Long-Term Solutions for Controlling Hay Fever Symptoms
Are pesky pollen allergies making life miserable? Hay fever, often triggered by pollen, can bring on sneezing fits, itchy eyes, and a stuffy nose. But fear not! With the right strategies, you can tackle hay fever head-on and enjoy the outdoors again. Let’s explore some simple yet effective ways to alleviate those bothersome symptoms and reclaim your comfort. Hay fever is a type of allergic reaction, specifically allergic rhinitis, that is caused by exposure to certain allergens such as pollen, mold, dust mites, and pet dander. Allergies, on the other hand, can refer to a range of allergic reactions that can be triggered by a variety of allergens, including those that cause hay fever. Both hay fever and other types of allergies involve an immune system overreaction to a normally harmless substance, resulting in a range of symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, rashes, and swelling. We will discuss the following topics:
Causes of hay fever and allergies
Risk factors for hay fever and allergies
Symptoms of hay fever and allergies
Diagnosing hay fever and allergies
How to prevent hay fever and allergies
How to treat hay fever and allergies
Types of allergies
Tips for easing the different types of allergies
Natural remedies and allergies
When to seek urgent medical care

Hay fever
Hay fever, also known as allergic rhinitis, is a type of allergic reaction that occurs when a person’s immune system overreacts to certain allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, or animal dander. It can be seasonal or year-round, depending on the allergens that trigger the reaction. The symptoms of include:
Allergies
Allergies are an overreaction of the immune system to a substance that is typically harmless to most people. These substances, called allergens, can include pollen, dust mites, mold spores, pet dander, insect venom, certain foods, and medications. When a person with allergies comes into contact with an allergen, their immune system produces an antibody called immunoglobulin E (IgE). The IgE antibodies then trigger the release of histamine and other chemicals in the body, leading to allergic symptoms. The symptoms can vary depending on the type of allergy and the severity of the reaction and can include:
- Sneezing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Skin rash or hives
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Difficulty breathing
Causes of hay fever and allergies
Hay fever and allergies are caused by an overreaction of the immune system to substances that are typically harmless to most people. These substances, known as allergens, can include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods.
When a person with allergies comes into contact with an allergen, their immune system produces antibodies that recognize the allergen as a threat. The next time the person is exposed to that allergen, their immune system releases chemicals such as histamine, which can cause symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and skin rash.
Some people are more susceptible to allergies than others, and there is often a genetic component to the condition. Environmental factors such as pollution, climate change, and exposure to certain chemicals can also play a role in the development of allergies.
Other factors that can contribute to allergies include stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, and certain medical conditions such as asthma and eczema. Additionally, some studies suggest that early exposure to allergens, particularly in infancy and early childhood, may increase the risk of developing allergies later in life.
Risk factors for hay fever and allergies
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing hay fever and allergies. These include:
- If a person has a family history of allergies or asthma, they are more likely to develop hay fever and allergies.
- Hay fever and allergies can occur at any age, but they often develop during childhood or adolescence. However, it is possible to develop allergies later in life.
- Gender: In general, boys are more likely to develop allergies than girls. However, this difference may disappear in adulthood.
- Exposure to certain environmental factors such as pollution, smoke, or chemicals can increase the risk of developing allergies.
- Certain occupations that involve exposure to allergens, such as farming, can increase the risk of developing allergies.
- If a person has previously had allergies, they are more likely to develop additional allergies in the future.
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke can increase the risk of developing allergies.
- Poor diet and exercise habits can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of developing allergies.
- Air conditioning can help reduce humidity levels in your home, which can help prevent the growth of mold and dust mites. However, air conditioning can also circulate allergens such as pollen and dust throughout your home, exacerbating allergy symptoms. It is important to clean and maintain your air conditioning system regularly to prevent the buildup of allergens.
- Vacuuming can help remove allergens such as dust mites, pet dander, and pollen from carpets and upholstery. However, if your vacuum does not have a HEPA filter, it may actually be stirring up allergens and spreading them throughout your home. It is important to use a vacuum with a HEPA filter and to vacuum regularly to help reduce allergen levels in your home.
- Mold can be a major trigger for allergies and can grow in damp or humid environments such as bathrooms and basements. It is important to regularly clean and dry areas where mold is likely to grow, and to fix any leaks or moisture problems that may be contributing to mold growth. If you have a mold allergy, it is best to avoid areas with visible mold and to use an air purifier to help remove mold spores from the air.
Diagnosing hay fever and allergies
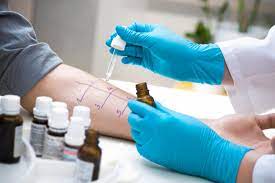
Hay fever and allergies can have similar symptoms, but there are some key differences that can help with diagnosis. Here are some steps to help diagnose hay fever and allergies:
- Identify the symptoms: Hay fever symptoms include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy eyes, nose and throat, and watery eyes. Allergy symptoms can vary depending on the allergen, but can include hives, itching, nasal congestion, and difficulty breathing.
- Determine the cause: Hay fever is caused by an allergic reaction to pollen, while allergies can be caused by a range of allergens, including pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods.
- Consider timing: Hay fever symptoms usually occur seasonally when the pollen count is high, while allergies can occur year-round.
