Ear Ache Relief: Effective Home Remedies and Treatments
Are you experiencing the discomfort of an ear ache? Don’t worry, relief is within reach! Ear aches can be caused by various factors such as infections, fluid buildup, or even allergies. Fortunately, there are plenty of effective remedies available to alleviate the pain and restore comfort. From simple home treatments to medical interventions, let’s explore the best ways to ease your EARACHE and get back to feeling your best. We will discuss the following topics:
The ear
Parts of the ear
Causes of earache
Ear infections
Symptoms of earache
Ear ache in children
Earwax
Swimmer’s ear
Ways to Get Water Out of Your Ear
Airplane ear
A foreign object in the ear
Tips to keep the ears healthy
Management of earache
Home remedies that may help alleviate earache
Complications of earache
When to seek urgent medical care
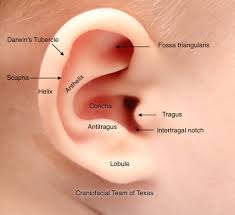
Parts of the ear
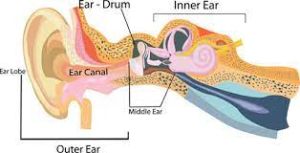
The ear is divided into three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. Each part has a unique structure and function:
Outer ear: The outer ear consists of the pinna (also known as the auricle) and the ear canal. The pinna is the visible part of the ear that protrudes from the side of the head and is responsible for collecting sound waves. The ear canal is a tube-like structure that leads from the pinna to the eardrum.
Middle ear: The middle ear is an air-filled space behind the eardrum. It contains three small bones called the ossicles (the malleus, incus, and stapes), which amplify and transmit sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear. The middle ear is also connected to the back of the throat by the Eustachian tube, which helps to equalize pressure on either side of the eardrum.
Inner ear: The inner ear is a complex structure that is responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals that the brain can interpret. It contains the cochlea, which is shaped like a snail shell and contains thousands of tiny hair cells that detect different frequencies of sound. The cochlea is a fluid-filled spiral structure lined with tiny hair cells that are sensitive to different frequencies of sound. The inner ear also contains the vestibular system, which is responsible for our sense of balance and spatial orientation. When sound vibrations reach the cochlea, they cause these hair cells to move, which sends signals to the brain that are interpreted as sound.
Each part of the ear is critical to our ability to hear and maintain our sense of balance. Problems with any of these parts can lead to hearing loss, tinnitus, dizziness, and other symptoms.
Causes of ear aches
There are several potential causes of earaches, including:
Infections: Ear infections are a common cause of earaches, especially in children. Middle ear infections (otitis media) can be caused by viruses or bacteria and can cause pain, fluid buildup, and hearing loss.
Injury: Injuries to the ear, such as a blow to the ear, can cause earaches. Injuries to the jaw or head can also cause referred pain in the ear.
Wax buildup: When earwax builds up in the ear canal, it can cause pressure and pain.
Eustachian tube dysfunction: The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. When it becomes blocked or doesn’t function properly, it can lead to earaches and a feeling of pressure or fullness in the ear.
Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses can cause pain and pressure in the ears.
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders: TMJ disorders can cause pain in the jaw, which can radiate to the ear.
Other medical conditions: Earaches can be a symptom of other medical conditions, such as a sore throat, tonsillitis, or an impacted wisdom tooth.
Allergies
Symptoms of ear aches
Earaches can have various symptoms, depending on the underlying cause. However, some of the most common symptoms of earaches include:
- Pain: Ear pain is usually the most noticeable symptom of an earache. The pain can be sharp, dull, or throbbing, and may worsen when lying down.
- Fullness: A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear may be present due to fluid buildup in the middle ear or an obstruction in the ear canal.
- Discharge: Discharge from the ear may occur if an infection or injury has caused the eardrum to rupture.
- Hearing loss: A temporary hearing loss may occur due to the fluid buildup in the middle ear.
- Ringing or buzzing: Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, may occur in some cases.
- Vertigo: Dizziness or a spinning sensation may occur due to a disturbance in the balance system of the inner ear.
- Headache: A headache may accompany an earache, especially if the pain is severe.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Earache in children
Earaches in children can be a common and painful problem. They are often caused by infections, such as ear infections or swimmer’s ear. Other causes can include allergies, sinus infections, and a build-up of earwax.
Some common signs of an earache in children may include pulling or tugging at the ear, crying or fussiness, trouble sleeping, fever, and a loss of appetite. It’s important to note that not all children with earaches will display these symptoms, and some may have no symptoms at all.
