Common Diagnostic Exams: Procedures, Purpose, and What to Expect
Diagnostic exams are an important tool for assessing and diagnosing a variety of medical conditions. These tests can be used to detect the presence of an illness, determine its severity, and aid in treatment decisions. Diagnostic exams can range from simple blood tests to complex imaging scans such as CT scans or X-rays. The results of these tests allow medical professionals to diagnose a wide array of medical conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, infectious diseases, neurological disorders, and genetic disorders. Diagnostic exams help physicians make informed decisions about treatments and medications that are best suited for their patients. In addition to helping improve patient outcomes, diagnostic testing also helps reduce the cost of healthcare by providing more accurate diagnoses and reducing the need for further testing and treatment. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
Preparing for diagnostic tests
X-Ray
MRI
Mammogram
Biopsy
Bone density scan
CT scan CTA
Ultrasound
Cardiac stress test
Thyroid uptake scan
HIDA
Colposcopy
HOW TO PREPARE FOR THE VARIOUS DIAGNOSTIC EXAMS
When making an appointment it would be wise to inform the office if one is
- Elderly
- Pregnant, breastfeeding, or thinks she may be pregnant
- Diabetic
- Taking any medications on a regular basis, including blood sugar medications
- Allergic to iodine or other medications
- Asthmatic
- Has any implanted devices such as pacemakers
Bring previous diagnostic images and pathology reports for comparison
If having a mammogram or breast MRI, avoid wearing deodorant, antiperspirant, powder, lotions, or creams under the arms or on breasts to avoid false results caused by the metallic particles found in these products
Wear warm, comfortable, loose-fitting clothes
Avoid clothes with heavy buckles or metal components which can interfere with the machine
X-RAY
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation with a wide range of uses in the medical field. They can help doctors detect abnormalities in the body, such as bone fractures and tumors, by allowing them to see through bone, soft tissue, and other structures. X-ray technology has been used for decades in many diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, ranging from dental x-rays to mammograms and CT scans. These diagnostic exams are very helpful in detecting cancerous cells early on before they have a chance to spread. The use of X-rays has saved countless lives over the years and will continue to be an invaluable tool in modern medicine.
Regular X-rays require no special preparation
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING- MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used to provide detailed images of the internal structure and composition of the human body. Utilizing strong magnetic fields, radio waves, and computer technology, MRI creates cross-sectional images of organs and systems within the body that can be viewed from any angle. MRI helps physicians diagnose a variety of conditions such as tumors, strokes, brain damage, neurological diseases, joint and skeletal abnormalities, and other soft tissue disorders. The information obtained from an MRI can also help guide treatments for many different types of health problems. The images produced by MRI are extremely detailed, meaning they provide much more detail than traditional X-rays or ultrasounds. This allows radiologists to accurately detect even subtle changes in tissue structure; something which was not possible with earlier imaging technologies. Furthermore, the use of non-ionizing radiation makes MRI safer than other modalities such as CT scans. Thus, MRI provides physicians with invaluable insight into the inner workings of their patients’ bodies.
- Walk with the request form written by the physician
- Take all usual medications, but inquire about taking sedation or pain medication prior to the procedure if one has a fear or anxiety of small spaces or cannot lie still for 30-60 minutes at a time
- Eating and drinking are not usually restricted
- Remove all metal including jewelry, coins etc. prior to entering the scan room
- It is wise to inform the technologists of any prosthetic device hip or knee replacement etc. prior to entering the scan room
- For persons who require sedation or tranquilizer, it would be wise to arrive with a companion 1/2 hour prior to the appointment to allow the sedation to commence working before the exam
- Eye makeup is not recommended for the scans as the metal it contains may distort the images
- Patients over 65 years are required to have BUN and creatinine blood work done no more than 45 days prior to the MRI with contrast scan.
- It is necessary that persons with cardiac stents present their card as proof of such
Contraindication to an MRI
- A Cardiac Pacemaker
- A Middle Ear Prothesis
- Had Surgery within The Past Week
- A Brain Aneurysm Clip
- Neurostimulators
MAMMOGRAM
A mammogram is a specialized type of breast imaging that utilizes low-dose x-rays to detect and diagnose any potential abnormalities in the breasts. This diagnostic tool is an invaluable resource for early detection and prevention of breast cancer as it can identify very small tumors or growths long before they can be felt by hand. Mammograms are recommended for women over the age of 40, or with a family history of breast cancer, as it is one of the most effective ways to detect cancer early and improve chances for successful treatment.