- Get a skin test: A skin test can help identify specific allergens that may be causing symptoms. In this test, a small amount of an allergen is placed on the skin, and the skin is then pricked to see if a reaction occurs.
- Blood test: can also be used to identify specific allergens that may be causing symptoms.
- Keep a symptom diary: Keeping a record of symptoms can help identify patterns and potential triggers.
How to prevent hay fever and allergies
Preventing hay fever and allergies can be challenging, but there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing these conditions or manage symptoms. Here are some tips:
- Avoid allergens: Try to identify the allergens that trigger symptoms and avoid them as much as possible. For example, stay indoors when pollen counts are high, use air purifiers to filter indoor air, and keep pets out of certain areas of the home.
- Wear a mask: When working outside or in areas with high allergen exposure, wearing a mask can help filter out allergens.
- Keep a clean environment: Regularly clean the home to reduce the presence of allergens such as dust mites and pet dander.
- Use medications: Over-the-counter or prescription medications such as antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal corticosteroids can help manage symptoms.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy involves exposing a person to small amounts of allergens over time to build up tolerance and reduce the severity of allergic reactions.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and reducing stress can help strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of allergies.
- Consult a healthcare professional: A healthcare professional can provide guidance on preventing and managing allergies, including identifying triggers, prescribing medications, and recommending immunotherapy.
Types of allergies
There are several types of allergies, including:
Seasonal allergies: Also known as hay fever, these allergies are triggered by airborne allergens such as pollen, mold spores, and dust mites. Symptoms include runny nose, sneezing, and itchy eyes.
Food allergies: These allergies occur when the immune system reacts to a particular food, such as peanuts, shellfish, or dairy products. Symptoms can range from mild (itchy mouth or hives) to severe (anaphylaxis).
Drug allergies: Some people may develop an allergic reaction to certain medications, such as antibiotics or aspirin. Symptoms can include rash, hives, and difficulty breathing.
Insect sting allergies: Allergic reactions to insect stings from bees, wasps, and other insects can range from mild swelling and itching to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
Contact allergies: These allergies occur when the skin comes into contact with an allergen, such as poison ivy or latex. Symptoms can include redness, itching, and rash.
Pet allergies: Some people may develop an allergic reaction to pet dander, saliva, or urine. Symptoms can include runny nose, sneezing, and itchy eyes.
It is important to note that not all allergies are the same, and symptoms and severity can vary widely between individuals. A healthcare professional can help identify the specific allergen and provide guidance on managing symptoms.
Here are some tips for easing the different types of allergies:
In general, it is important to identify the triggers that cause your allergies and take steps to avoid them. Talk to a healthcare professional about allergy testing and treatment options if your symptoms are severe or persistent.
- Food allergies: The best way to prevent food allergies is to avoid the foods that trigger them. Read food labels carefully and ask restaurant staff about ingredients and cooking methods. Carry an epinephrine auto-injector with you at all times in case of a severe allergic reaction.
-
Drug allergies: If you have a known drug allergy, avoid taking that medication in the future. Inform all healthcare professionals, including doctors, dentists, and pharmacists, of your drug allergy. Consider wearing a medical alert bracelet or necklace that lists your allergy.
-
Contact allergies: Contact allergies are triggered by direct contact with a substance that your skin is sensitive to. Avoiding contact with the substance is the best way to prevent contact allergies. Wear protective clothing or gloves if you need to handle the substance and wash your skin thoroughly after exposure.
-
Insect allergies: If you are allergic to insect stings, it is important to carry an epinephrine auto-injector with you at all times. Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants when outdoors and avoid wearing brightly colored clothing or perfume that may attract insects. Seek medical attention immediately if you are stung and experience symptoms such as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face or throat.
-
Pet allergies: If you are allergic to pets, it is best to avoid contact with them. Keep pets out of the bedroom and use a HEPA air purifier to help remove pet dander from the air. Bathe pets regularly to help reduce dander levels and vacuum your home frequently to remove pet hair and dander.
-
Seasonal Allergies: Here are some tips for easing seasonal allergies:
- Stay indoors: On days when pollen counts are high, try to stay indoors as much as possible, especially during midday and afternoon hours.
- Keep windows closed: Keep windows and doors closed during pollen season to minimize the amount of allergens that enter the home.
- Use air conditioning: Use air conditioning, which can help filter out allergens from the air. Make sure to clean the filters regularly.
- Use a HEPA filter: Consider using a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter in the home to reduce allergens in the air.
- Avoid outdoor activities: Avoid outdoor activities such as gardening or mowing the lawn during peak pollen season.
- Shower after being outside: Shower and change clothes after spending time outside to remove pollen and other allergens from the skin and clothing.
- Use saline nasal spray: Saline nasal sprays can help relieve nasal congestion and flush out allergens from the nasal passages.
- Use over-the-counter medications: Over-the-counter medications such as antihistamines and nasal corticosteroids can help relieve symptoms.
- Consider allergy shots: Allergy shots, also known as immunotherapy, can help reduce the severity of allergic reactions over time by exposing the body to small amounts of allergens.
It is important to note that not all treatments are suitable for everyone, and it may take time and patience to find an effective treatment for each individual. A healthcare professional can provide guidance on the best treatment options based on a person’s symptoms and medical history.
How to treat hay fever and allergies

