The Impact of High Cholesterol on Heart Health: Prevention and Control
Struggling with high cholesterol levels? You’re not alone. But don’t worry—there are plenty of effective strategies to help you manage it and protect your heart health. Cholesterol is a type of lipid, or fat, that is essential for the normal functioning of the body. It is found in all cells of the body and is important for the production of hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids, which help digest fats. From simple dietary adjustments to regular exercise routines, we’ll explore practical tips and lifestyle changes that can make a real difference in lowering your cholesterol levels and promoting overall well-being. Let’s embark on this journey toward better health together as we discuss the following:
Benefits of cholesterol
Causes of high cholesterol
Symptoms of high cholesterol
Risk factors for high cholesterol
Diagnosis of high cholesterol
Complications of high cholesterol
Prevention of high cholesterol
Treatment of high cholesterol
Management of high cholesterol
Ways to lower your cholesterol
Natural remedies for high cholesterol
When to seek urgent medical care
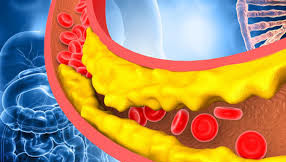
Benefits of cholesterol
Cholesterol is an essential component of our body and plays several important roles in maintaining our overall health. Some of the benefits of cholesterol include:
- Production of hormones: Cholesterol is required for the production of several hormones, including estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol. These hormones play important roles in regulating various bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth, and stress response.
- Production of vitamin D: Cholesterol is also a precursor to vitamin D, which is essential for maintaining bone health and plays a role in regulating immune function.
- Digestion: Cholesterol is needed for the production of bile acids, which are necessary for the digestion and absorption of fats.
- Cell membrane integrity: Cholesterol is a structural component of cell membranes and helps maintain their integrity and fluidity.
- Brain function: Cholesterol is important for the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and low levels of cholesterol have been associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment and dementia.
While cholesterol is important for our health, it is important to maintain healthy levels of cholesterol and manage any risk factors for heart disease to prevent health problems associated with high levels of cholesterol.
Pathophysiology of high cholesterol
High cholesterol, or hypercholesterolemia, occurs when there is an excessive amount of cholesterol in the blood. This can occur due to a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, and lifestyle.
The pathophysiology of high cholesterol involves the accumulation of cholesterol in the walls of blood vessels. Cholesterol is transported in the blood by lipoproteins, and when there is an excess of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, it can build up in the arterial walls, leading to the formation of plaque. This plaque can cause narrowing of the arteries, reducing blood flow to vital organs such as the heart and brain.
Over time, the buildup of plaque can cause atherosclerosis, a condition in which the arterial walls become thickened and hardened. This can increase the risk of developing various cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
In addition to genetics, factors such as a diet high in saturated and trans fats, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and obesity can contribute to high cholesterol levels. These risk factors can cause an imbalance between the production and removal of cholesterol from the body, leading to increased levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood.
Treatment for high cholesterol may involve lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes, exercise, and weight management, as well as medications such as statins and other cholesterol-lowering drugs. Effective management of high cholesterol is important to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and other health complications associated with hypercholesterolemia.
Symptoms of high cholesterol
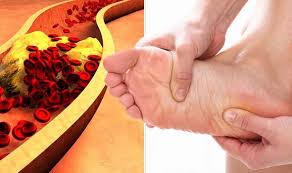
High cholesterol, also known as hypercholesterolemia, usually does not cause any symptoms in itself. It is often called a “silent” condition because it does not have any obvious signs or symptoms.
However, over time, high cholesterol can cause damage to the arteries and increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. These conditions may have symptoms that are related to the reduced blood flow to the affected organs.
Some of the symptoms associated with cardiovascular diseases caused by high cholesterol include:
- Chest pain or angina
- Shortness of breath
- Numbness or weakness in the legs or arms
- Slurred speech or difficulty speaking
- Confusion or memory loss
- Heart palpitations
- Leg pain during walking
- Vision problems
It is important to get regular cholesterol screenings to monitor cholesterol levels, even if there are no obvious symptoms. This can help detect and manage high cholesterol before it leads to more serious health problems.
Risk factors for high cholesterol
High cholesterol levels, also known as hypercholesterolemia, can be caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. These include:
- Unhealthy diet: Consuming a diet that is high in saturated and trans fats, such as red meat, fried foods, processed snacks, and baked goods, can increase LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Lack of physical activity: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to an imbalance between cholesterol production and removal in the body, contributing to high cholesterol levels.
