Lumps in Body: Types, Causes, and When to Seek Medical Help
Lumps in the body can be a source of concern and uncertainty for many individuals. Understanding the causes, types, and potential implications of is essential for informed decision-making and proactive health management.
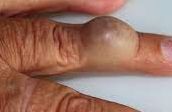
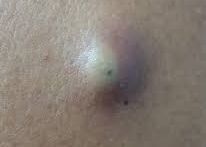
Discovering a lump anywhere in your body can be a cause for concern. While many turn out to be harmless, some can signal underlying health issues, including cancer. In this post, we will delve into what you should know about a lump including types, causes, and the importance of seeking medical evaluation.
Types of Lumps:
They can come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics:
1. Cysts: These are fluid-filled sacs that can occur just beneath the skin or in deeper tissues. Cysts are typically benign and may feel soft to the touch.
2. Lipomas: Lipomas are benign growths made up of fatty tissue. They are usually painless and can be moved around under the skin.
3. Lymph Node Swelling: Swollen lymph nodes are a common cause of lumps, often occurring in response to infections or other immune system responses. They may feel like small, rubbery nodes and can be painful when pressed.
4. Tumors: A lump can also be caused by a tumor, which can be benign or malignant (cancerous). Malignant tumors may grow rapidly and invade nearby tissues.
Causes:
Understanding the cause of a lump is crucial in determining the appropriate course of action:
1. Infections: Some may result from localized infections, such as abscesses. These are usually painful and may be accompanied by redness and warmth in the affected area.
2. Inflammation: Inflammatory conditions, like rheumatoid arthritis, can lead to the development of lumps in the joints or surrounding tissues.
3. Trauma: Injury or trauma to an area can cause the formation of a lump, often due to the accumulation of blood (hematoma) or scar tissue.
4. Cancer: While not all lumps are cancerous, some can be a sign of malignancy. Rapidly growing, irregularly shaped ones should raise concern and warrant immediate medical attention.
Seeking Medical Evaluation:
If you discover a lump, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation:
1. Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will examine the lump, noting its size, location, and texture. They may also ask about any associated symptoms, such as pain or changes in skin color.
2. Medical History: Sharing your medical history, including family history of cancer or other relevant conditions, can provide valuable insights.
3. Imaging and Tests: Depending on their initial assessment, your doctor may order imaging tests like ultrasounds, MRIs, or CT scans. In some cases, a biopsy may be needed to determine the nature of the lump.

Red Flags:
Certain characteristics should prompt immediate medical attention:
1. Rapid Growth: A lump that grows quickly may raise concerns and should be evaluated promptly.
2. Pain: Persistent or severe pain associated with a lump may indicate a problem that requires investigation.
3. Skin Changes: Changes in the skin over a lump, such as redness, dimpling, ulceration, or discharge, can be worrisome and require assessment.
In conclusion, lumps in the body can have various causes, and while many are benign, it’s essential to take them seriously. If you discover a lump, don’t delay seeking medical evaluation. Early detection and diagnosis are key to effectively addressing any underlying health issues. Your health and well-being should always be your top priority.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.