- DO not wear deodorant, powder or lotion on the breast or underarm area
- Be sure to carry previous mammogram films for comparison
- Alert the office if breastfeeding or newly post-delivery
- Avoid ingesting caffeine 2 days prior to the test
- It is prudent to schedule the appointment after premenstrual soreness has decreased
BIOPSY
A biopsy is an essential medical procedure used to accurately diagnose diseases and illnesses. It involves the removal of a small sample of tissue from the body, which is then examined under a microscope for any abnormal cells or other signs of illness. Biopsy results can provide critical information about diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, infections and more. With the help of modern technologies, biopsies are now highly accurate, minimally invasive and often painless procedures that can quickly provide vital insight into a person’s health.
Breast Biopsy Preparation:
- Avoid taking Aspirin the day of or the day before the exam to avoid bleeding.
- Stop taking blood thinners at least 3 to 5 days before the exam to avoid bleeding.
- Take a pain reliever at least 30-60 minutes preceding the appointment time.
DEXA/ BONE DENSITY SCAN
A bone scan is an imaging test that can detect any abnormalities in the bones. It is a non-invasive procedure that uses a small amount of radioactive material, which is injected into the bloodstream and absorbed by the bones. This material gives off gamma rays which are detected by a special camera and interpreted by a radiologist to identify areas of increased activity or damage in the bones. Bone scans are commonly used to diagnose fractures, infections, arthritis, tumors, and other metabolic disorders. They can also be used to monitor how well treatments such as chemotherapy are working. Bone scans are safe and painless tests that provide vital information about the health of our skeletal system. Before the examination:
- Avoid taking any multivitamins, calcium, or iron 24 hours before the examination.
- Bring in a detailed list of all medications currently being taken.
CT SCAN HEAD OR BODY WITH CONTRAST
A CT scan (Computerized Tomography) is a medical imaging test that uses X-ray beams to capture detailed cross-sectional images of the head or body. A CT scan can be performed with or without contrast, depending on the type of information needed from the scan. When performed with contrast, a special dye is injected into the body in order to better highlight certain structures or features, such as tumors and blood vessels. A scan without contrast is used to obtain general anatomical information, such as bone structure and soft tissue abnormalities like enlarged lymph nodes. Both types of scans are noninvasive and painless, making them an important tool for helping to diagnose and treat many medical conditions.
- A BUN and creatinine test are required 4 weeks before the test in diabetics or persons 65 or older
- For CT scans that require (IV) intravenous contrast (head, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis), the patient must have NO food or drink 4 hours prior to exam
- The patient may take medications with a small amount of water
COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA)
Computerized Tomography Angiography (CTA) is a type of imaging that uses X-ray technology to create detailed images of the organs and tissues in the body. CTA utilizes advanced 3D reconstruction techniques to produce images of the vascular system, providing physicians with valuable information on blood flow and structure, as well as any abnormalities or blockages. CTA can be used for diagnosis and treatment, including detection of aneurysms, emboli or arteriovenous malformations and evaluation of diseases such as stroke and coronary artery disease. It is an invaluable tool for cardiologists and radiologists in diagnosing and monitoring patients.
- Avoid caffeine, tobacco or other stimulants for 24 hours before the exam
- No food or water for 4 hours before the exam
- For patients requiring IV contrast, BUN and CREATNIN tests are needed 45 days prior to exam
- One must avoid exercising for 24 to 48 hours prior to the PET/CT scan
- Continue to take any medication prescribed by the physician
- The last meal before the scan should be high in protein and low in carbohydrates
- Breakfast: eggs, bacon, sausage. No breakfast should be eaten if you have an appointment before noon
- Dinner: steak, baked chicken, fish, cheese, asparagus, broccoli, mushrooms. No pasta, potatoes, rice, or bread
- No eating, drinking (except water) or chewing gum for 6 hours before the test
Oral contrast is required for the following:
For abdominal imaging:
- Abdomen with and without IV contrast: 1 bottle (wait 30 minutes before the exam after consuming contrast).
- Abdomen without IV contrast: No preparation mentioned.
For pelvic imaging:
- Pelvis with and without IV contrast: 2 bottles (wait 1 hour before the exam after consuming contrast).
- Pelvis without IV contrast: No preparation mentioned.
For combined abdominal-pelvic imaging:
- Abdomen-Pelvis with and without IV contrast: 2 bottles (wait 1 hour before the exam after consuming contrast).
- Abdomen-Pelvis without IV contrast: No preparation mentioned.
Additionally, inform the technologist of any history of iodine allergy or anaphylactic reaction.