If you suspect that your child has an earache, it’s important to take them to their pediatrician or primary care physician for an evaluation. The doctor will perform a physical exam and may recommend treatment such as pain medication, ear drops, or antibiotics if an infection is present.
In the meantime, you can help to ease your child’s discomfort by applying a warm compress to the affected ear, giving them over-the-counter pain medication as directed by their doctor, and making sure they get plenty of rest and fluids.
Earwax
Earwax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the glands in the ear canal. It plays an important role in protecting the ear by trapping dirt, dust, and other foreign particles before they can reach the eardrum. Normally, earwax will gradually migrate out of the ear on its own, and can be removed during routine bathing or showering.
However, in some cases, excess earwax can build up and cause symptoms such as:
Earache
Hearing loss
Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
Itching
Vertigo (dizziness)
If you are experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare provider to determine if excess earwax is the cause. They may recommend using eardrops to soften the wax and facilitate its removal, or may perform a procedure called ear irrigation to flush the wax out of the ear canal using a gentle stream of water.
It’s important to avoid using cotton swabs, hairpins, or other objects to clean the ear canal, as this can push the wax deeper into the ear and cause further blockage or damage to the ear canal or eardrum. If you are prone to excess earwax buildup, your healthcare provider may recommend regular ear cleaning using a safe and effective method.
Swimmer’s ear

Swimmer’s ear, also known as otitis externa, is an infection of the outer ear canal that occurs when water becomes trapped in the ear, creating a moist environment that promotes bacterial growth. It is a common condition that can cause pain and discomfort, and if left untreated, can lead to complications.
Symptoms of swimmer’s ear include:
Pain, which can be severe and worsens when the earlobe is pulled or the jaw is moved
Redness and swelling of the ear canal
Itching or a feeling of fullness in the ear
Drainage from the ear
Decreased hearing or a feeling of plugged ears
Treatment for swimmer’s ear typically involves prescription eardrops that contain an antibiotic to treat the infection, as well as a steroid to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. In some cases, oral antibiotics may also be prescribed. It’s important to avoid inserting anything into the ear canal or attempting to clean the ear on your own, as this can cause further irritation and may make the infection worse.
To prevent swimmer’s ear, it’s important to keep the ears dry, especially after swimming or showering. You can use a towel to dry your ears thoroughly, and tilt your head to each side to allow any remaining water to drain out. Wearing earplugs while swimming can also help prevent water from entering the ear canal.
Ways to Get Water Out of Your Ear
Getting water stuck in your ear can be a frustrating and uncomfortable experience. Here are some ways to help get water out of your ear:
Tilt your head: Tilt your head to the side with the affected ear facing down. Gently tug on your earlobe and jump up and down to help the water come out.
Use gravity: Lie down on your side with the affected ear facing down. Stay in this position for a few minutes to allow the water to drain out.
Create a vacuum: Place your palm flat against your ear and press it firmly. Quickly remove your palm, creating a vacuum that can help to pull the water out.
Use a hair dryer: Set your hair dryer to the lowest heat setting and hold it several inches away from your ear. Move it back and forth to help dry out the water.
Try alcohol and vinegar solution: Mix equal parts of rubbing alcohol and white vinegar, then lie on your side with the affected ear facing up. Use a dropper to place a few drops of the solution into your ear, and let it sit for a few minutes before tilting your head to let the solution and water drain out.
Adding more water to your ear to remove excess water might seem counterintuitive, but it can actually be an effective way to get water out of your ear if it’s done correctly. Here’s how to do it:
- Tilt your head to the side with the affected ear facing down.
- Use a clean dropper to place a few drops of warm water into your ear.
- Tilt your head in the opposite direction, allowing the water to flow out of your ear along with the trapped water.
- Use a soft towel or tissue to gently dry your ear.
- This method works because the warm water helps to loosen the trapped water in your ear and allows it to flow out more easily. It’s important to use warm water that is not too hot, as hot water can damage your ear canal and cause further irritation or infection. Additionally, do not insert the dropper or any other object into your ear canal, as this can cause injury and further complications.
It’s important to note that if you experience pain, dizziness, or if the water does not come out after trying these methods, it’s best to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional to prevent potential ear infections or other complications.
Airplane ear

Airplane ear is caused by changes in air pressure during takeoff and landing. Here are some tips to help prevent airplane ear:
Swallow frequently: Swallowing helps to equalize the pressure in the ears. Chewing gum, sucking on hard candy, or drinking water can all help encourage swallowing.
