Kidney Disease: Understanding, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
The kidney is one of the most important organs in the human body. It plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. The kidney is a bean-shaped organ located in the abdominal cavity. It is approximately the size of a fist and weighs around 120-150 grams. Each person has two kidneys, one on each side of the spine. Kidney disease, also known as renal disease, is a condition in which the kidneys are damaged and are not able to function properly. The kidney is made up of millions of tiny filters called nephrons, which are responsible for filtering the blood. The kidney works by filtering waste products from the blood and removing excess fluids from the body. The nephrons in the kidney filter the blood by removing waste products such as urea, creatinine, and excess salts. These waste products are then excreted from the body in the form of urine. We will discuss the following topics:
Physiology of the kidney
Pathophysiology of kidney diseases
Types of kidney disease
Causes of a kidney disease
Risk factors for a kidney disease
Symptoms of a kidney disease
Complications of kidney diseases
Diagnosis of a kidney disease
Prevention of a kidney disease
Treatment of kidney disease
Natural remedies
Herbal remedies
Myths and the kidney
When to seek urgent medical care
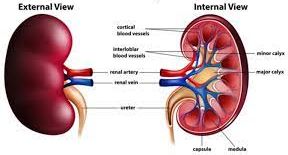
Functions of the kidney
The kidneys perform a number of essential functions, including:
- Regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance: The kidneys help maintain the right balance of fluids and electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, etc.) in the body. The kidney helps to regulate the amount of fluid in the body by removing excess fluids through urine.
- Removal of waste products: The kidneys filter out waste products, such as urea and creatinine, and excess salts from the blood and excrete them in the urine.
- Regulation of blood pressure: The kidneys play a key role in regulating blood pressure by controlling the amount of fluid in the body and releasing hormones that affect the constriction and dilation of blood vessels.
- Production of hormones: The kidneys produce hormones called renin that stimulate the production of red blood cells and help regulate calcium and phosphate levels in the body.
- Activation of vitamin D: The kidneys play a role in converting inactive vitamin D to its active form, which helps regulate calcium levels in the body.
- Producing red blood cells: The kidney produces a hormone called erythropoietin, which stimulates the production of red blood cells.
Pathophysiology of kidney diseases
When the kidneys are not functioning properly, it can lead to a variety of kidney diseases that can have serious consequences for a person’s health. The pathophysiology of kidney disease can vary depending on the underlying cause, but there are some common mechanisms involved.
- Inflammation: is a common feature of kidney disease, and it can be triggered by a variety of factors, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, or exposure to toxins. The inflammation can damage the kidneys’ filtering units (nephrons), leading to decreased kidney function.
- Glomerular damage: The glomeruli are tiny blood vessels in the kidneys that filter the blood. Damage to the glomeruli can occur due to a variety of factors, such as high blood pressure or diabetes. When the glomeruli are damaged, they may not be able to filter waste products and excess fluids properly, leading to a buildup of toxins in the body.
- Tubular damage: The tubules are structures in the kidneys that reabsorb useful substances from the filtered blood and excrete waste products in the urine. Damage to the tubules can occur due to factors such as infections, medications, or exposure to toxins. When the tubules are damaged, they may not be able to properly reabsorb essential substances, leading to imbalances in fluid and electrolyte levels.
- Obstruction: of the urinary tract can occur due to a variety of factors, such as kidney stones or tumors. Obstruction can prevent the kidneys from properly excreting waste products and excess fluids, leading to a buildup of toxins in the body and kidney damage.
- Genetics: Some kidney diseases are caused by genetic mutations that affect the development or function of the kidneys. For example, polycystic kidney disease is caused by mutations that lead to the formation of cysts in the kidneys, which can impair kidney function over time.
Types of kidney disease
There are several different types of kidney disease, each with its own causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is a sudden and severe condition that occurs when the kidneys stop functioning properly within a short period. It is often caused by a sudden drop in blood flow to the kidneys, dehydration, exposure to toxic substances injury, infection, or medication. Acute kidney injury can be potentially life-threatening and may require hospitalization. Symptoms include decreased urine output, swelling in the legs and feet, fatigue, and confusion. If left untreated, AKI can lead to permanent kidney damage or even kidney failure.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term condition that occurs when the kidneys are damaged, diseased or gradually lose function over time (for more than three months). It is often caused by underlying health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or glomerulonephritis or autoimmune diseases. Symptoms include fatigue, muscle cramps, swelling in the legs and feet, and frequent urination. If left untreated, CKD can lead to kidney failure, which requires dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Glomerulonephritis is a type of kidney disease that occurs when the tiny filters in the kidneys called glomeruli become inflamed and damaged. It is often caused by infections such as strep throat or autoimmune diseases such as lupus. Symptoms include blood in the urine, foamy urine, high blood pressure, and swelling in the face, hands, and feet. Treatment for glomerulonephritis depends on the underlying cause and may include medications to reduce inflammation and control blood pressure.
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder that causes numerous fluid-filled cysts to form in the kidneys. These cysts can grow and enlarge over time, leading to kidney damage and eventually kidney failure. Symptoms include back pain, high blood pressure, and blood in the urine. There is no cure for PKD, but treatment can help manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease.
Kidney Stones are hard mineral deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain when they pass through the urinary tract. They are often caused by dehydration, a diet high in salt or protein, or underlying health conditions such as gout or hyperparathyroidism. Symptoms include severe pain in the back or side, nausea, vomiting, and blood in the urine. Treatment for kidney stones may include pain medication, drinking plenty of fluids, and in severe cases, surgery.
Nephrotic Syndrome is a condition that occurs when the kidneys leak large amounts of protein into the urine. This is a condition in which the kidneys excrete too much protein in the urine, leading to swelling, fatigue, and other symptoms. Nephrotic syndrome can be caused by a variety of factors, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, or medications. It is often caused by underlying health conditions such as diabetes or lupus. Symptoms include swelling in the legs and feet, foamy urine, fatigue, and weight gain. Treatment for Nephrotic Syndrome may include medications to reduce inflammation and control blood pressure.
Interstitial Nephritis is a type of kidney disease that occurs when the tissue between the kidney tubules becomes inflamed and damaged. It is often caused by medications such as antibiotics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Symptoms include blood in the urine, fever, rash, and swelling in the legs and feet. Treatment for Interstitial Nephritis may include stopping the use of the medication that caused the condition and medications to reduce inflammation.
Causes and Risk Factors for a kidney disease
There are many different causes of kidney disease, and in many cases, the exact cause is not known. Some of the most common causes include:
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their function over time. Diabetes is one of the leading causes of kidney disease. High blood sugar levels can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney damage over time.
High blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to impaired kidney function over time.
Urinary tract obstruction: Obstruction of the urinary tract can prevent the kidneys from properly excreting waste products and excess fluids, leading to a buildup of toxins in the body and kidney damage.
Infections: Infections, such as pyelonephritis, can damage the kidneys and impair their function over time.
Autoimmune diseases: Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or IgA nephropathy, can cause inflammation and damage to the kidneys.
Medications: Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and some antibiotics, can damage the kidneys over time if taken in high doses or for long periods of time.
Lupus: Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation in the kidneys, leading to kidney damage over time.
Aging: As we age, our kidneys naturally begin to lose function, which can lead to kidney disease over time.
Family history: If you have a family history of kidney disease, you may be at a higher risk of developing the condition yourself.
Cardiovascular disease: People with a history of heart disease or stroke are at a higher risk of developing kidney disease.
Symptoms of a kidney disease
The symptoms of kidney diseases can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, kidney diseases may not cause any symptoms until they have progressed to an advanced stage. Some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Changes in urination, such as decreased urine output, foamy urine, or blood in the urine
- Muscle cramps or twitching
- Itching or skin rashes
- Trouble sleeping
- High blood pressure
Complications of kidney diseases
Untreated kidney diseases can lead to a range of complications, including high blood pressure, anemia, bone disease, and nerve damage. In some cases, kidney diseases can progress to end-stage renal disease, which requires dialysis or kidney transplant to manage. There are several complications that can arise from kidney disease, particularly if the condition is not properly managed. Some of the most common complications include:
High blood pressure: Kidney disease can lead to high blood pressure, which can in turn further damage the kidneys and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. One of the most common complications of kidney disease is high blood pressure. The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating blood pressure by filtering excess fluids and waste products from the body. When the kidneys are damaged, they may not be able to perform this function effectively, leading to high blood pressure. Symptoms of high blood pressure include headaches, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Anemia: Kidney disease can cause a decrease in the production of red blood cells, leading to anemia and fatigue. Another complication of kidney disease is anemia. The kidneys produce a hormone called erythropoietin, which stimulates the production of red blood cells. When the kidneys are damaged, they may not produce enough erythropoietin, leading to a decrease in red blood cells. Symptoms of anemia include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Bone disease: The kidneys play a role in maintaining the body’s balance of calcium and phosphorus. When the kidneys are not functioning properly, it can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures. Kidney disease can also lead to bone disease. The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of calcium and phosphorus in the body. When the kidneys are damaged, they may not be able to regulate these minerals effectively, leading to bone disease. Symptoms of bone disease include bone pain, fractures, and deformities.
Nerve damage: Kidney disease can cause nerve damage, leading to numbness, tingling, and other symptoms. Kidney disease can also lead to nerve damage. The kidneys play a crucial role in removing waste products from the body, including toxins that can damage nerves. When the kidneys are damaged, they may not be able to remove these toxins effectively, leading to nerve damage. Symptoms of nerve damage include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hands and feet.
Fluid buildup: Kidney disease can cause a buildup of fluids in the body, leading to swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, as well as shortness of breath and other symptoms. Kidney disease can also lead to fluid buildup in the body. The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating the balance of fluids in the body. When the kidneys are damaged, they may not be able to perform this function effectively, leading to fluid buildup. Symptoms of fluid buildup include swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet.
Cardiovascular disease: Kidney disease can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke. People with kidney disease are at an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease. This is because kidney disease can lead to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Symptoms of cardiovascular disease include chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations.
Sexual Dysfunction: People with kidney disease may also experience sexual dysfunction. This is because kidney disease can lead to hormonal imbalances that can affect sexual function. Symptoms of sexual dysfunction include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and infertility.
Depression and Anxiety Kidney disease can also lead to depression and anxiety. This is because kidney disease can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, leading to feelings of sadness and anxiety. Symptoms of depression and anxiety include feelings of hopelessness, loss of interest in activities, and difficulty sleeping.
Malnutrition People with kidney disease may also experience malnutrition. This is because the kidneys play a crucial role in regulating the balance of nutrients in the body. When the kidneys are damaged, they may not be able to perform this function effectively, leading to malnutrition. Symptoms of malnutrition include weight loss, fatigue, and weakness.
Kidney failure: In severe cases, kidney disease can lead to kidney failure, which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant to manage.
End-Stage Renal Disease The most severe complication of kidney disease is end-stage renal disease (ESRD). ESRD occurs when the kidneys are no longer able to function properly, and dialysis or a kidney transplant is required to sustain life. Symptoms of ESRD include fatigue, nausea, and difficulty concentrating.
Diagnosis of a kidney disease
Diagnosing kidney diseases typically involves a combination of physical exams, blood tests, urine tests, and imaging studies. Blood tests can be used to measure levels of creatinine and other waste products in the blood, while urine tests can be used to detect the presence of protein or blood in the urine. Imaging studies, such as ultrasounds or CT scans, can be used to visualize the kidneys and identify any abnormalities.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of kidney disease, your doctor may recommend a series of tests to diagnose the condition. These tests may include:
- Medical history and physical exam: Your doctor will ask about your medical history and any symptoms you are experiencing. They will also perform a physical exam to check for signs of kidney disease, such as swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet.
- Blood tests: can be used to measure the levels of various substances in your blood, such as creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN). Abnormal levels of these substances can indicate kidney disease. One of the most common tests is a blood test that measures the level of creatinine in the blood. Creatinine is a waste product that is normally filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. If the level of creatinine is high, it may indicate that the kidneys are not functioning properly.
- Urine tests: can be used to measure the amount of protein and other substances in your urine. Abnormal levels of these substances can indicate kidney disease.
- Imaging tests: such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, can be used to visualize the kidneys and check for any abnormalities or damage. In addition to blood and urine tests, imaging tests may also be used to diagnose kidney disease. One common imaging test is an ultrasound, which uses sound waves to create images of the kidneys. An ultrasound can help identify any abnormalities in the kidneys, such as cysts or tumors. Another imaging test that may be used is a CT scan, which uses X-rays to create detailed images of the kidneys and surrounding structures.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be necessary to diagnose kidney disease. This involves taking a small sample of kidney tissue for examination under a microscope. In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be necessary to diagnose kidney disease. A kidney biopsy involves removing a small piece of tissue from the kidney and examining it under a microscope. This can help identify the cause of the kidney disease and determine the best course of treatment.
Prevention of a kidney disease
This involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing any underlying health conditions that can contribute to kidney damage. While not all cases of kidney disease can be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the condition. There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing kidney disease, or to slow its progression if you already have the condition. Some of the most important steps include:
- Manage underlying health conditions: If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or other health conditions that can increase the risk of kidney disease, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to manage these conditions effectively.
- Maintain a healthy diet: A diet that is low in salt, saturated fat, and added sugars and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help protect your kidneys.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help flush toxins out of your kidneys and reduce the risk of kidney stones.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce blood pressure, and improve overall kidney function.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption: Smoking can damage blood vessels throughout the body, including those in the kidneys. Drinking alcohol in moderation may be safe for most people, but excessive alcohol consumption can damage the kidneys.
- Take medications as prescribed: Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can damage the kidneys if taken for long periods of time. Be sure to take medications only as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help detect kidney disease early, when it is most treatable.
- Avoiding exposure to toxins
Treatment of kidney disease
The treatment for kidney disease will depend on the underlying cause of the condition.
In some cases, Lifestyle changes may be enough to slow the progression of the disease. These changes may include:
- Eating a healthy diet low in salt and protein
- Exercising regularly
- Quitting smoking
- Managing blood sugar levels if you have diabetes
- Managing blood pressure levels if you have high blood pressure
Medications for Kidney Disease In addition to lifestyle changes, medications may also be used to treat kidney disease. One common medication is an ACE inhibitor, which helps lower blood pressure and reduce protein in the urine. Other medications may be used to treat specific symptoms of kidney disease, such as anemia or bone disease.
Dialysis In some cases, dialysis may be necessary to treat kidney disease. Dialysis is a process that uses a machine to filter waste products from the blood when the kidneys are no longer able to do so. There are two types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis involves using a machine to filter the blood outside of the body, while peritoneal dialysis involves using a catheter to fill the abdomen with a special fluid that helps remove waste products from the blood.
Kidney Transplant For some people with kidney disease, a kidney transplant may be necessary. A kidney transplant involves replacing a diseased kidney with a healthy kidney from a donor. This can be a lifesaving procedure for people with advanced kidney disease.
Natural remedies

1. Dietary Changes One of the most important natural remedies for kidney disease is dietary changes. A diet that is low in sodium, phosphorus, and protein can help to reduce the workload on the kidneys. Foods that are high in potassium, such as bananas and avocados, should also be limited. Instead, focus on eating a variety of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. A diet that is low in protein may help to reduce the workload on the kidneys, as excess protein can be hard for the kidneys to process.
2. Herbal Supplements have been used for centuries to treat a variety of health conditions, including kidney disease. Some of the most effective herbs for kidney disease include dandelion root, nettle leaf, and ginger. These herbs can help to improve kidney function and reduce inflammation in the body. Some herbs, such as stinging nettle and dandelion, have been traditionally used to support kidney health. However, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking any herbal supplements, as they can interact with other medications and may not be safe for everyone.
3. Exercise is essential for maintaining good health, and it can also be beneficial for people with kidney disease. Exercise helps to improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and lower blood pressure. It can also help to reduce stress, which is important for overall health.
4. Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It has been shown to be effective in treating a variety of health conditions, including kidney disease. Acupuncture can help to improve kidney function, reduce inflammation, and relieve pain.