ULTRASOUND
Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses sound waves to create an image of the inside of the body. It is a non-invasive technique that can provide detailed images and even be used to guide procedures such as biopsies. Ultrasound has many different applications including diagnosing various conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and fetal development during pregnancy. Ultrasound technology is continually advancing in sophistication, with 3D and 4D imaging providing real-time images of internal organs and structures with high resolution. By bouncing high-frequency sound waves off tissues in the body, ultrasound helps create a detailed picture without exposing the patient to radiation or contrast agents. With its versatility and safety, ultrasound remains one of the most important imaging tools used by doctors today.
ULTRASOUND – ABDOMINAL
- Nothing to eat or drink past midnight or 8 hours prior to the exam
- Take prescribed medications with sip of water
- Diabetics: Consult the doctor for medication advice. Bring something to eat after the exam
- Pediatrics: Nothing to eat/drink 4 hours before the exam
- Infants: Nothing to eat/drink 2 hours before exam
- No smoking 4 hours prior to examination
ULTRASOUND – PELVIC
- Drink 32 oz. or 6 glasses of water 1 hour before schedule exam
- Do not urinate after drinking water; a full bladder is needed
- Do not eat, drink, or consume anything else by mouth (other than water) for 8 hours prior to examination
- No smoking 4 hours prior to exam
ULTRASOUND -OBSTERICS
- May require empty bladder if fetus is < 12 weeks, otherwise, drink 32 oz. of fluid 1 hour preceding to scan and do not empty or relieve bladder
- Day of Exam: For a morning test: Eat light breakfast. For an afternoon test: Eat light breakfast and eat a light lunch
- If BLADDER exam is included:
- Drink 32 oz. or 6 glasses of water 1 hour before pelvic portion of exam
- Do not urinate after drinking water; a full bladder is needed
ULTRASOUND – TRANSVAGINAL
A transvaginal ultrasound is a type of medical imaging procedure that allows doctors to observe detailed images of the female pelvic organs, such as the uterus and ovaries. The procedure involves inserting a small probe into the vagina and using sound waves to create an image. The image provides information about the size, shape, and location of the organs, as well as any abnormalities or other issues that may be present. Additionally, transvaginal ultrasounds can also be used to diagnose conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, ovarian cysts, infertility, and developmental problems in unborn babies. With its non-invasive nature and high accuracy rate, transvaginal ultrasound has become one of the most popular diagnostic techniques for women’s health issues.
- No special preparation required. Menstruation does not interfere with this procedure
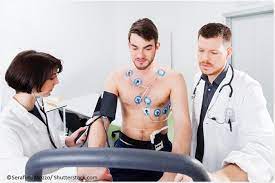
CARDIAC STRESS TEST
A cardiac stress test, also known as an exercise stress test or treadmill test, is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate how well the heart responds during physical activity. This non-invasive test is typically administered by a cardiologist and uses electrocardiogram (ECG) readings to measure the heart rate, rhythm and electrical conduction system during periods of rest and exercise. During the test, a patient will be asked to walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike while their heart rate, blood pressure and ECG readings are monitored. By comparing these results at rest and during exercise, physicians can determine if there are any abnormalities in the functioning of the heart’s chambers or valves that may indicate cardiovascular problems.
- No caffeine for 24 hours
- Stop taking the following medication 24 hours before the procedure: acebutol (Sectral®), atenolol (Tenormin®), betaxolol (Kerlone®), bisoprolol (Zebeta®), carvedilol (Coreg®), esmolol (Brevibloc®), labetelol (Trandate®, Normodyne®), metoprolol (Lopressor®, Tropol XL®), nadolol (Corgard®), penbutolol (Levatol®), pindolol (Visken®), propranolol (Inderal®, Inderal LA®), sotalol (Betapace®, Betapace-AF®), timolol (Blocadren®)
- No food or drink 6 hours prior to test
- Bring a light snack
- If able to use the treadmill, wear walking shoes
- Bring a light jacket and dress comfortably
THYROID UPTAKE/ SCAN
A thyroid uptake scan is a medical imaging test used to evaluate the function of the thyroid gland. It involves injecting a very small amount of radioactive material into the body, which is then taken up by the thyroid cells. The uptake of radioactive material is then measured using a gamma camera or other imaging device, allowing doctors to accurately assess how much of the material has been absorbed. The results can provide important information about the health and functioning of the thyroid and can be used to help diagnose and manage many different conditions related to this important endocrine organ.
