When to Seek Emergency Care: Recognizing Life-Threatening Symptoms
An emergency is a potentially dangerous or life-threatening situation that requires immediate attention and action. An emergency is something serious that requires urgent medical attention. Emergencies can vary greatly in scope and severity, ranging from medical emergencies like heart attacks to natural disasters like hurricanes. In times of crisis, people must be ready to take immediate and appropriate steps to protect themselves, their loved ones, and their property. Emergency responders such as firefighters, paramedics, police officers, and medical personnel are often dispatched to the scene of an emergency in order to provide assistance and restore order. People should also be prepared for emergencies by having an evacuation plan in place, stockpiling supplies such as food, water and medicine, staying informed about potential threats in their area, and having access to important documents like birth certificates. By being prepared for emergencies before they happen, individuals can ensure that they are able to respond quickly and effectively if the worst happens. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
Kinds of emergencies
Steps to take when an emergency occurs
Allergic reaction
Infection

KINDS OF MEDICAL EMERGENCIES
-
Burns: Injuries caused by exposure to heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation, leading to tissue damage.
- Bleeding: Loss of blood from damaged blood vessels due to injury or medical conditions, which can range from minor to life-threatening.
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): Emergency procedure to revive a person whose heart has stopped beating or who is not breathing.
- Chest Problems: Any condition affecting the chest area, including heart attacks, collapsed lungs, or other respiratory issues.
- Choking: Obstruction of the airway, typically by a foreign object, preventing normal breathing.
- Head Injury: Trauma to the head, ranging from minor bumps to severe concussions or skull fractures.
- Issues with the heart: Various cardiac emergencies such as heart attacks, arrhythmias, or heart failure.
- Intoxication: Poisoning or overdose from ingesting harmful substances, including drugs, alcohol, or toxic chemicals.
- Issues affecting the brain: Conditions like strokes, seizures, or traumatic brain injuries that affect brain function and may require urgent medical attention.
- A disaster: a sudden and widespread event that causes significant disruption, damage, destruction, and distress to a community or society. These events can be natural, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, wildfires, or tsunamis, or they can be human-made, including industrial accidents, terrorist attacks, or pandemics.
STEPS TO TAKE WHEN AN EMERGENCY ARISES
When an emergency arises, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Here are essential steps to follow:
- Assess the situation: Quickly evaluate the environment for potential dangers or hazards to yourself and others.
- Prioritize: Address the most serious issues first, such as attending to individuals with life-threatening injuries or securing safety for those in immediate danger.
- Avoid moving injured individuals: If there’s a possibility of spinal injury, refrain from moving the person unless absolutely necessary to prevent further harm.
- Check for injuries such as broken bones or severe bleeding that require immediate attention.
-
Contact emergency services such as paramedics or firefighters by dialing the appropriate emergency number. If possible, ask bystanders for assistance.
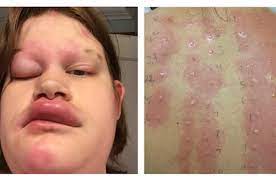
ALLERGIC REACTION
An allergic reaction is a response by the body’s immune system to a foreign substance, such as pollen, pet dander, or food. This response can range from mild to severe and oftentimes results in uncomfortable symptoms like itchy eyes, rashes, sneezing, and difficulty breathing. An allergy is an overreaction of the immune system to a harmless substance. When someone comes into contact with an allergen, their body releases histamines as defense which causes the release of inflammatory chemicals that lead to the uncomfortable symptoms of an allergic reaction. People who are prone to allergies may carry an EpiPen: a device containing epinephrine which helps reduce swelling and constricts blood vessels. Allergies can be managed through avoidance of allergens or by taking medications like antihistamines or decongestants which help ease symptoms.
COMMON THINGS WHICH ONE MIGHT BE ALLERGIC TO
- Food: Examples include nuts, shellfish, dairy products, eggs, soy, and wheat.
- Certain medications like penicillin, aspirin, or specific antibiotics can trigger allergic reactions.
- Pet or animal dander: Proteins found in the skin, saliva, or urine of pets like cats, dogs, or rodents can cause allergies.
- Venom: Insect stings or bites from bees, wasps, hornets, or fire ants can induce allergic reactions in susceptible individuals.
- Latex gloves, balloons, or rubber products contain proteins that may trigger allergies.
- Substances found in the workplace: Chemicals, dust, or fumes present in certain work environments can provoke allergic reactions.
- Cosmetics: Ingredients in makeup, skincare products, or hair dyes can cause allergic skin reactions.
- Pollen grains from trees, grasses, or weeds can trigger seasonal allergies, also known as hay fever.
SIGNS OF AN ALLERGIC REACTION
Signs can vary depending on the severity and type of allergen involved. Common signs include:
- Sudden rash and hives on the skin
- Swelling of the face, throat, tongue, or other body parts
- Difficulty breathing, including wheezing or shortness of breath
- Tightness or constriction in the chest
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sneezing
- Coughing
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Loss of consciousness or fainting
To address an allergic reaction, here are some steps you can take:
- Use epinephrine if available: If you have been prescribed an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen), administer it immediately following the instructions provided. Then go to the nearest healthcare facility.
- Remove or avoid the allergen: If possible, move away from the allergen or eliminate exposure to it to prevent further reactions.
- Seek medical assistance: Call emergency services or go to the nearest emergency room for further evaluation and treatment.
- Stay calm: Panic can exacerbate symptoms, so try to remain as calm as possible while seeking help.
- Follow medical advice: Once medical assistance is received, follow the instructions provided by healthcare professionals for managing the allergic reaction and preventing future occurrences.
- Consider wearing a medical bracelet: If you have severe allergies, wearing a medical bracelet or necklace indicating your allergens can help alert others in case of an emergency.
- Always Inform healthcare providers of any known allergies before receiving treatment or medication to prevent adverse reactions.
INFECTION
An infection is a major health concern that affects millions of people around the world. It occurs when an organism, such as a bacteria or virus, enters and multiplies within the body. Infections can range from mild to severe, with some even potentially fatal. Symptoms vary depending on the type of infection and may include fever, fatigue, coughing, diarrhea or rash. Prevention strategies include proper hygiene practices such as hand washing, avoiding sharing personal items like towels or toothbrushes, getting vaccinated and eating a healthy diet. Treatment options depend on the type of infection but often involve antibiotics or other medications. Taking precautions can help minimize your risk for infection and keep you healthy.
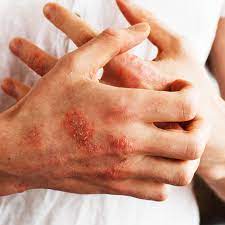
Signs of an infection can vary depending on the type and location of the infection. However, common signs and symptoms may include:
- Elevated body temperature is a typical response to infection as the body’s immune system fights off the invading pathogens.
- Feeling tired or exhausted can occur as the body redirects energy resources to combat the infection.
- Pain or discomfort: Pain, tenderness, or aching sensations may be present at the site of the infection or in nearby areas.
- Inflammation and swelling can occur as the body’s immune response attempts to isolate and eliminate the infectious agent.
- Increased blood flow to the infected area can cause redness or warmth.
- Infections may produce pus, mucus, or other abnormal fluids, depending on the affected area.
- Respiratory infections may cause symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain.
- Gastrointestinal infections can lead to digestive symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain.
- Skin infections may cause redness, swelling, warmth, or the development of rashes, blisters, or sores.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs) may cause symptoms such as burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, or cloudy or bloody urine.
-
Infections, particularly those affecting the respiratory or central nervous system, may cause headaches or migraines.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