- Age and gender: Cholesterol levels tend to increase with age, and men typically have higher cholesterol levels than women until menopause.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase LDL cholesterol levels and decrease HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of developing hypercholesterolemia.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the arterial walls, increasing the risk of plaque buildup and narrowing of the arteries, which can lead to high cholesterol levels.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and an underactive thyroid, can increase the risk of developing hypercholesterolemia.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and some types of birth control pills, can increase LDL cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Genetics: Some people have a genetic predisposition to high cholesterol, which can cause elevated cholesterol levels even with a healthy diet and exercise routine.
Diagnosis of high cholesterol
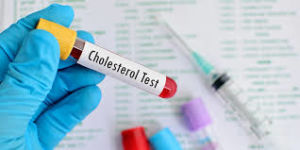
The diagnosis of high cholesterol, also known as hypercholesterolemia, is usually made through a blood test called a lipid profile. This test measures the levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, as well as other lipid markers such as HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol.
A lipid profile typically includes the following measurements:
- Total cholesterol: This measures the total amount of cholesterol in the blood, including LDL and HDL cholesterol.
- LDL cholesterol: This is known as the “bad” cholesterol, as high levels can contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease.
- HDL cholesterol: This is known as the “good” cholesterol, as high levels can help protect against cardiovascular disease.
- Triglycerides: High levels of triglycerides in the blood can also contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease.
A healthcare provider may recommend a lipid profile test for people who have risk factors for high cholesterol, such as a family history of high cholesterol or heart disease, or for those who have symptoms of cardiovascular disease. The American Heart Association recommends that all adults over the age of 20 have a lipid profile test every 4-6 years.
If the results of the lipid profile show high cholesterol levels, lifestyle modifications such as improving the diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and/or taking medication may be recommended to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Complications of high cholesterol
High cholesterol, also known as hypercholesterolemia, can lead to a number of complications if left untreated. These complications are related to the buildup of cholesterol in the arteries, which can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition in which the arteries become narrowed and hardened. Some of the complications of high cholesterol include:
- Heart disease: Atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries can lead to the development of heart disease, including angina, heart attack, and heart failure.
- Stroke: Atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to the brain can lead to the development of a stroke, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked.
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD): Atherosclerosis in the arteries of the legs and feet can lead to the development of PAD, which can cause leg pain during walking and increase the risk of infections and ulcers.
- Aneurysm: High cholesterol levels can contribute to the development of an aneurysm, which occurs when a weakened area of an artery bulges and may rupture.
- Vision problems: High cholesterol can contribute to the development of blockages in the arteries leading to the eyes, which can cause vision problems and even blindness.
It is important to get regular cholesterol screenings to monitor cholesterol levels and manage high cholesterol to prevent the development of these complications. This may involve lifestyle changes, such as improving the diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and/or taking medication to lower cholesterol levels.
Prevention of high cholesterol

There are several steps you can take to help prevent high cholesterol:
- Maintain a healthy diet: A healthy diet can help reduce the risk of high cholesterol. Choose foods that are low in saturated fats and trans fats, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and improve cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity on most days of the week.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase cholesterol levels, so maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of high cholesterol.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking damages the arterial walls, increasing the risk of plaque buildup and narrowing of the arteries, which can lead to high cholesterol levels.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase cholesterol levels and contribute to the development of high blood pressure and heart disease.
- Manage other health conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and an underactive thyroid can increase the risk of developing high cholesterol. Managing these conditions can help prevent the development of hypercholesterolemia.
- Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor cholesterol levels and identify risk factors for high cholesterol.
By adopting these healthy habits, you can help reduce the risk of developing high cholesterol and prevent the development of cardiovascular disease.
Treatment of high cholesterol

Treatment of high cholesterol involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medication, if necessary. The specific approach to treatment will depend on the severity of the hypercholesterolemia and other individual factors.
Lifestyle modifications include:
- Diet: Eating a diet that is low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can help lower your cholesterol levels. This can include eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, as well as avoiding or limiting foods that are high in saturated fats and trans fats.
- Weight management: Losing weight, if overweight or obese, can help improve cholesterol levels.