There are several treatment options available for hay fever and allergies. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s response to previous treatments. Here are some common treatment options:
- Medications: Over-the-counter or prescription medications such as antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal corticosteroids can help manage symptoms.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy involves exposing a person to small amounts of allergens over time to build up tolerance and reduce the severity of allergic reactions.
- Eye drops: Eye drops can help relieve itchy, red, or swollen eyes caused by allergies.
- Nasal irrigation: Rinsing the nasal passages with a saline solution can help reduce nasal congestion and flush out allergens.
- Avoid allergens: Try to identify the allergens that trigger symptoms and avoid them as much as possible.
- Wear a mask: When working outside or in areas with high allergen exposure, wearing a mask can help filter out allergens.
- Keep a clean environment: Regularly clean the home to reduce the presence of allergens such as dust mites and pet dander.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine technique, has been shown to help relieve hay fever symptoms in some people.
Natural remedies and allergies
It is important to talk to a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies for allergies, as some remedies may interact with medications or have side effects. It is also important to continue taking any prescribed medications or following other recommended treatments. There are several natural remedies that may help ease allergy symptoms:
Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial to your health, especially your digestive and immune systems. Several studies have investigated the effects of probiotics on allergies, and while the evidence is mixed, some studies suggest that probiotics may help reduce allergy symptoms.
One theory is that probiotics may help balance the immune system, reducing the likelihood of an overactive immune response that leads to allergy symptoms. Probiotics may also help strengthen the gut barrier, reducing the absorption of allergens into the bloodstream.
A review of several studies on probiotics and allergies published in the journal Allergy in 2018 found that probiotics may be effective in reducing symptoms of allergic rhinitis (hay fever), but more research is needed to confirm this. Another study published in the journal International Archives of Allergy and Immunology in 2015 found that probiotics may help reduce eczema symptoms in children.
While probiotics are generally safe for most people, it is important to talk to a healthcare professional before starting a probiotic supplement, especially if you have a weakened immune system or are taking medication. The dosage and strain of probiotics may also vary depending on the type of allergy or condition being treated, so it is important to follow recommended guidelines.
Green tea