- Stop taking thyroid medication 4 weeks prior to the exam
- No Lugol’s solution 4 weeks prior to exam
- No contrast test containing iodine 4 weeks prior to exam
- No fish oils 10 days prior to exam
- No food or drink 6 hours prior to scan
HEPATOBILIARY IMINODIACETIC ACID (HIDA)
HEPATOBILIARY IMINODIACETIC ACID (HIDA) is a radioactive material often used for diagnostic imaging. It is injected intravenously, and the radiation emitted from HIDA allows medical professionals to view the organs of the hepatobiliary system in greater detail than other imaging techniques. HIDA is a derivative of iminodiacetic acid, which binds to certain compounds within the liver to enable enhanced visibility of its function. In addition, HIDA is also able to track bile excretion and monitor hepatic blood flow via gamma-ray emission. Furthermore, by combining HIDA with computed tomography (CT) scans and ultrasound imaging, clinicians are better equipped to diagnose problems within the gallbladder and other related organs.
- No food or drink 6 hours prior to scan
- No pain medication 24 hours prior to exam
RENAL SCAN
A renal scan, also known as a renal scintigraphy or a Nuclear Renal Scan, is an imaging test used to assess the functioning of the kidneys. It provides a detailed overview of the anatomy and physiology of the kidneys by using a radioactive tracer and two-dimensional images. This procedure is commonly used to diagnose and monitor kidney conditions such as kidney stones, obstructions, urinary tract infections, cysts, tumors, and chronic kidney diseases. Renal scans can help detect problems from early stages before any symptoms appear, providing doctors with valuable diagnostic information that can aid in treatment decisions.
- Drink one large glass of water 30 minutes before procedure
GASTRIC EMPTYNG SCANS
A gastric emptying scan is a medical test that measures the rate of how quickly food leaves the stomach. By using a radioactive tracer, this scan allows physicians to observe how quickly food moves through the digestive tract. This test can be beneficial in diagnosing and treating conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and gastroparesis, as well as certain types of abdominal pain. The scan itself is noninvasive, typically only taking about 45 minutes to complete. Patients may need to alter their diet prior to the exam and will receive detailed instructions from their doctor regarding this. During the scan, patients will be asked to consume a meal with a small amount of radioactive material mixed in; afterwards, special cameras will be used to track how fast this material passes through the gastrointestinal tract. Doctors can then analyze the results to assess how well food is being digested within the stomach.
- No food or drink 4-6 hours prior to the scan
- Refrain from taking stomach medication 24 hours prior to exam
- Drink plenty of fluids
DaTSCAN™
DaTSCAN is a specialized type of brain imaging test used to diagnose Parkinson’s disease and other neurological disorders. It uses single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) to create 3-dimensional images of the brain, providing doctors with greater detail than conventional imaging techniques, such as MRI or CT. DaTSCAN is able to detect dopamine transporter density in the basal ganglia area of the brain, allowing for an accurate diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and other degenerative conditions. DaTSCAN technology has the potential to revolutionize how these conditions are diagnosed and treated, giving patients access to faster and more precise treatments.
- Drink plenty of fluids
- On the day of the procedure, arrive early for an injection and return 3.5 hours later for the scan
WHOLE- BODY BONE SCAN
A Whole-Body Bone Scan is an imaging test that uses a radioactive tracer, such as Technetium-99m, to produce detailed images of the skeletal system. This test can identify areas where bone has been damaged or destroyed, and can help diagnose conditions such as osteoporosis, fractures, trauma, infection, cancer, and arthritis. A Whole-Body Bone Scan is a safe procedure that is relatively quick and painless and produces detailed images of all areas of the skeletal system. It allows doctors to quickly identify and monitor any changes in bone structure over time.
- No special preparation required, but drink plenty of fluids
Colposcopy
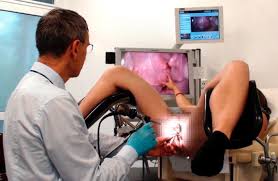
Colposcopy is an important diagnostic tool for medical professionals to examine the female reproductive system. It is a non-invasive procedure that uses a magnifying device and a light source to help doctors identify abnormal cells in the cervix, vagina, and vulva. During the procedure, a doctor will be able to observe the patient’s reproductive system and possibly pinpoint the cause of any abnormalities. The doctor may then take a biopsy, if needed, to determine the condition of the tissue. Colposcopy is a valuable tool in helping to diagnose and treat issues related to the female reproductive system.
- A 20 to 30-minute test done to obtain a closer look at the cervix
- The woman will remove her clothing from the waist down and covered with a bedsheet
- The woman will lay on her back, with the legs bent and knees apart
- The doctor will lubricate a speculum then insert it into the vagina so that the doctor can visualize the cervix
- The doctor will then use a microscope containing a light to visualize the cervix. The microscope will not be inserted into the body
- The doctor will place a small amount of special liquid on the cervix to detect abnormal areas
- A sample of the cells will be collected and sent to the lab for testing
Possible effects of the colposcopy procedure
- -Discomforts
- -Cramping
- -Spotting
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions. Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams Diagnostic exams