- Smoking cessation: Smoking can increase cholesterol levels and contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease. Quitting smoking can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of developing heart disease.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase cholesterol levels and contribute to the development of high blood pressure and heart disease.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help lower cholesterol levels, as well as improve overall cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Reduce alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase cholesterol levels and contribute to the development of high blood pressure and heart disease. Limit alcohol consumption to no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be necessary to lower cholesterol levels. This can include statins, bile acid sequestrants, PCSK9 inhibitors, or ezetimibe. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to determine if medication is necessary and which medication is appropriate for your individual situation.
- Statins: These medications work by blocking the enzyme that the liver uses to produce cholesterol, thereby reducing cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Bile acid sequestrants: These medications work by binding to bile acids in the intestine, which prevents them from being reabsorbed by the body. This forces the liver to use more cholesterol to produce more bile acids, which ultimately leads to a reduction in cholesterol levels.
- PCSK9 inhibitors: These medications work by targeting a protein that interferes with the liver’s ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood, resulting in lower LDL cholesterol levels.
- Ezetimibe: This medication works by blocking the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine, leading to lower cholesterol levels in the blood.
It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan for high cholesterol. This may involve regular monitoring of cholesterol levels and adjusting treatment as necessary. In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may be enough to manage high cholesterol, while in other cases, medication may be necessary in addition to lifestyle modifications.
Natural remedies for high cholesterol

There are several natural remedies that may help lower cholesterol levels, but it is important to note that these remedies should not replace medication or medical treatment recommended by a healthcare professional. It is important to talk to a healthcare professional before using natural remedies to lower cholesterol levels, as some remedies may interact with medications or have side effects. A healthcare professional can also help determine if these remedies are appropriate for an individual’s specific health needs. Some natural remedies that may help lower cholesterol include:
Plant sterols and stanols: These are compounds found in certain fruits, vegetables, and grains that can help lower LDL cholesterol levels. They work by blocking the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines. Plant sterols and stanols are added to some margarines, orange juice, and yogurt. The recommended intake is 2 grams per day.
Soluble fiber: This type of fiber is found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and can help lower LDL cholesterol levels. It works by binding to cholesterol in the intestines and preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream. Soluble fiber is found in many plant-based foods, including oats, barley, beans, and fruits. To incorporate more soluble fiber into your diet, aim to eat at least five servings of fruits and vegetables per day, choose whole-grain products instead of refined grains, and include legumes in your meals.
Omega-3 fatty acids: These fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and tuna, as well as in flaxseed and chia seeds, can help lower triglyceride levels and may also help raise HDL cholesterol levels. Omega-3 fatty acids are found in fish oil supplements, as well as in fatty fish such as salmon and tuna. The American Heart Association recommends eating fish twice per week. Fish oil supplements are available in capsule form and should be taken with food.
Garlic:  has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties, particularly in people with high LDL cholesterol levels. Garlic can be consumed fresh or as a supplement. The recommended dose for a supplement is 600 to 1,200 mg per day, divided into two or three doses.
has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties, particularly in people with high LDL cholesterol levels. Garlic can be consumed fresh or as a supplement. The recommended dose for a supplement is 600 to 1,200 mg per day, divided into two or three doses.
Niacin: Niacin, a B vitamin, can help raise HDL cholesterol levels and lower triglyceride levels. It is important to note, however, that high doses of niacin can cause side effects and should only be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Niacin supplements are available in tablet or capsule form. The usual dose is 500 to 2,000 mg per day, taken with meals. It is important to work with a healthcare provider when taking high doses of niacin due to the risk of side effects.
Green tea:  contains compounds called catechins that may help lower cholesterol levels. Green tea can be consumed as a hot or cold beverage. The recommended dose is three to five cups per day.
contains compounds called catechins that may help lower cholesterol levels. Green tea can be consumed as a hot or cold beverage. The recommended dose is three to five cups per day.
Berberine:  is a natural compound found in several plants, including barberry and goldenseal. It has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels, as well as triglycerides and total cholesterol levels. It works by inhibiting an enzyme involved in cholesterol production in the liver. Berberine supplements are available in capsule form. The usual dose is 500 mg, taken two to three times per day, with meals.
is a natural compound found in several plants, including barberry and goldenseal. It has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels, as well as triglycerides and total cholesterol levels. It works by inhibiting an enzyme involved in cholesterol production in the liver. Berberine supplements are available in capsule form. The usual dose is 500 mg, taken two to three times per day, with meals.
Cholest-off: is a dietary supplement that contains plant sterols and stanols, which have been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. These compounds work by blocking the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines. Cholest-off supplements are available in capsule form. The recommended dose is two capsules taken twice per day with meals.