Yawning: Yawning can also help equalize the pressure in the ears. Try to yawn intentionally or encourage children to yawn.
Valsalva maneuver: Pinch your nose and gently exhale through your nostrils. This can help equalize the pressure in the ears.
Stay awake: If you’re prone to ear pain during air travel, avoid sleeping during takeoff and landing. Swallowing, yawning, or using the Valsalva maneuver are less effective when you’re asleep.
Decongestants: If you have a cold or allergies, consider taking a decongestant before your flight. This can help reduce congestion in the sinuses and ears.
Earplugs: Some people find that wearing earplugs during takeoff and landing can help alleviate ear pain.
It’s important to note that if you have a pre-existing ear condition or are experiencing severe or persistent ear pain during air travel, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
A foreign object in the ear
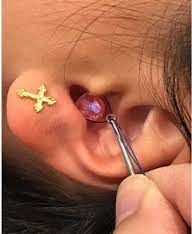
If you or someone else has a foreign object stuck in the ear, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Here are some things you can do in the meantime:
- Do not try to remove the object yourself with tweezers, cotton swabs, or any other tools, as this can push the object further into the ear canal and cause damage.
- Do not attempt to flush out the object with water or any other liquid, as this can also push the object further into the ear canal or cause injury.
- Stay calm and keep the affected person calm as well, especially if they are a child.
- Cover the affected ear with a clean, dry cloth or bandage to prevent any further foreign objects from entering.
- Seek medical attention immediately. Your doctor or a specialist may use specialized instruments to safely remove the object from the ear. It is important to remember that foreign objects in the ear can be serious and should not be ignored. Prompt medical attention is key to preventing any further damage or injury.
Management of ear ache
You can try some self-care measures to alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with earache. These may include applying a warm compress to the affected ear, using over-the-counter pain relievers, and avoiding exposure to loud noises and other irritants. It is also important to avoid inserting anything into the ear, as this can aggravate the condition and lead to further complications.
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil) and naproxen (Aleve), can be effective in relieving ear ache. These medications work by reducing inflammation and pain in the body. However, it’s important to follow the dosage instructions carefully and not exceed the recommended amount, as overuse of these medications can cause side effects such as liver damage and stomach ulcers.
It’s also important to note that over-the-counter pain relievers may only provide temporary relief, and should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment if the ear ache is caused by an underlying condition or infection. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional.
Prescribed ear drops
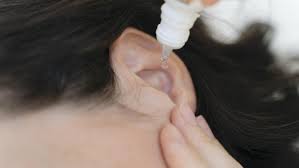
Ear drops can be an effective treatment for earache, especially if the pain is caused by an ear infection or excessive earwax buildup. Here are some commonly used ear drops for earache relief:
Antibiotic ear drops: These ear drops contain antibiotics to treat bacterial infections that can cause earache. They are typically prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Hydrogen peroxide ear drops: These drops can help soften and remove excess earwax that can cause earache. They can be purchased over-the-counter at a pharmacy.
Mineral oil ear drops: These drops can also help soften and remove excess earwax that can cause earache. They can be purchased over-the-counter at a pharmacy.
Steroid ear drops: These ear drops contain a steroid to reduce inflammation and pain in the ear. They are typically prescribed by a healthcare professional.
It’s important to follow the instructions for use carefully when using ear drops, and to never use them if there is a perforation or other damage to the ear. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional.
Here are some home remedies that may help alleviate earache:
Propping the head

Prop the head on a pillow to help the ear decrease pain. Propping the head on a pillow can be a helpful technique to alleviate earache, especially if the pain is caused by pressure changes in the ear. Propping the head on a pillow can help to alleviate pressure on the ear and reduce pain. However, it is important to note that this technique may not be effective for all types of ear ache, and it should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment if the earache is caused by an underlying condition or infection. If your ear ache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. Here’s how to use a pillow to alleviate earache:
Lie down on your side with the affected ear facing upward.
Place a pillow under your head to elevate it.
Remain in this position for 10-15 minutes.
Repeat this process several times a day as needed.
Rubbing alcohol, also known as isopropyl alcohol, is a commonly used antiseptic that can be used to clean the outer ear and alleviate ear ache. Here’s how to use rubbing alcohol for earache relief:
- Mix equal parts of rubbing alcohol and white vinegar.
- Soak a cotton ball in the mixture and squeeze out the excess liquid.
- Tilt your head to the side and gently insert the cotton ball into the ear canal.
- Leave the cotton ball in the ear for a few minutes.
- Remove the cotton ball and tilt your head to the opposite side to allow the liquid to drain out of the ear.
Rubbing alcohol can help to dry out excess moisture in the ear canal, which can lead to infection and earache. However, it is important to note that rubbing alcohol should never be used if there is a perforation or other damage to the ear. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. Additionally, rubbing alcohol should be used with caution and not be ingested or applied to open wounds.
Valsalva maneuver
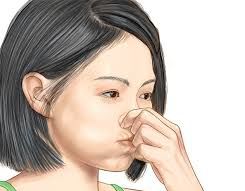
The Valsalva maneuver helps to equalize the pressure in the middle ear with the pressure outside the ear, which can relieve earache caused by pressure changes. However, it’s important to note that the Valsalva maneuver should not be performed if you have a sinus infection, nasal congestion, or any other condition that could be affected by changes in pressure. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. Start by taking a deep breath. With the mouth closed, hold your breath whilst pinching your nose shut. Blow your nose gently for 5 seconds. The Valsalva maneuver is a technique that can be used to relieve earache caused by pressure changes in the ear. Here’s how to perform the Valsalva maneuver:
Close your mouth and pinch your nostrils shut with your fingers.
Take a deep breath and exhale gently while keeping your nostrils pinched shut.
Repeat this process several times, or until you feel a popping sensation in your ears.
Distraction
Distraction can be a helpful technique to manage earache, especially if the pain is mild or moderate. Here are some distractions that you can try to help take your mind off the earache:
Listen to music or a podcast: Listening to something engaging can help to distract your mind from the earache.
Watch a movie or TV show: Similar to listening to something engaging, watching a movie or TV show can help to take your mind off the earache.
Engage in a hobby: Doing something that you enjoy, such as painting, reading, or playing a game, can help to distract your mind from the earache.
Spend time with friends or family: Socializing can help to distract your mind from the earache and provide emotional support.
Take a walk or exercise: Physical activity can help to release endorphins, which are natural painkillers, and also provide a distraction from the earache.
While distraction can be a helpful technique to manage earache, it’s important to note that it should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment if the earache is severe or persistent. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional.
Yawning
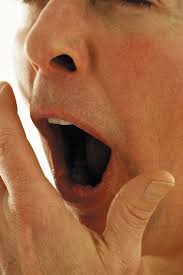
Yawning can be a natural way to help alleviate earache, especially if the pain is caused by pressure changes in the ear. Here’s how yawning can help with earache:
Yawning helps to open up the Eustachian tube, which is the tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the throat.
When the Eustachian tube is open, it allows air to flow in and out of the middle ear, which can help to equalize the pressure in the ear.
Equalizing the pressure can help to alleviate earache caused by pressure changes.
So, if you are experiencing earache, try yawning several times to help open up the Eustachian tube and equalize the pressure in your ear. However, it’s important to note that yawning may not be effective for all types of earache, and it should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment if the earache is caused by an underlying condition or infection. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional.
Swallowing
Swallowing can be a natural way to help alleviate earache, especially if the pain is caused by pressure changes in the ear. Here’s how swallowing can help with earache:
Swallowing helps to activate the muscles that control the Eustachian tube, which is the tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the throat.
When these muscles are activated, they help to open up the Eustachian tube and allow air to flow in and out of the middle ear.
Equalizing the pressure can help to alleviate earache caused by pressure changes.
So, if you are experiencing earache, try swallowing several times to help activate the muscles that control the Eustachian tube and equalize the pressure in your ear. However, it’s important to note that swallowing may not be effective for all types of earache, and it should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment if the earache is caused by an underlying condition or infection. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional.
Warm compress

Placing a warm, damp washcloth or heating pad over the affected ear can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. A warm compress can be a simple and effective home remedy for earache relief. A warm compress helps to increase blood flow to the affected area, which can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Here’s how to use a warm compress for ear ache relief:
Start by soaking a clean washcloth in warm water. Be sure to wring out the excess water so that the cloth is damp, but not dripping.
Hold the warm compress against the affected ear for 10-15 minutes. You can repeat this process several times a day, as needed.
For added relief, you can add a few drops of essential oil to the warm water before soaking the washcloth. Lavender, eucalyptus, and tea tree oil are all good choices for earache relief.