5. Massage Therapy is another natural remedy that can be beneficial for people with kidney disease. It can help to improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and relieve pain. Massage therapy can also help to reduce stress, which is important for overall health.
6. Meditation is a practice that involves focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity. It has been shown to be effective in reducing stress, anxiety, and depression. Meditation can also help to improve kidney function and reduce inflammation in the body.
7. Yoga is a form of exercise that combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation. It has been shown to be effective in reducing stress, improving circulation, and lowering blood pressure. Yoga can also help to improve kidney function and reduce inflammation in the body.
8. Aromatherapy is a practice that involves using essential oils to promote health and well-being. Some essential oils, such as lavender and peppermint, have been shown to be effective in reducing stress and anxiety. Aromatherapy can also help to improve kidney function and reduce inflammation in the body.
9. Hydrotherapy is a form of therapy that involves using water to promote health and well-being. It can include hot and cold compresses, baths, and showers. Hydrotherapy can help to improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and relieve pain.
10. Mind-Body Therapies such as biofeedback and hypnotherapy, can be beneficial for people with kidney disease. These therapies can help to reduce stress, improve kidney function, and reduce inflammation in the body.
11. Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help to flush out toxins and waste products from the kidneys.
12. Manage blood sugar and blood pressure: Controlling blood sugar and blood pressure levels is crucial for people with kidney disease, as high levels of these can damage the kidneys. This can be done through a combination of diet, exercise, and medication.
Herbal remedies
While there are many conventional treatments available for kidney disease, some people prefer to use herbal remedies to manage their symptoms. There are some herbs that have been traditionally used to support kidney health and function. However, it is important to note that not all herbal remedies are safe or effective, and some may even be harmful, especially if taken in large amounts or combined with certain medications. It is crucial to speak with a healthcare provider before taking any herbal remedies if you have kidney disease. Here are a few herbs that are commonly used to support kidney health:
1. Dandelion Root  is a natural diuretic that can help to flush excess fluids from the body. It also contains antioxidants that can help to protect the kidneys from damage. Dandelion root can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.Dandelion root has diuretic properties and may help to increase urine output, which can help to flush out toxins from the kidneys. It may also help to reduce inflammation.
is a natural diuretic that can help to flush excess fluids from the body. It also contains antioxidants that can help to protect the kidneys from damage. Dandelion root can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.Dandelion root has diuretic properties and may help to increase urine output, which can help to flush out toxins from the kidneys. It may also help to reduce inflammation.
2. Ginger Ginger has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. It also has diuretic properties that can help to flush out excess fluids from the body. Ginger can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.
3. Turmeric Turmeric is a spice that has anti-inflammatory properties. It can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys and protect them from damage. Turmeric can be consumed as a spice in cooking or taken in supplement form.
4. Nettle Leaf  is a natural diuretic that can help to flush excess fluids from the body. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. Nettle leaf can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.
is a natural diuretic that can help to flush excess fluids from the body. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. Nettle leaf can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.
5. Corn Silk  is a natural diuretic that can help to flush excess fluids from the body. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. Corn silk can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.
is a natural diuretic that can help to flush excess fluids from the body. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. Corn silk can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.
6. Hibiscus  is a natural diuretic that can help to flush excess fluids from the body. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. Hibiscus can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.
is a natural diuretic that can help to flush excess fluids from the body. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. Hibiscus can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.
7. Astragalus  is an herb that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. It has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. Astragalus can be taken in supplement form.
is an herb that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. It has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. Astragalus can be taken in supplement form.
8. Ginkgo Biloba  is an herb that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. It has antioxidant properties that can help to protect the kidneys from damage. Ginkgo biloba can be taken in supplement form.
is an herb that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. It has antioxidant properties that can help to protect the kidneys from damage. Ginkgo biloba can be taken in supplement form.
9. Milk Thistle  is an herb that has been used for centuries to treat liver and kidney problems. It has antioxidant properties that can help to protect the kidneys from damage caused by toxins. Milk thistle can be taken in supplement form.
is an herb that has been used for centuries to treat liver and kidney problems. It has antioxidant properties that can help to protect the kidneys from damage caused by toxins. Milk thistle can be taken in supplement form.