Coenzyme Q10: is a compound found in the body that is involved in energy production. It has also been shown to have antioxidant properties and may help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Coenzyme Q10 supplements are available in capsule form. The recommended dose is 100 to 200 mg per day, taken with meals.
Psyllium:  is a type of soluble fiber that is found in certain plants, including the seeds of the Plantago ovata plant. It has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the intestines and preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream. Blond psyllium can be taken as a powder, capsule, or in food products such as cereal or snack bars. The recommended dose of psyllium is 10-20 grams per day. It is important to drink plenty of water when taking psyllium to prevent constipation. Psyllium supplements are available in capsule or powder form. The recommended dose is 10 to 12 grams per day, taken with water.
is a type of soluble fiber that is found in certain plants, including the seeds of the Plantago ovata plant. It has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the intestines and preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream. Blond psyllium can be taken as a powder, capsule, or in food products such as cereal or snack bars. The recommended dose of psyllium is 10-20 grams per day. It is important to drink plenty of water when taking psyllium to prevent constipation. Psyllium supplements are available in capsule or powder form. The recommended dose is 10 to 12 grams per day, taken with water.
Red yeast rice:  is a fermented rice product that contains a compound called monacolin K, which is similar in structure to the cholesterol-lowering medication lovastatin. It has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Red yeast rice can be taken as a supplement in capsule form. The recommended dose of red yeast rice extract is 1.2-2.4 grams per day. It is important to consult a healthcare provider before using red yeast rice, especially if you are taking medications. Red yeast rice supplements are available in capsule form. The recommended dose is 1,200 mg twice per day with meals.
is a fermented rice product that contains a compound called monacolin K, which is similar in structure to the cholesterol-lowering medication lovastatin. It has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Red yeast rice can be taken as a supplement in capsule form. The recommended dose of red yeast rice extract is 1.2-2.4 grams per day. It is important to consult a healthcare provider before using red yeast rice, especially if you are taking medications. Red yeast rice supplements are available in capsule form. The recommended dose is 1,200 mg twice per day with meals.
Policosanol:  is a natural compound found in sugarcane wax that has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. It works by inhibiting the production of cholesterol in the liver. Policosanol supplements are available in tablet or capsule form. The recommended dose is 10 to 20 mg per day.
is a natural compound found in sugarcane wax that has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. It works by inhibiting the production of cholesterol in the liver. Policosanol supplements are available in tablet or capsule form. The recommended dose is 10 to 20 mg per day.
Guggul:  is a resin extracted from the Commiphora mukul tree and has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels, as well as triglycerides and total cholesterol levels. Guggul supplements are available in capsule or tablet form. The recommended dose is 500 to 1,000 mg per day, taken with water.
is a resin extracted from the Commiphora mukul tree and has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels, as well as triglycerides and total cholesterol levels. Guggul supplements are available in capsule or tablet form. The recommended dose is 500 to 1,000 mg per day, taken with water.
Barley:  is a whole grain that is high in soluble fiber, which has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. It can be added to soups, salads, or used as a substitute for rice or pasta. Barley can be consumed as a food, in the form of whole-grain bread, cereal, or soup. It can also be taken as a supplement in capsule form.
is a whole grain that is high in soluble fiber, which has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. It can be added to soups, salads, or used as a substitute for rice or pasta. Barley can be consumed as a food, in the form of whole-grain bread, cereal, or soup. It can also be taken as a supplement in capsule form.
Broccoli sprouts:  are a rich source of sulforaphane, a compound that has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties. Sulforaphane works by inhibiting an enzyme involved in cholesterol production in the liver. Broccoli sprouts can be added to salads or sandwiches or consumed as a supplement in capsule form.
are a rich source of sulforaphane, a compound that has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties. Sulforaphane works by inhibiting an enzyme involved in cholesterol production in the liver. Broccoli sprouts can be added to salads or sandwiches or consumed as a supplement in capsule form.
Fish:  such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to help lower triglyceride levels and may also help raise HDL cholesterol levels. Fish can be baked, grilled, or broiled. The recommended intake is two servings per week.
such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to help lower triglyceride levels and may also help raise HDL cholesterol levels. Fish can be baked, grilled, or broiled. The recommended intake is two servings per week.
