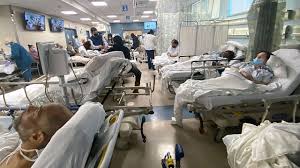
The Crisis of Hospital Bed Shortages: When Hospitals Have No Beds
in today’s healthcare landscape, hospital bed shortages present a significant challenge. These shortages impact patient care, strain healthcare providers, and highlight the critical need for proactive solutions. Understanding the causes and consequences of hospital bed shortages is essential to implementing effective strategies that ensure equitable access to medical care.

The healthcare system is grappling with a critical issue: the scarcity of available hospital beds. This predicament profoundly impacts patients, healthcare providers, and the overall efficacy of medical care. In this exploration, we delve into the underlying causes of hospital bed shortages, the ramifications for patients and healthcare professionals alike, and propose actionable steps to mitigate this pressing problem.
Understanding the bed shortage Crisis
Hospital bed shortages stem from a combination of factors:
- Rising Healthcare Demands: The increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses, an aging population, and frequent outbreaks of contagious diseases result in heightened hospital admissions that exceed available bed capacities.
- Lengthy Hospital Stays: Patients with complex medical conditions often require extended hospitalization periods, tying up beds that could otherwise accommodate new admissions.
- Delayed Patient Discharges: Challenges in securing post-hospital care options, such as nursing homes or home healthcare services, contribute to delayed patient discharges and thereby exacerbate bed shortages.
- Emergency Department Pressures: Overcrowded emergency rooms (ERs) serve as the primary gateway for hospital admissions, often causing admitted patients to languish in the ER until a bed becomes available.
The Consequences of bed shortage

The scarcity of hospital beds precipitates far-reaching consequences:
- Impaired Patient Care:
- Treatment Delays: Patients in need of urgent medical attention may experience significant delays in receiving necessary treatments, potentially exacerbating their conditions.
- Postponed Surgeries: Non-emergency surgeries may be postponed due to prioritizing emergency cases, resulting in prolonged patient discomfort and increased risks.
- Strain on Emergency Departments:
- Extended Waiting Times: Overcrowded ERs can lead to prolonged wait times for patients seeking critical care, delaying crucial diagnoses and interventions.
- Ambulance Diversion: Overburdened ERs may divert incoming ambulances to alternative facilities, causing further delays in emergency medical services.
- Burden on Healthcare Providers:
- Increased Workload: Healthcare professionals face intensified workloads and heightened stress levels, potentially compromising the quality of care provided.
- Patient Safety Concerns: Fatigue-induced errors and lapses in care may jeopardize patient safety and recovery outcomes.
- Healthcare System Challenges:
- Infection Risks: Overcrowded hospitals can facilitate the spread of infections among vulnerable patients, exacerbating health risks.
- Resource Allocation Struggles: Limited bed availability poses challenges in effectively allocating resources to meet the diverse needs of patients.
Addressing the root causes of hospital bed shortages necessitates a concerted effort to promote proactive health management and preventive care strategies:
- Personal Responsibility: Individuals are encouraged to prioritize their health by adopting healthy lifestyle practices. This includes:
- Quitting Smoking and Limiting Alcohol: Avoiding tobacco and moderating alcohol consumption significantly reduces the risk of chronic illnesses and associated hospital admissions.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity promotes overall health, strengthens immunity, and lowers the likelihood of developing conditions that may necessitate hospitalization.
- Nutritious Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports optimal health and helps prevent diet-related diseases.
- Early Intervention and Regular Check-ups: Routine medical screenings and proactive management of chronic conditions can mitigate the progression of illnesses, thereby reducing the need for hospital admissions.
- Community and Public Health Initiatives: Collaborative efforts to enhance health education, promote healthy behaviors, and expand access to preventive care services play a crucial role in reducing the burden on hospital resources.

Taking proactive steps to prioritize personal health not only fosters individual well-being but also contributes to alleviating the strain on our healthcare system. By making informed choices today—such as adopting healthy habits, seeking timely medical care, and embracing preventive measures—we can collectively mitigate the impact of hospital bed shortages. Let us empower ourselves and our communities to embrace healthier lifestyles, thereby fostering a resilient healthcare environment that meets the needs of all.
In conclusion, the shortage of hospital beds underscores the importance of individual responsibility and proactive healthcare practices. Together, through sustained efforts to promote health and wellness, we can mitigate the challenges posed by hospital overcrowding and ensure equitable access to quality medical care for all.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.


I?¦m not sure where you’re getting your info, but good topic. I needs to spend a while learning much more or working out more. Thank you for excellent information I used to be in search of this information for my mission.
As soon as I noticed this website I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
Outstanding post, you have pointed out some superb details , I likewise believe this s a very fantastic website.
This really answered my problem, thank you!