Understanding Ear Infection Symptoms and Their Impact
Ear Infections: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention Strategies
Dealing with ear infections can be uncomfortable and worrisome, especially when they affect our ability to hear and function comfortably. From the common otitis media in children to the painful otitis externa in adults, they can disrupt our daily lives. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and relief. Let’s explore the world of ear infections together and learn how to tackle them head-on for a healthier, happier you. Please keep reading for details about the following
Common symptoms of an ear infection
Tips to help keep your ears healthy
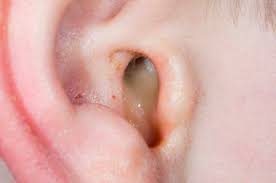
Also known as otitis media, this is an inflammation of the middle ear. It is a common condition, especially in children. They can be caused by bacteria or viruses and often occur after a cold or upper respiratory infection. The infection causes fluid to build up behind the eardrum, leading to pain, discomfort, and sometimes a temporary hearing loss.
Some of the common symptoms include:
Ear pain: Ear pain is usually the first and most noticeable symptom of an ear infection. The pain can be sharp, dull, or throbbing, and may worsen when lying down.
Fluid discharge: Some people may experience discharge from the ear, which can be a sign that the eardrum has ruptured.
Hearing loss: Hearing loss may occur due to the fluid buildup in the middle ear.
Fever: A fever may accompany an ear infection, especially in children.
Dizziness: Some people may experience dizziness or vertigo due to the infection.
Ear fullness: A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear may be present due to the fluid buildup.
Middle ear infections
They occur when fluid builds up behind the eardrum and becomes infected by bacteria or viruses. They are most common in children but can also occur in adults.
Some of the common symptoms of otitis media include:
Ear pain the most common symptom. The pain can be mild to severe and can last several hours to a few days.
A fever may accompany an ear infection, especially in children.
Hearing loss may occur due to the fluid buildup in the middle ear.
A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear may be present due to the fluid buildup.
Fluid or pus may drain from the ear if the eardrum ruptures.
Children with may be irritable, fussy, or have difficulty sleeping.
Treatment typically involves antibiotics, pain relievers, and sometimes decongestants to help clear the Eustachian tubes. In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend ear drops or antihistamines to help manage symptoms. Most people recover fully within a few days to a week with appropriate treatment. It’s important to see a healthcare provider if you suspect you have otitis media, as complications can occur if left untreated.
Outer ear infections
Also known as otitis externa or swimmer’s ear, this is an infection of the outer ear canal. It is most commonly caused by bacteria but can also be caused by fungi or viruses. They are more common in people who swim frequently, as water that gets trapped in the ear canal can create a moist environment that promotes bacterial growth.
Some of the common symptoms of otitis externa include:
Ear pain: Ear pain is usually the first and most noticeable symptom of an outer ear infection. The pain may worsen when the ear is touched or when chewing.
Itching: Itching in the ear canal may occur before the pain starts.
Discharge: Discharge from the ear canal may be present and may be clear or yellowish in color.
Swelling: Swelling of the ear canal and nearby lymph nodes may occur.
Redness: The skin of the ear canal may become red and inflamed.
Decreased hearing: The buildup of fluid and swelling can lead to a temporary hearing loss.
Treatment typically involves antibiotics, ear drops, and pain relievers. In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend antifungal medication if the infection is caused by a fungus. It’s important to keep the ear canal dry during treatment, as water can exacerbate the infection. Most people recover fully from this condition within a few days to a week with appropriate treatment.
Here are some tips to help keep your ears healthy:

