Stay Active and Healthy: Men’s Health Tips for All Ages
Men’s health encompasses a wide range of topics, from sperm quality to prostate problems and sexual issues. We’ll delve into common concerns such as erectile problems, testicular lumps, and more, offering insights and solutions for a healthier life.
When it comes to men’s health, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Every man is different, and what works for one may not work for another. That’s why it’s important to understand the range of issues that can affect men’s health and the best ways to prevent and treat them. By taking proactive steps for your health, you can lead a healthier, more fulfilling life. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
Factors affecting the quality of the sperm
Sore and smelly penis
Erectile problems
Lumps and swelling to the testicles
Testicular cancer
PSA
Gynecomastia
Prostate problems
Sexual problems
Conditions that affect one’s ability or desire for sex
Treatment options for sexual problems

THE ROLE OF SPERM IN MEN’S HEALTH
Sperm are male reproductive cells produced in the testes as part of the process of spermatogenesis. Sperm is a vital part of the reproductive system, playing an essential role in helping to create new life. It’s produced in the testicles, and consists of a combination of genetic material, enzymes and proteins. When sperm is released, it travels through the reproductive tract and fertilizes the egg, if it succeeds in reaching it. Sperm are also important for their ability to help protect against certain diseases, such as prostate cancer. Here are some key aspects of sperm:
- Sperm production begins in the testes within structures called seminiferous tubules. Immature cells called spermatogonia undergo a series of divisions and maturation processes to develop into sperm cells, a process known as spermatogenesis.
- The cells are small, highly specialized cells with a distinct structure. They consist of a head, midpiece, and tail. The head contains the nucleus, which houses the genetic material (DNA) required for fertilization. The midpiece contains mitochondria, which provide energy for sperm motility. The tail, also known as the flagellum, propels the sperm forward through the female reproductive tract.
- The cells are motile and capable of swimming through the female reproductive tract to reach the egg. This motility is essential for fertilization to occur. Sperm motility is facilitated by the movement of the tail (flagellum) and energy provided by mitochondria in the midpiece.
- Sperm cells have a limited lifespan outside of the male reproductive tract. Once ejaculated, sperm can survive for a few hours to several days in the female reproductive tract, depending on various factors such as environmental conditions and cervical mucus.
- The primary function of sperm is to fertilize the female egg (oocyte) during sexual intercourse. This process typically occurs in the fallopian tubes, where sperm encounter and penetrate the egg, resulting in the formation of a fertilized embryo.
- The cells contribute genetic material to the offspring, including half of the genetic information required for embryo development. The genetic material carried by sperm combines with that of the egg to form a complete set of chromosomes in the fertilized embryo.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE QUALITY OF SPERM

Sperm temperature
Wearing tight underwear
Drinking excessive alcohol
Usage of recreational drugs
Some medications such as prolonged use of antibiotics
Poor dietary habits
Being overweight or obese
SORE AND SMELLY PENIS
Are you suffering from a sore and smelly penis? If so, you’re not alone. Many men are affected by this common and uncomfortable condition. Fortunately, there are a variety of treatments available to help you get relief and feel more comfortable. We’ll now explore the causes of sore and smelly penis and provide some tips on how to treat and prevent it.
CAUSES OF SORE AND SMELLY PENIS
Smegma – a lubricant produced by the body to keep the penis moist. If the penis is not washed daily, It builds up to form a cheesy-looking substance
Balanitis- infection and swelling to the head of the penis due to poor hygiene practices
A sexually transmitted infection
Non-specific urethritis- the inflammation or infection of the tube transporting urine from the bladder to the tip of the penis
Prostatitis- the inflammation of the prostate gland
ERECTILE PROBLEMS
Erectile dysfunction can be a difficult and embarrassing condition to deal with. It can cause a range of physical and mental issues, from reduced self-esteem to relationship problems. Fortunately, there are a number of treatments available that can help men address their erectile problems and lead a more fulfilling sex life.
CAUSES OF ERECTILE PROBLEMS
Drinking too much alcohol
CAUSES OF LUMPS AND SWELLING TO THE TESTICLES
Varicocele –inflamed veins in the testicles
Hydrocele – a buildup of around the testicle
Epididymal cyst – a collection of fluid in the epididymis
Testicular torsion – twisting of the penis manifested by sudden pain and swelling
Epididymitis –swelling and tenderness inside the scrotum (ball sack)
Testicular cancer
TESTICULAR CANCER
Testicular cancer is a type of cancer that affects the testicles and can be life-threatening if not detected and treated in time. It is the most common cancer in males aged 15-35 and can be caused by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle and environment. Early detection is key, so it’s important to be aware of the symptoms and risk factors associated with the disease. Treatment options vary depending on the stage of the cancer, but may include surgery, radiation therapy or chemotherapy. By taking the necessary precautions and having regular check-ups, you can help to reduce your risk of developing this type of cancer.

SIGNS OF TESTICULAR CANCER
Signs of testicular cancer
A lump inside the testicle
Swelling of one testicle
Firm sensation to the testicle
Pain to the testicle
Difference in size or sensation between the two testicles
PROSTATE SPECIFIC ANTIGEN (PSA)

Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the prostate gland in men and is one of the most important biomarkers used to detect prostate cancer. PSA is measured in a simple blood test, which is used to detect any abnormality in the prostate. Elevated PSA levels can indicate the presence of prostate cancer, or other conditions such as prostatitis or an enlarged prostate. Knowing your PSA levels is a key factor in the early detection of prostate cancer and should be checked regularly.
An increase in the size of the prostate gland
Infection of the prostate
PRECAUTIONS BEFORE A PSA TEST
No ejaculation 2 days before taking the test
No vigorous exercise 2 days before taking the test
Ensure that there is no active UTI prior to the test
Wait 6 weeks after a prostate biopsy prior to do the test
GYNECOMASTIA
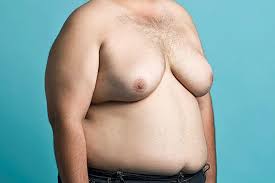
Gynecomastia, commonly referred to as “man boobs”, is a medical condition that affects nearly half of all men, causing them to develop enlarged breasts (larger than normal). The condition can be caused by hormonal imbalances, certain medications, aging, and other factors. Fortunately, there are treatments available to help reduce the size and appearance of the breasts in those affected.
CAUSES OF GYNECOMASTIA
Hormonal imbalance- a decrease in testosterones, causing estrogen to increase breast tissue
Passage of estrogen from the mother to the newborn baby boy
Side effects of a medication
A medical condition
Inflammation of the testicles
TREATMENT OF GYNECOMASTIA
-
Observation: In some cases, especially in adolescents, gynecomastia may resolve on its own without any intervention. Observation over time may be recommended to monitor changes in breast size and assess whether further treatment is necessary.
- Medications: Hormonal imbalances are a common cause of gynecomastia. In such cases, medications may be prescribed to address the hormonal imbalance and reduce breast tissue. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) such as tamoxifen or raloxifene may be used to block estrogen receptors in breast tissue and reduce breast size.
- Surgery (Mastectomy): Surgical removal of excess breast tissue is often recommended for persistent or severe cases of gynecomastia. This procedure, known as mastectomy or reduction mammoplasty, involves removing glandular tissue and excess skin to achieve a flatter, more masculine chest contour. Liposuction may also be used in combination with mastectomy to remove excess fat from the chest area.
- Lifestyle Changes: In cases where obesity or weight gain contributes to gynecomastia, adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise routine may help reduce breast size by decreasing overall body fat.
- Management of Underlying Conditions: If gynecomastia is caused by an underlying medical condition or medication, addressing the underlying cause may help alleviate symptoms. This may involve adjusting medications, treating hormonal imbalances, or managing underlying health conditions such as liver disease or hypogonadism.
- Psychological Support: Gynecomastia can have significant psychological and emotional impacts, particularly in adolescents. Counseling or support groups may be beneficial in helping individuals cope with body image issues and improve self-esteem.
The appropriate treatment for gynecomastia will depend on individual factors such as the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and patient preferences. It’s important for individuals experiencing gynecomastia to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment approach for their specific situation.
PROSTATE PROBLEMS
Are you struggling with prostate problems? Prostate issues can be a source of discomfort and embarrassment, but there are treatments and solutions available. With the right care and attention, you can get your prostate health back on track and feel more comfortable in your own body. Let’s explore the various ways you can take control of your prostate health. Prostate problems encompass a range of conditions that affect the prostate gland, a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder in men. These conditions can cause a variety of symptoms and complications. Some common prostate problems include:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Also known as prostate enlargement, BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that occurs as men age. Symptoms may include urinary frequency, urgency, weak urinary stream, difficulty starting or stopping urination, and nocturia (frequent urination at night).
- Prostatitis: Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland, which can be acute or chronic. Symptoms may include pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, urinary problems, sexual dysfunction, and flu-like symptoms.
- Prostate Cancer: Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, typically affecting older men. It occurs when abnormal cells in the prostate gland grow out of control. Symptoms may include difficulty urinating, blood in the urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, pain in the hips, back, or pelvis, and bone pain.
- Prostate Infections: Prostate infections, or bacterial prostatitis, occur when bacteria infect the prostate gland. Symptoms may include urinary urgency, frequency, pain or burning with urination, pain in the pelvic area or genitals, and flu-like symptoms.
- Prostate Stones: Prostate stones are small calcifications that can develop in the prostate gland, often as a result of chronic prostatitis. They may cause urinary symptoms or discomfort.
- Prostate Nodules: Prostate nodules are small, firm lumps that can develop within the prostate gland. They may be benign or cancerous and can sometimes be felt during a digital rectal exam.
- Prostate Obstruction: In severe cases of BPH, the enlarged prostate gland can obstruct the flow of urine from the bladder, leading to urinary retention and other complications.
HOW TO PREVENT PROSTATE PROBLEMS
-
Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit consumption of red meat and high-fat foods. Consider incorporating foods rich in antioxidants, such as tomatoes, berries, and nuts, which may help reduce the risk of prostate problems.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of prostate issues. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is associated with an increased risk of prostate problems, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help lower this risk.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of prostate problems. Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels, if at all.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer and other prostate issues. If you smoke, quitting can improve your overall health and lower your risk of prostate problems.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help keep your urinary tract healthy and reduce the risk of urinary symptoms associated with prostate problems, such as BPH.
- Get Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce the risk of prostate problems and improve overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Maintain Regular Medical Check-ups: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help detect prostate problems early when they are more easily treated. Discuss your risk factors and any concerns you may have with your doctor.
- Consider Prostate Health Supplements: Some supplements, such as saw palmetto or beta-sitosterol, may help promote prostate health and reduce the risk of prostate problems. However, always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, as they may interact with other medications or conditions.
-
Know Your Family History: If you have a family history of prostate problems or prostate cancer, you may be at a higher risk yourself. Discuss your family history with your healthcare provider and follow their recommendations for screening and prevention.
SEXUAL PROBLEMS

