circulation. In Placenta Previa, this placenta implants at the lower end of the uterus and covers part or all of the cervix. This can result in severe bleeding during labor, potentially placing both mother and baby in life threatening situations. Other complications associated with Placenta Previa include preterm birth, preterm rupture of membranes, low birth weight and stillbirth. Women who are at risk for developing Placenta Previa should be monitored more closely throughout their pregnancy so that potential problems can be identified and managed appropriately. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
Risk factors of placenta previa
Symptoms of placenta previa
Management of placenta previa
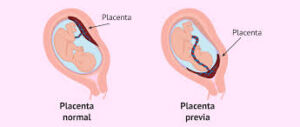
Types of Placenta Previa
- Complete (Total) Placenta Previa:
- The placenta completely covers the cervix. Vaginal delivery is typically not possible, and a cesarean section (C-section) is often required.
- Partial Placenta Previa:
- The placenta partially covers the cervix. It may allow for some degree of vaginal delivery, but a C-section is often preferred to avoid complications.
- Marginal Placenta Previa:
- The placenta is located at the edge of the cervix, which may allow for vaginal delivery, depending on the extent of coverage.
- Low-lying Placenta:
- The placenta is located in the lower part of the uterus but does not cover the cervix. Depending on its position as the pregnancy progresses, vaginal delivery may be possible.
RISK FACTORS OF PLACENTA PREVIA
The exact cause of placenta previa is not always clear, but several factors may increase the risk of developing this condition:
- Previous Cesarean Section: The risk increases in women who have had prior C-sections due to scarring of the uterus.
- Advanced Maternal Age: Women over the age of 35 may have a higher risk.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Women who have had several pregnancies are more likely to experience placenta previa.
- Previous Placenta Previa: Women who have had placenta previa in a previous pregnancy are at increased risk in subsequent pregnancies.
- Multiple Gestations: Pregnancies involving more than one baby (twins, triplets) may be associated with placenta previa.
- Uterine Abnormalities: Abnormalities in the structure of the uterus may contribute to an increased risk.
- Smoking and Drug Use: Smoking during pregnancy and drug use can increase the likelihood of placenta previa.
- Previous surgery in the uterus
SYMPTOMS OF PLACENTA PREVIA
- Painless Vaginal Bleeding: The most common symptom is bright red vaginal bleeding, typically occurring after the 20th week of pregnancy. It may start off light but can become heavy.
- Abdominal Pain: In some cases, women may experience discomfort or cramping, but bleeding is usually painless.
- Preterm Labor: In some cases, bleeding may trigger early labor.
- Fetal Movement and Heart Rate: Although the placenta may block the cervix, it doesn’t directly affect the baby’s movement or heart rate. However, any signs of fetal distress should be closely monitored.
HOW PLACENTA PREVIA IS DIAGNOSED
Placenta previa is usually diagnosed through ultrasound imaging. It may be detected during a routine ultrasound in the second trimester.
- Transabdominal Ultrasound: An initial scan may be done to identify the position of the placenta.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: This may be done later in the pregnancy to get a clearer view of the placenta’s location, especially if it’s near the cervix.
MANAGEMENT OF PLACENTA PREVIA depends on:
The amount of blood being lost
Whether the mother or baby’s life is at risk
The woman’s gestational age
The severity of the condition
Treatment goals are to minimize risks to both mother and baby and to ensure a safe delivery.
Conservative Management:
- Rest: Bedrest or limited physical activity may be advised to reduce bleeding and complications. Avoid strenuous activity
- Avoidance of Sexual Activity: Intercourse may be restricted to avoid stimulating contractions or additional bleeding. Avoid inserting any object into the vagina
- Hospitalization: In cases of significant bleeding or preterm labor, hospitalization may be necessary for monitoring and management.
- Blood Transfusion: If there is significant blood loss, the mother may need a blood transfusion.
- A pelvic exam can puncture the placenta and lead to heavy bleeding, thus should not be performed
- One who does not require hospitalization must:
- Seek urgent medical care whenever bleeding from the vagina is noted
- Both mother and baby would be monitored closely
- Fetal heart monitoring will be done
- Medication will be given to develop the baby’s lungs
- If the woman is preterm and contracting, medication will be given to stop the contractions
- Whilst on bed rest medication will be given to prevent blood clot
Delivery Plan:
- Cesarean Section (C-Section): If the placenta previa persists or is diagnosed later in pregnancy, a cesarean section is often the preferred delivery method to avoid the risk of heavy bleeding during vaginal delivery.
- Timing of Delivery: The timing of a C-section is usually planned based on the gestational age and the extent of bleeding. It is typically performed at 36-37 weeks’ gestation if there are no other complications.
- Close Monitoring: Regular ultrasounds and fetal monitoring are used to assess the baby’s well-being and the placenta’s position.
- A premature baby will be treated in the neonatal intensive care unit
Potential Complications
- Heavy Bleeding (Hemorrhage):
- Placenta previa can lead to significant bleeding, especially as the cervix dilates during labor. This can cause complications for both the mother and baby.
- Preterm Birth:
- Due to bleeding and the potential for premature labor, placenta previa increases the risk of preterm birth.
- Infection:
- If there is extensive bleeding or if the placenta partially separates from the uterine wall, there may be an increased risk of infection.
- Fetal Distress:
- Heavy bleeding may affect the oxygen supply to the baby, leading to fetal distress.
- Placenta Accreta:
- In some cases, the placenta may grow too deeply into the uterine wall, a condition called placenta accreta. This can complicate the delivery and require a hysterectomy after delivery.
Prognosis
With appropriate management, most women with placenta previa are able to have a successful pregnancy outcome. The key is early diagnosis and careful monitoring to prevent complications. The majority of women with a diagnosed placenta previa early in pregnancy will need a cesarean section, but with proper care, the risks to both mother and baby can be minimized.
It is important to know when to seek urgent medical care, as delaying appropriate treatment can lead to further health complications. If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should seek medical help immediately. If you have any doubts about whether you should seek medical care, it is always better to err on the side of caution and consult with your doctor.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