10. Chanca Piedra  is an herb that has been used in traditional medicine for centuries to treat kidney stones. It has diuretic properties that can help to flush out excess fluids from the body. Chanca piedra can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.
is an herb that has been used in traditional medicine for centuries to treat kidney stones. It has diuretic properties that can help to flush out excess fluids from the body. Chanca piedra can be consumed as a tea or taken in supplement form.
11. Stinging nettle  has diuretic properties and may help to increase urine output and flush out toxins from the kidneys. It may also help to reduce inflammation.
has diuretic properties and may help to increase urine output and flush out toxins from the kidneys. It may also help to reduce inflammation.
12. Cordyceps  is a type of mushroom that has been traditionally used in Chinese medicine to support kidney health and function.
is a type of mushroom that has been traditionally used in Chinese medicine to support kidney health and function.
13. Lemonade, particularly those made with fresh lemon juice, may help prevent the formation of kidney stones due to its high citrate content. Citrate helps prevent the formation of kidney stones by binding with calcium in the urine, which can otherwise contribute to stone formation. Additionally, drinking plenty of fluids, including lemonade, can help flush out the kidneys and reduce the concentration of minerals that can form stones.
14. Cranberry juice may also be beneficial for preventing kidney stones due to its ability to acidify urine, which can help prevent the formation of certain types of stones. Additionally, some studies suggest that cranberry juice may help prevent the formation of bacteria in the urinary tract, which can also contribute to kidney stone formation.
Again, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking any herbal remedies if you have kidney disease, as they can interact with other medications and may not be safe for everyone.
Myths and the kidney
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding kidney health that can lead to confusion and misinformation. Here are a few common ones:
Myth Drinking plenty of water can prevent kidney disease: While staying hydrated is important for overall kidney health, drinking plenty of water alone cannot prevent kidney disease. There are many factors that can contribute to kidney disease, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and family history.
Myth Drinking lots of water is bad for your kidneys: One of the most common myths about kidney health is that drinking too much water can damage your kidneys. However, this is not true. In fact, drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining healthy kidneys. Water helps to flush out toxins and waste products from the body, which reduces the workload on the kidneys. Dehydration, on the other hand, can cause kidney damage over time.
Myth Kidney disease only affects older adults: Another common myth about kidney health is that kidney disease only affects older people. While it is true that the risk of kidney disease increases with age and kidney function tends to decline with age, anyone can develop kidney disease at any age. In fact, some types of kidney disease, such as glomerulonephritis, are more common in children and young adults.
Myth Drinking cranberry juice can cure a urinary tract infection (UTI): Antibiotics are typically needed to treat a UTI. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common condition that can cause pain and discomfort. There is a myth that drinking cranberry juice can cure UTIs. While cranberry juice may help to prevent UTIs by preventing bacteria from sticking to the bladder wall, it is not a cure for UTIs. If you have a UTI, you should see a doctor for proper treatment.
Myth Kidney disease is always accompanied by symptoms Kidney disease is often referred to as a “silent killer” because it can develop without any noticeable symptoms. In the early stages of kidney disease, there may be no symptoms at all. In fact, many people with kidney disease do not experience any symptoms until the disease has progressed to an advanced stage. That’s why it’s essential to get regular kidney function tests if you are at risk for kidney disease.
Myth Kidney disease is always caused by high protein intake: There is a common belief that eating a high-protein diet can damage your kidneys. However, this is not entirely true. While it is true that excessive protein intake can put a strain on the kidneys, moderate protein intake is not harmful to healthy kidneys. In fact, protein is essential for maintaining muscle mass and overall health. Other factors, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and certain medications, can also contribute to kidney disease.
Myth Kidney stones are caused by drinking too much milk Kidney stones are a common condition that can cause severe pain and discomfort. There is a myth that drinking too much milk can cause kidney stones. However, this is not true. While excessive calcium intake can contribute to the formation of kidney stones, moderate calcium intake from milk and other dairy products is not harmful.