Do you struggle with sexual problems? Sexual problems refer to difficulties or issues that interfere with a person’s ability to engage in satisfying sexual activity. These problems can affect both men and women and may have physical, psychological, or relational causes. Whether you are dealing with a lack of desire, difficulty with arousal, or pain during intercourse, it is important to know that you are not alone. While it can be a sensitive subject, it is important to take the time to understand your sexual issues and seek help to address them in a safe and effective way.
COMMON SEXUAL PROBLEMS IN MEN
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection sufficient for sexual activity.
- Decreased Libido (Sexual Desire): Reduced interest or desire for sexual activity.
- Premature Ejaculation: Ejaculation that occurs too quickly during sexual activity, often before or shortly after penetration.
- Delayed Ejaculation: Difficulty reaching orgasm or delayed ejaculation during sexual activity.
- Orgasmic Disorders: Inability to achieve orgasm or reduced intensity of orgasm during sexual activity.
- Penile Curvature (Peyronie’s Disease): Abnormal curvature of the penis, which can interfere with sexual function and cause pain.
- Genital Pain or Discomfort: Pain or discomfort in the genitals during sexual activity or at other times.
- Performance Anxiety: Anxiety or fear related to sexual performance, which can lead to difficulties in arousal or maintaining an erection.
- Body Image Issues: Negative feelings about one’s body or appearance, which may affect sexual confidence and performance.
- Relationship Problems: Issues within a relationship, such as communication problems, conflict, or lack of intimacy, which can impact sexual function and satisfaction.
CONDITIONS THAT AFFECT ONE’S ABILITY OR DESIRE FOR SEX
-
Vascular Diseases: Conditions such as High cholesterol, atherosclerosis, hypertension, or peripheral vascular disease can impair blood flow to the genitals, leading to erectile dysfunction or reduced sexual desire.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can damage nerves and blood vessels, contributing to sexual problems such as erectile dysfunction and decreased libido.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Disorders affecting hormone levels, such as low testosterone (hypogonadism) or thyroid dysfunction, can impact sexual function and desire.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions like multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, or spinal cord injuries can affect nerve function, leading to sexual dysfunction.
- Obesity: Obesity is associated with hormonal imbalances, vascular diseases, and self-esteem issues, all of which can contribute to sexual problems.
- Cardiovascular Conditions: Heart disease, stroke, or heart failure can affect blood flow and contribute to erectile dysfunction or reduced sexual stamina.
- Medications: Certain medications, including antidepressants, antihypertensives, and some cancer treatments, can have side effects that affect sexual function.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow, increasing the risk of erectile dysfunction and other sexual problems.
- Alcohol and Substance Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption or substance abuse can impair sexual function and desire.
- Psychological Factors: Mental health conditions such as Depression, Anxiety, or Stress can interfere with sexual desire and performance.
-
Relationship Issues: Difficulties within a relationship, such as communication problems, conflict, or lack of intimacy, can affect sexual desire and satisfaction.
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR SEXUAL PROBLEMS IN MEN
Treatment options for sexual problems in men vary depending on the underlying cause. Here are some common approaches:
- Seek urgent medical care: If there’s sudden onset of severe sexual problems or complications, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial.
- Counseling for Stress Management: Addressing stress, anxiety, or other psychological factors through counseling or therapy can often improve sexual function.
- Medications for Erectile Problems: Various medications, such as phosphodiesterase inhibitors (e.g., Viagra, Cialis), can help treat erectile dysfunction by increasing blood flow to the penis.
- Treatment for Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal imbalances affecting sexual function may require hormone replacement therapy or other medications to restore balance.
- Medical Devices for Erection Assistance: Devices like vacuum erection devices or penile implants can help men achieve and maintain erections.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases of penile deformities or severe erectile dysfunction, surgical procedures like penile implants or corrective surgeries may be considered as a last resort.
These treatment options should be discussed with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable approach based on individual needs and medical history.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions. Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health Men’s Health
Men’s health Men’s health Men’s health Men’s health V V V V V Men’s health Men’s health Men’s health Men’s health