Nuts:  such as almonds and walnuts, are a good source of healthy fats and fiber, which have been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Nuts can be consumed as a snack or added to salads or baked goods. The recommended intake is a handful per day.
such as almonds and walnuts, are a good source of healthy fats and fiber, which have been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Nuts can be consumed as a snack or added to salads or baked goods. The recommended intake is a handful per day.
Black tea:  contains compounds called theaflavins, which have been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties. Drinking black tea regularly may help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Black tea can be consumed hot or cold. The recommended intake is three to five cups per day.
contains compounds called theaflavins, which have been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties. Drinking black tea regularly may help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Black tea can be consumed hot or cold. The recommended intake is three to five cups per day.
Tomato juice:  Tomatoes are a good source of lycopene, a compound that has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties. Drinking tomato juice regularly may help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Tomato juice can be consumed as a beverage. The recommended intake is one to two glasses per day.
Tomatoes are a good source of lycopene, a compound that has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties. Drinking tomato juice regularly may help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Tomato juice can be consumed as a beverage. The recommended intake is one to two glasses per day.
Cranberry juice:  is a good source of antioxidants, which have been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Cranberry juice can be consumed as a beverage. The recommended intake is one to two glasses per day.
is a good source of antioxidants, which have been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Cranberry juice can be consumed as a beverage. The recommended intake is one to two glasses per day.
Hawthorn:  is a plant that has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties and may also help improve cardiovascular health. Hawthorn can be taken as a tea, tincture, or capsule. The recommended dose of hawthorn extract is 300-600 mg per day. It is important to consult a healthcare provider before using hawthorn, especially if you are taking medications.
is a plant that has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties and may also help improve cardiovascular health. Hawthorn can be taken as a tea, tincture, or capsule. The recommended dose of hawthorn extract is 300-600 mg per day. It is important to consult a healthcare provider before using hawthorn, especially if you are taking medications.
Astragalus:  is a plant that has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties and may also help improve immune function. Astragalus can be taken as a tea, tincture, or capsule. The recommended dose of astragalus extract is 500-1,000 mg per day. It is important to consult a healthcare provider before using astragalus, especially if you are taking medications.
is a plant that has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering properties and may also help improve immune function. Astragalus can be taken as a tea, tincture, or capsule. The recommended dose of astragalus extract is 500-1,000 mg per day. It is important to consult a healthcare provider before using astragalus, especially if you are taking medications.
Ground flaxseed:

Ground flaxseed is a popular natural remedy for managing cholesterol. Flaxseed contains high levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid that can help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Ground flaxseed can be added to food such as smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal. The recommended dose of flaxseed is 2-4 tablespoons per day. It is important to drink plenty of water when taking flaxseed to prevent constipation. Here are some guidelines on how to use ground flaxseed for managing cholesterol:
Add to food: Ground flaxseed can be added to a variety of foods, including smoothies, yogurt, oatmeal, and baked goods. Start with a small amount, such as one tablespoon per day, and gradually increase to two to four tablespoons per day.
Drink plenty of water: It is important to drink plenty of water when taking ground flaxseed to prevent constipation.
Store properly: Ground flaxseed should be stored in an airtight container in the refrigerator to prevent it from going rancid.
Be aware of potential interactions: Flaxseed can interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners and diabetes medications. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using flaxseed if you are taking any medications.
Start slowly: If you have never consumed flaxseed before, start with a small amount and gradually increase the dosage to avoid any digestive discomfort.
It is important to note that while ground flaxseed can be helpful in managing cholesterol, it should not be used as a substitute for prescribed medications without consulting with a healthcare provider.
When to seek urgent medical care
If you have high cholesterol, there may be times when it is necessary to seek urgent medical care. Some situations that may require urgent medical attention include:
Chest pain or pressure: Chest pain or pressure can be a sign of a heart attack, which can be a life-threatening emergency. Seek medical attention immediately if you experience chest pain or pressure, especially if it is accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea.
Stroke symptoms: High cholesterol can increase the risk of stroke. If you experience sudden weakness or numbness on one side of your body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, or sudden vision changes, seek medical attention immediately.
Severe side effects from medication: If you are taking medication to lower your cholesterol levels and experience severe side effects, such as muscle pain or weakness, seek medical attention immediately.
Difficulty breathing: High cholesterol can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, which can lead to shortness of breath or difficulty breathing. Seek medical attention if you experience sudden onset of difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms that concern you, even if they are not listed here. A healthcare professional can help determine if urgent medical care is necessary and provide appropriate treatment.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