Myth Only people with high blood pressure or diabetes are at risk for kidney disease While high blood pressure and diabetes are two of the leading causes of kidney disease, anyone can develop kidney disease regardless of their blood pressure or blood sugar levels. Other risk factors for kidney disease include a family history of kidney disease, smoking, obesity, and a history of kidney infections.
Myth You only need one kidney to live a healthy life While it is true that you can live a healthy life with just one kidney, it is not true that you only need one kidney. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and excess fluid from the body, and having two healthy kidneys is always better than having one.
Myth Drinking alcohol is bad for your kidneys While excessive alcohol consumption can damage the kidneys, moderate alcohol consumption is not harmful to healthy kidneys. In fact, some studies have shown that moderate alcohol consumption may even have a protective effect on the kidneys.
Myth Kidney disease is always irreversible While some types of kidney disease are irreversible, such as end-stage renal disease, many types of kidney disease can be treated and even reversed if caught early enough. That’s why it’s essential to get regular kidney function tests if you are at risk for kidney disease.
When to seek urgent medical care
If you have kidney disease or are at risk for it, it is important to seek urgent medical care if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Severe pain or discomfort in the back, side, or abdomen: This could be a sign of a kidney infection, kidney stones, or other kidney-related issues that require prompt medical attention.
Blood in the urine: This could be a sign of a urinary tract infection, kidney stones, or other kidney-related issues that require prompt medical attention.
High fever: This could be a sign of a kidney infection or other serious infection that requires prompt medical attention.
Sudden and Severe Pain in the Abdomen or Back can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and fever. If you experience sudden and severe pain in your abdomen or back, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. This could be a sign of a kidney infection, kidney stones, or other serious complications.
Difficulty Breathing is another symptom that should not be ignored if you have kidney disease. This could be a sign of fluid buildup in the lungs, which can occur when the kidneys are not functioning properly. If you experience shortness of breath, chest pain, or wheezing, seek medical attention right away.
Swelling in the Legs, Feet, Face or Ankles is a common symptom of kidney disease. This occurs when the kidneys are unable to remove excess fluid from the body, leading to fluid buildup in the tissues. While mild swelling may not require urgent medical attention, sudden and severe swelling could be a sign of a more serious complication such as heart failure or pulmonary edema.
High Blood Pressure is a common complication of kidney disease. This occurs when the kidneys are unable to regulate blood pressure, leading to an increase in blood pressure levels. If you have kidney disease and experience sudden and severe spikes in your blood pressure, seek medical attention immediately. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to serious complications such as stroke, heart attack, and kidney failure.
Changes in Urination are another symptom that should not be ignored if you have kidney disease. This could include a decrease in urine output, blood in the urine, or difficulty urinating. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention right away. These could be signs of a urinary tract infection, kidney stones, or other serious complications.
Fatigue and Weakness are common symptoms of kidney disease. This occurs when the kidneys are unable to remove waste products from the body, leading to a buildup of toxins in the bloodstream. If you experience sudden and severe fatigue or weakness, seek medical attention immediately. This could be a sign of anemia or other serious complications.
Nausea and Vomiting are common symptoms of kidney disease. This occurs when the kidneys are unable to remove waste products from the body, leading to a buildup of toxins in the bloodstream. If you experience sudden and severe nausea or vomiting, seek medical attention immediately. This could be a sign of a kidney infection or other serious complications.
Confusion and Disorientation are serious symptoms that should not be ignored if you have kidney disease. This could be a sign of a buildup of toxins in the bloodstream, which can affect brain function. If you experience sudden and severe confusion or disorientation, seek medical attention immediately.
Chest Pain is a serious symptom that should not be ignored if you have kidney disease. This could be a sign of a heart attack, which can occur when the kidneys are not functioning properly. If you experience sudden and severe chest pain, seek medical attention immediately.
Seizures are a rare but serious complication of kidney disease. This occurs when the buildup of toxins in the bloodstream affects brain function. If you experience a seizure, seek medical attention immediately.
It is important to seek urgent medical care if you experience any of these symptoms, as prompt treatment can help to prevent serious complications. If you are unsure whether your symptoms require urgent medical attention, it is always best to err on the side of caution and seek medical advice.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

