Anemia Symptoms: Fatigue, Weakness, and Other Indicators to Watch Out For
Anemia is a medical condition characterized by a low level of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the body. This condition can be caused by various factors such as poor diet, chronic diseases, blood loss, or genetic disorders. Iron deficiency is one of the leading causes of anemia, as iron is necessary for the production of hemoglobin. Please keep reading for details on the following topics:
Symptoms of anemia
Diagnosing anemia
Treatment of anemia
What are iron tablets
Side effects of iron tablets
Precautions to take when taking iron tablets
Causes of Anemia
- Blood Loss:
- Acute bleeding: Trauma, surgery, or childbirth.
- Chronic bleeding: Heavy menstrual periods, gastrointestinal ulcers, or colon cancer.
- Decreased Production of Red Blood Cells:
- Nutritional deficiencies: Lack of iron, vitamin B12, or folate.
- Chronic diseases: Kidney disease, cancer, or autoimmune conditions.
- Bone marrow disorders: Aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndrome.
- Increased Destruction of Red Blood Cells:
- Hemolytic anemia: Caused by autoimmune diseases, inherited disorders (e.g., sickle cell anemia), or certain medications.
- Other Causes:
- Pregnancy: Increased demand for blood production.
- Infections or toxins: Certain diseases or exposure to chemicals.
Types of Anemia
- Iron-Deficiency Anemia:
- Caused by insufficient iron, leading to decreased hemoglobin production.
- Commonly due to poor diet, blood loss, or increased demand (e.g., pregnancy).
- Vitamin Deficiency Anemia:
- Vitamin B12 deficiency: Can lead to pernicious anemia.
- Folate deficiency: Often linked to poor dietary intake or absorption issues.
- Aplastic Anemia:
- A rare condition where the bone marrow doesn’t produce enough blood cells.
- Hemolytic Anemia:
- Red blood cells are destroyed faster than they are produced.
- Sickle Cell Anemia:
- An inherited condition where RBCs are abnormally shaped, leading to reduced oxygen transport and blockages in blood vessels.
- Chronic Disease Anemia:
- Associated with long-term conditions like kidney disease or inflammatory disorders.
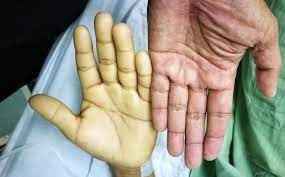
SYMPTOMS OF ANEMIA
Weakness and tiredness
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Irritability
Headaches
Paleness
Inability to concentrate
Shortness of breath during exercise
Pale or yellowish skin
Craving substances that are not food (pica)
Irregular or Rapid heartbeat
Fragile finger and toenails
Cracked lips
Smooth, sore tongue
Muscle pain during exercise
Difficulty swallowing
Cold hands and feet
Hair loss
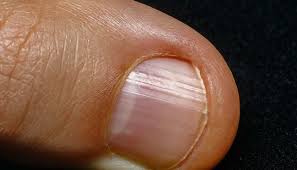 This is an example of a fragile fingernail
This is an example of a fragile fingernail
SYMPTOMS OF ANEMIA IN BABIES AND CHILDREN
Fussiness
Having a short attention span
Slow growth
Delayed walking and talking
DIAGNOSING IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Physical exam
- Checking for pallor, jaundice, or other visible signs.
An interview will be conducted to obtain information about the symptoms and medical history.
- Questions about symptoms, diet, family history, and medical conditions.
A complete blood count (CBC), to measure the size, shape, color and number of blood cells as well as hemoglobin, hematocrit, and RBC count.
Iron studies: Ferritin and serum iron levels. A ferritin level test- reflects how much iron may be stored in the body. Iron tests determine the type and severity of the anemia by measuring the amount of iron in the blood
Reticulocyte count to help determine the cause of anemia- Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells produced by bone marrow and released into the bloodstream
Vitamin levels: B12 and folate.
Peripheral blood smear: Examines RBC shape and size.
A fecal occult blood test (FOBT), checks for blood in stool samples
A colonoscopy inspects the entire large intestine (colon) using a long, flexible, instrument to look for causes of bleeding
An upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy uses a thin, flexible, lighted viewing instrument, to help identify causes of bleeding
For a Video capsule endoscopy, the patient swallows a capsule that contains a tiny camera which travels through the body to take pictures of the small intestine to show the location of the bleeding
X-ray tests such as an upper GI series or barium enema
Bone marrow biopsy (in severe cases). Bone marrow aspiration removes a small amount of bone marrow fluid through a needle inserted into the bone to determine the amount of iron in the body
TREATMENT OF ANEMIA
-
Iron-Deficiency Anemia:
- Iron supplements or iron-rich foods (e.g., red meat, spinach, lentils).
- Treat underlying causes of blood loss (e.g., ulcers, heavy menstruation).
-
Vitamin Deficiency Anemia:
- Vitamin B12 injections or oral supplements.
- Folate supplementation.
- Pregnant women taking prenatal vitamins
-
Aplastic Anemia:
- Blood transfusion, bone marrow transplant, or medications to stimulate blood production.
-
Hemolytic Anemia:
- Treat the underlying cause, manage autoimmune reactions, or use medications like corticosteroids.
-
Sickle Cell Anemia:
- Pain management, blood transfusions, and medications like hydroxyurea.
-
Chronic Disease Anemia:
- Manage the underlying disease and, in some cases, erythropoietin injections.
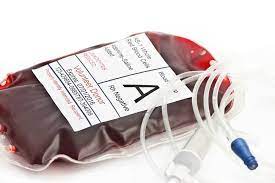 A bag containing packet red blood cells to treat someone with anemia
A bag containing packet red blood cells to treat someone with anemia
WHAT ARE IRON TABLETS
Iron tablets are often prescribed as a treatment option for anemia caused by iron deficiency. These tablets provide a concentrated source of iron that is absorbed by the body and used to increase the production of red blood cells. Iron tablets come in various forms and strengths and can be an effective way to treat anemia when taken as directed by a healthcare professional.
SIDE EFFECTS OF IRON TABLETS
Stomach discomfort
Dark stool
Allergic reaction
PRECAUTIONS TO TAKE WHEN TAKING IRON TABLETS
Iron is absorbed better if taken on an empty stomach
Tablets can be taken with food if stomach problems exist
Any side effects must be reported to the doctor
It is wise to take the tablets with vitamin C to assist with absorption into the body
Avoid taking the tablet within 2 hours of taking antacids or tetracycline (an antibiotic)
Avoid taking the tablet with foods containing caffeine and milk
Avoid taking the tablets without medical advice
Keep iron tablets out of the reach of small children
Prevention of Anemia
- Dietary Changes:
- Include iron-rich foods (e.g., lean meats, leafy greens).
- Consume foods rich in vitamin C to enhance iron absorption.
- Incorporate B12 and folate-rich foods like dairy, eggs, and fortified cereals.
- Regular Health Check-ups:
- Monitor conditions that may lead to anemia, such as chronic illnesses.
- Supplements:
- Pregnant women and individuals at risk may need iron or multivitamin supplements.
When to See a Doctor
- Persistent fatigue or weakness.
- Unexplained bruising or bleeding.
- Shortness of breath or chest pain.
- Signs of jaundice (yellow skin or eyes).
Anemia can often be treated effectively when diagnosed early. Proper nutrition, medical management, and addressing underlying causes are key to improving outcomes.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