It’s important to note that a warm compress should never be hot or scalding, as this can cause burns and damage to the skin. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional.
Salt

Heat up some salt in a pan, put it in a cloth, and apply it over the affected ear for 10 to 15 minutes. The heat helps reduce pain and swelling. Salt can be a simple and effective home remedy for earache relief. Salt is a natural antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent that can help reduce pain and inflammation in the ear. Here are some ways you can use salt for earache relief:
Saltwater solution: Mix 1/4 to 1/2 teaspoon of salt into 1 cup of warm water. Soak a cotton ball in the saltwater solution and place it in the affected ear for 10-15 minutes. Repeat this process 2-3 times a day as needed.
Salt sock: Heat up a clean sock filled with coarse sea salt in the microwave for 30-60 seconds, or until warm. Place the warm sock over the affected ear for 10-15 minutes. The warmth and salt may help reduce pain and inflammation.
Gargle with salt water: Mix 1/2 to 1 teaspoon of salt into a glass of warm water. Gargle the saltwater solution for 30 seconds and then spit it out. This can help reduce inflammation in the throat and ears.
It’s important to note that while salt may help alleviate ear pain and inflammation, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional.
Garlic oil

Garlic is another natural remedy that has been used for centuries to alleviate ear pain and infection. Garlic has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Warm some garlic oil and apply it to the ear using a cotton ball. Garlic oil is a natural remedy that has been used for centuries to alleviate ear pain and infection. Garlic contains allicin, a compound with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce pain and inflammation in the ear. It is important to note that while garlic may help alleviate ear pain and infection, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. Here are some ways to use garlic for earache relief:
Garlic oil: Crush a few cloves of garlic and mix them with a carrier oil, such as olive oil or coconut oil. Heat the mixture over low heat for a few minutes, strain the oil, and let it cool to body temperature. Use a dropper to put a few drops of the garlic oil into the affected ear. Tilt your head to the side and allow the oil to remain in the ear for a few minutes. Then, tilt your head to the other side to let the oil drain out.
Garlic poultice: Crush a few cloves of garlic and mix them with a little bit of olive oil to create a paste. Apply the paste to a clean cloth and place the cloth on the affected ear for 10-15 minutes. The warmth and anti-inflammatory properties of the garlic may help alleviate pain and inflammation.
Garlic capsules: Garlic supplements are available in capsule form and may be taken orally to help boost the immune system and reduce inflammation in the body.
It’s important to note that while garlic oil may help alleviate ear pain and infection, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. Additionally, garlic oil should not be used if there is a perforation or other damage to the ear.
Essential oils
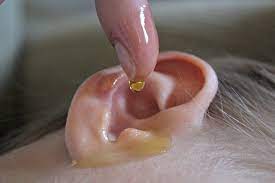
Some essential oils, such as tea tree oil and lavender oil, have natural anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties. Mix a few drops with a carrier oil and apply it to the outside of the ear. Essential oils are concentrated plant extracts that can have a variety of therapeutic benefits, including pain relief and anti-inflammatory properties that may help alleviate earache. It’s important to note that essential oils should never be applied directly to the ear without diluting them with a carrier oil, and they should never be ingested. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. Additionally, essential oils should not be used if there is a perforation or other damage to the ear. Here are some essential oils that are commonly used for earache relief:
Tea tree oil: Tea tree oil has antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties, which may help reduce inflammation and fight infections in the ear. Mix a few drops of tea tree oil with a carrier oil, such as coconut oil or olive oil, and use a dropper to put a few drops into the affected ear.
Lavender oil: Lavender oil has soothing and calming properties that may help relieve pain and inflammation in the ear. Mix a few drops of lavender oil with a carrier oil and use a dropper to put a few drops into the affected ear.
Eucalyptus oil: Eucalyptus oil has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce pain and inflammation in the ear. Mix a few drops of eucalyptus oil with a carrier oil, and use a dropper to put a few drops into the affected ear.
Olive oil: has been used as a home remedy for earaches for many years. It is believed that olive oil can help relieve pain and inflammation in the ear by reducing wax buildup and moisturizing the ear canal. It is important to note that using olive oil for earaches is generally safe for adults, but not recommended for children or anyone who has a ruptured eardrum or other ear problems. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional.
