Understanding EKG Interpretation: A Beginner’s Guide
An electrocardiogram (EKG or ecg) is a medical test that measures the electrical rhythm of the heart in order to diagnose and monitor various conditions such as heart attack, arrhythmia, heart disease, and other cardiac issues. An EKG records the electrical waves of the heart over a period of time by placing electrodes on the body and displaying their signal on a computer screen for review. This allows doctors to measure the rate and regularity of electrical impulses in order to detect any abnormalities or irregularities in the heartbeat. In addition to providing an accurate diagnosis, an EKG can also be used to monitor changes in a patient’s condition over time. By keeping track of these changes, doctors can determine if treatment is working or if further interventions may be necessary. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
Indications for an EKG
How and EKG is done
Factors affecting the accuracy of an EKG
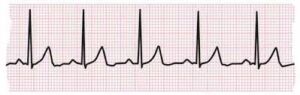
What an EKG Measures
- Heart Rhythm: The regularity or irregularity of the heartbeat.
- Heart Rate: The number of beats per minute.
- Electrical Conduction: The pathway and speed of electrical impulses through the heart.
- Heart Conditions: Identifies issues like arrhythmias, heart attacks, or structural abnormalities.
Types of EKGs
- Resting EKG: Performed while the patient is at rest.
- Stress Test: Conducted during physical activity to evaluate heart function under stress.
- Holter Monitor: Continuous monitoring over 24–48 hours using a portable device.
- Event Monitor: A wearable device that records heart activity when symptoms occur.
INDICATIONS FOR AN EKG
To detect abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmias)
To identify the cause of chest pain or a heart attack
To determine whether someone had a heart attack
To determine whether treatments are working e.g. medications or pacemaker
Patient with chest pain
Dizziness, lightheadedness or confusion
Heart palpitations
Rapid pulse
Shortness of breath
Weakness, fatigue or a decline in ability to exercise
To monitor heart health in patients with risk factors like high blood pressure or diabetes.
Preparing for an EKG
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing.
- Avoid using lotions or oils on the chest.
- Inform your doctor of any medications or symptoms.
HOW AN EKG IS DONE
One may be given a hospital gown
Jewelry such as watch, or any object that might interfere with the test will be removed
The patient will be allowed to lay on an examination table or bed
The chest and limbs will be exposed and shaved if necessary to allow the electrodes to stick
The patient will be advised to lay flat and avoid moving
Six stickers will be placed on different parts of the chest then one on each limb
An electrode which connects to a machine will be attached to each sticker
The machine records the information displays it as waves on a monitor or on paper
A print out of the reading will be performed
The electrodes and stickers will be removed and patient will be allowed to resume to previous activities
The results will be interpreted by the doctor
THINGS THAT CAN AFFECT THE ACCURACY OF THE RESULTS
Obesity
Pregnancy
Fluid buildup in the abdomen (Ascites)
Anatomical considerations, such as the size of the chest and the location of the heart within the chest
Movement during the test
Exercise or smoking before the test
Certain medicines
Electrolyte imbalances, such as too much or too little potassium, magnesium, or calcium in the blood
Excess hairs
Presence of jewelry
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