Green tea is a type of tea made from the Camellia sinensis plant. Unlike black tea, which is fermented, green tea is made by steaming or pan-frying the leaves. This minimal processing helps to preserve the natural compounds found in the tea leaves, which are thought to provide various health benefits. Green tea is known for its high concentration of antioxidants, particularly polyphenols called catechins, which have been studied for their potential health benefits. These antioxidants may help protect the body against damage from free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can contribute to chronic diseases.
Some potential benefits of drinking green tea include:
Improved brain function: Green tea contains caffeine, which can help improve alertness and concentration. It also contains an amino acid called L-theanine, which may help promote relaxation and reduce stress.
Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease: Studies suggest that drinking green tea may help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Weight loss: Green tea may help boost metabolism and increase fat burning, which can aid in weight loss.
Reduced risk of certain types of cancer: Some studies have suggested that drinking green tea may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer.
Improved dental health: The catechins in green tea may help reduce the risk of dental caries (cavities) and improve overall dental health.
Green tea may have some benefits for people with allergies due to its anti-inflammatory properties. Allergies occur when the immune system overreacts to a harmless substance, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, and triggers an inflammatory response. The catechins in green tea have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, which may help reduce symptoms of allergies.
In addition, green tea contains a compound called epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), which has been shown to help regulate the immune system and reduce allergic reactions in animal studies. However, more research is needed to determine the extent of EGCG’s effects in humans with allergies.
It is important to note that green tea contains caffeine, which can act as a stimulant and may exacerbate symptoms for some people with allergies. Additionally, green tea can interact with certain medications, so it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before adding green tea to your diet if you have allergies or are taking any medications.
While green tea is generally considered safe for most people, it can interact with certain medications and may not be suitable for everyone. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before adding any new supplement or beverage to your routine.
Honey

Honey has been touted as a natural remedy for allergies due to its potential to reduce allergy symptoms. The idea behind this is that by consuming small amounts of local honey, a person can expose themselves to small amounts of the pollen from local plants, which can help desensitize the immune system to the allergens. Eating local honey may help reduce allergy symptoms, as it contains small amounts of pollen from local plants. However, more research is needed to confirm this.
However, the evidence supporting the use of honey as a treatment for allergies is limited. While some studies have suggested that consuming honey can reduce symptoms of allergies, such as sneezing and runny nose, the results have been inconsistent and the studies have been small.
Additionally, it is important to note that honey can cause an allergic reaction in some people. People who are allergic to pollen or bee venom may also be allergic to honey, and consuming it could trigger an allergic reaction.
Overall, while honey may be a tasty addition to a healthy diet, it is not a proven treatment for allergies. People with allergies should consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for their symptoms.
Nasal rinse

Nasal rinses, also known as nasal irrigation or nasal lavage, can be an effective way to relieve allergy symptoms. The technique involves flushing out the nasal passages with a saline solution using a device called a neti pot or nasal irrigator. Saline nasal irrigation uses a neti pot or saline nasal spray to help flush out allergens and mucus from your nasal passages, reducing congestion and inflammation.
Nasal rinses work by helping to remove mucus, allergens, and other irritants from the nasal passages, which can help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms such as congestion, sneezing, and runny nose. In addition, nasal rinses can help moisturize the nasal passages and reduce the risk of infections.
Several studies have suggested that nasal rinses can be a safe and effective treatment for allergic rhinitis (hay fever), particularly when used in combination with other treatments such as antihistamines or corticosteroids.
It is important to note that while nasal rinses can be a helpful tool in managing allergy symptoms, they are not suitable for everyone. People with certain medical conditions, such as a deviated septum or frequent nosebleeds, may not be able to use nasal rinses. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment for allergies.
Vitamin C

Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that plays many important roles in the body, including supporting the immune system. Some research has suggested that vitamin C may also have benefits for people with allergies.
One study found that people who consumed more vitamin C had a lower risk of developing allergies, and another study found that vitamin C supplements reduced symptoms of seasonal allergies in some people.
Vitamin C may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is a key component of allergies. It may also help stabilize mast cells, which are immune cells that play a role in allergic reactions.
While vitamin C is generally safe and can be found in many foods such as oranges, strawberries, and broccoli, it is important to note that high doses of vitamin C supplements can cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and cramps. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements, especially if you have any medical conditions or take medications.
Omega-3

Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that are important for overall health and have been linked to a variety of health benefits, including reducing inflammation in the body. Some research has suggested that omega-3 fatty acids may also have benefits for people with allergies.
One study found that people who consumed more omega-3 fatty acids had a lower risk of developing allergic rhinitis (hay fever), and another study found that omega-3 supplements reduced symptoms of allergic rhinitis in some people.
Omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is a key component of allergies. They may also help regulate the immune system and reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
While omega-3 fatty acids are generally safe and can be found in foods such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, it is important to note that high doses of omega-3 supplements can increase the risk of bleeding and interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements, especially if you have any medical conditions or take medications.
Spicy food

There is no clear evidence to suggest that eating spicy foods can have a direct effect on allergies. However, some people with allergies may find that eating spicy foods can exacerbate their symptoms.
Spicy foods contain capsaicin, which is a compound that can cause a burning sensation and irritation in the nasal passages and airways. For people with allergies, this irritation can worsen existing symptoms such as nasal congestion, sneezing, and runny nose.
Additionally, some spicy foods such as curries, hot sauces, and chili peppers may contain histamine or other compounds that can trigger allergic reactions in some people. Histamine is a natural compound that is released by the immune system in response to allergens, and can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, and swelling.
It is important to note that spicy foods can be part of a healthy and varied diet, and may have other health benefits such as improving digestion and metabolism. However, people with allergies should pay attention to how their body reacts to spicy foods and avoid them if they worsen their symptoms.
Steam

Steam can be a helpful tool in managing allergy symptoms, particularly those related to the respiratory system. Inhaling steam can help moisturize and soothe the nasal passages and airways, which can help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms such as congestion, coughing, and sore throat.
There are several ways to use steam for allergies, including:
Steam inhalation: Boil a pot of water and carefully pour it into a bowl. Place your face over the bowl and drape a towel over your head to create a tent, trapping the steam inside. Breathe deeply for 5-10 minutes.
Steam shower: Take a hot shower and inhale the steam. This can help moisturize the nasal passages and airways and provide relief from allergy symptoms.
Humidifier: Use a humidifier to add moisture to the air in your home. This can help prevent dryness and irritation in the nasal passages and airways, which can worsen allergy symptoms.
It is important to note that steam can be hot and may cause burns or other injuries if not used carefully. People with certain medical conditions, such as asthma, may also need to use caution when using steam. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatments for allergies.
Quercetin

Quercetin is a flavonoid, a type of plant pigment that is found in many fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Some studies have suggested that quercetin may have anti-inflammatory, antihistamine and antioxidant properties that could be beneficial for people with allergies. It may help reduce allergy symptoms such as sneezing and runny nose.
Quercetin may help reduce the release of histamine, a natural compound that is released by the immune system in response to allergens and can cause symptoms such as itching, hives, and swelling. It may also help stabilize mast cells, which are immune cells that play a role in allergic reactions.
While there is some evidence to suggest that quercetin may be helpful for people with allergies, more research is needed to fully understand its effects. Additionally, quercetin is not well absorbed by the body and is quickly metabolized, so it may not be effective in supplement form.
Foods that are high in quercetin include apples, onions, broccoli, berries, and citrus fruits. Incorporating these foods into your diet may be a helpful way to boost your intake of quercetin and potentially reduce allergy symptoms. However, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements or making significant changes to your diet.
Herbal butterbur

Butterbur is a herb that has been traditionally used in herbal medicine to treat a variety of conditions, including allergies. Some studies have suggested that butterbur may be effective in reducing allergy symptoms, such as sneezing, itching, and congestion, particularly those related to hay fever.
The active compounds in butterbur are petasin and isopetasin, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antihistamine effects. These properties may help reduce the release of histamine and other inflammatory compounds that are involved in allergic reactions.
While butterbur may be effective in reducing allergy symptoms, it is important to note that the herb contains compounds called pyrrolizidine alkaloids, which can be toxic to the liver and may cause other side effects. For this reason, it is important to only use butterbur supplements that have been specifically labeled as “PA-free,” meaning that they have been processed to remove the harmful compounds.
Additionally, butterbur may interact with certain medications, so it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements. It is also important to note that the long-term effects of butterbur on health are not well understood, so it should be used with caution.
When to seek urgent medical care
While hay fever and allergies are generally not life-threatening, there are some situations where urgent medical care should be sought. These include:
Severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis): Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, rapid pulse, and loss of consciousness. Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment, including the use of epinephrine.
Asthma attack: People with asthma are at higher risk of developing severe symptoms during an allergic reaction, including difficulty breathing and wheezing. If symptoms are severe or do not respond to rescue inhaler use, urgent medical care should be sought.
Severe or worsening symptoms: If symptoms are severe or worsening despite treatment, or if new symptoms develop, it is important to seek medical attention.
Eye infection: Allergies can increase the risk of eye infections. If symptoms include eye pain, discharge, or sensitivity to light, medical attention should be sought.
Persistent or recurrent sinus infections: Chronic sinus infections can be a complication of allergies, and may require medical treatment.
It is important to note that not all treatments are suitable for everyone, and it may take time and patience to find an effective treatment for each individual. A healthcare professional can provide guidance on the best treatment options based on a person’s symptoms and medical history. In general, if symptoms are causing significant discomfort or interfering with daily activities, it is advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide guidance on the best course of treatment based on a person’s symptoms and medical history.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions. hay fever hay fever Hay fever hay fever hay fever hay fever hay fever hay fever hay fever hay fever hay fever hay fever hay fever.