Chewing gum
Chewing gum can help relieve pressure in the ears and alleviate ear pain caused by changes in altitude, such as during air travel. It’s important to note that home remedies should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. If you experience severe or persistent ear pain, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Neck exercise

If you have an earache, it is important to seek medical attention and avoid any exercises or activities that could aggravate the condition. Neck exercises, in particular, may not be helpful or recommended for ear pain, as they could potentially worsen the symptoms.
It is important to remember that neck exercises should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional, particularly if you have a pre-existing medical condition or are experiencing pain or discomfort in the ear.
Vinegar
White vinegar is a natural remedy that can help alleviate earache caused by an infection or excessive earwax buildup. Vinegar has antibacterial properties that can help fight off infection, and its acidic properties can help dissolve earwax. Here’s how to use white vinegar for earache relief:
Mix equal parts of white vinegar and water.
Soak a cotton ball in the mixture and squeeze out the excess liquid.
Place the cotton ball in the affected ear and leave it in for 5-10 minutes.
Tilt your head to the side and let the liquid drain out of your ear.
Repeat this process 2-3 times a day as needed.
OR
Mix equal parts of apple cider vinegar and warm water, soak a cotton ball in the mixture, and place it in the ear for a few minutes. This can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
It’s important to note that while white vinegar may help alleviate earache, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. Additionally, white vinegar should not be used if there is a perforation or other damage to the ear.
Ginger

Ginger is a natural anti-inflammatory and pain reliever, and it may be helpful in reducing the pain and inflammation associated with an earache. Here are some ways you can use ginger to alleviate ear pain:
Ginger tea: Boil a few slices of fresh ginger root in water and let it steep for a few minutes. Strain the tea and let it cool to room temperature. Drink the ginger tea slowly to help relieve pain and inflammation.
Ginger oil: Mix a few drops of ginger essential oil with a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil. Use a dropper to put a few drops of the mixture into the affected ear. Be sure to warm the mixture to body temperature before putting it in your ear.
Ginger compress: Grate fresh ginger and mix it with hot water to create a paste. Apply the paste to a clean cloth and place the cloth on the affected ear for 15-20 minutes. The warmth and anti-inflammatory properties of the ginger may help relieve pain and discomfort.
It is important to note that while ginger may help alleviate ear pain, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. If your earache persists or worsens, seek medical attention from a healthcare professional.
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a common household solution that is sometimes used to clean and disinfect small wounds and cuts. However, it is NOT recommended for use in the ear to alleviate ear pain or remove earwax. In fact, using hydrogen peroxide in the ear can be dangerous and cause harm, particularly if there is a perforation or other damage to the ear. Here are some reasons why hydrogen peroxide should not be used in the ear:
Can cause harm: Hydrogen peroxide can cause chemical burns and damage to the delicate tissues in the ear, particularly if the eardrum is perforated or there is an infection present.
Can make earwax worse: Contrary to popular belief, earwax is a normal and necessary substance that helps protect the ear canal from infection and irritation. Using hydrogen peroxide in the ear can actually push earwax further into the ear canal and make the problem worse.
Not effective for ear infections: While hydrogen peroxide may have some antibacterial properties, it is not an effective treatment for ear infections. In fact, using hydrogen peroxide in the ear can actually worsen the infection and cause further harm.
It is important to note that if you are experiencing ear pain or have excessive earwax buildup, it is best to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional rather than attempting to treat the problem yourself with hydrogen peroxide or other home remedies.
Complications of earache
If left untreated, an earache can lead to various complications in children. Some of the complications of an earache may include:
Hearing loss: If the earache is caused by a middle ear infection, it can lead to fluid buildup in the ear, which can cause temporary or permanent hearing loss.
Ruptured eardrum: An untreated ear infection can lead to a rupture of the eardrum, which can cause pain, hearing loss, and discharge from the ear.
Spread of infection: An untreated ear infection can also spread to other parts of the body, such as the brain, causing meningitis or a brain abscess.
Speech and language development: If the earache is chronic and untreated, it can affect a child’s speech and language development.
Chronic ear infections: Children who have frequent ear infections are at risk of developing chronic ear infections, which can lead to permanent hearing loss and require surgery.
When to seek urgent medical care
If you are experiencing earache, it is important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Depending on the underlying cause of the earache, treatment may involve medications such as pain relievers, antibiotics, or ear drops. In some cases, more advanced treatments such as surgery may be necessary. symptoms to report include:
Severe headache
Discharge from the ear
Worsening dizziness or hearing loss
Weakness to one side of the face
Pain to the ear lasting several days
Swelling around the ear
Continued symptoms after taking antibiotic treatment
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

