How Diet Affects Your Cholesterol Levels: Foods to Eat and Avoid
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on cholesterol, where we demystify the intricacies of this vital substance. It is a fundamental molecule for bodily functions, yet understanding its types, effects, and maintaining healthy levels is crucial for overall well-being. Join us as we unravel the complexities surrounding cholesterol and empower you with essential insights to make informed decisions for a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Cholesterol is a fat molecule that is essential for various bodily functions. While it is crucial for cell structure and hormone production, excessive levels in the blood can pose health risks. In this post, we will explore the basics of cholesterol, its types, its role in the body, and how to maintain a healthy balance for overall well-being.
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood that is essential for the proper functioning of your body. While it is necessary for various bodily functions, having high levels can increase your risk of heart disease and other health problems. In this post, we will delve into the different types of cholesterol, their effects on your health, and ways to maintain healthy levels.
Factors Affecting Cholesterol Levels
Various factors can influence levels, including genetics, diet, physical activity, weight, age, and certain medical conditions. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices to manage their levels effectively.
Types of Cholesterol
Cholesterol is transported through the bloodstream by lipoproteins, which are composed of fat and protein. There are two main types of lipoproteins: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
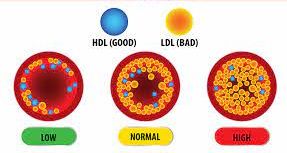
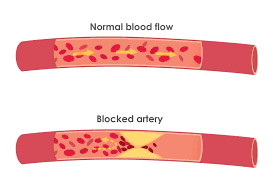
1. LDL Cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, is responsible for carrying cholesterol from the liver to the cells in your body. However, when there is an excess of LDL levels in your bloodstream, it can build up in the walls of your arteries, forming plaques. These plaques can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
2. HDL Cholesterol is known as “good” cholesterol, helps remove excess cholesterol from your bloodstream and carries it back to the liver for disposal. Higher levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a lower risk of heart disease. It acts as a protective mechanism against the harmful effects of LDL cholesterol.
Effects of High Cholesterol
Having high levels of LDL levels can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Over time, this can narrow the arteries and restrict blood flow to vital organs, such as the heart and brain. If a plaque ruptures, it can cause a blood clot, leading to a heart attack or stroke. The effects of high cholesterol include:

1. Heart Disease High cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart disease. It can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque accumulates on the artery walls, narrowing and hardening them. When the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup, it can result in chest pain (angina), heart attacks, or even heart failure. Lowering LDL levels can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.
This can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Understanding cholesterol’s role in heart health is crucial for adopting preventive measures.
2. Stroke A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced. If a blood clot forms in a narrowed artery leading to the brain, it can cause a stroke. High cholesterol increases the likelihood of developing these blood clots, making it a significant risk factor for stroke.
3. Peripheral Artery Disease Peripheral artery disease (PAD) occurs when plaque buildup narrows the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, typically the legs. This can lead to pain, numbness, and reduced circulation in the affected area. High levels contribute to the development of PAD and can worsen its symptoms.
Maintaining Healthy Cholesterol Levels
Regular screenings are essential for early detection of high levels. Knowing your numbers allows you to take appropriate actions to manage your health effectively. Fortunately, there are several lifestyle modifications and medical interventions that can help maintain healthy levels and reduce the risk of associated health problems.

1. Diet: A heart-healthy diet is crucial for managing cholesterol levels. Limiting saturated and trans fats found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods can help lower LDL levels. Instead, focus on consuming foods rich in soluble fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, as they can help reduce LDL levels. Incorporating foods high in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, and fruits, can help lower LDL levels. Additionally, reducing saturated and trans fats from processed and fried foods can have a positive impact on levels.
2. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can raise HDL levels and lower LDL levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises can further improve your cholesterol profile.

3. Medications: In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to manage the levels. Cholesterol-lowering medications, such as statins, fibrates, or bile acid sequestrants, may be prescribed by a healthcare professional to complement lifestyle modifications. It is essential to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations and regularly monitor your levels.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Regular physical activity is beneficial for raising HDL levels and improving overall heart health. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol consumption can also positively influence levels.


Understanding cholesterol and its impact on health is crucial for making informed decisions to lead a heart-healthy lifestyle. It plays a vital role in the body, but maintaining healthy levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Understanding the different types and their effects on your health empowers you to make informed decisions about your lifestyle and diet. By adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and, if necessary, taking prescribed medications, you can effectively manage your cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider will ensure that your levels are monitored and any necessary interventions are implemented.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.