Blood Clots Overview – Causes, Risks, and Prevention Tips
Blood clots are a critical aspect of our body’s defense mechanism, essential for healing. However, understanding the risks and intricacies surrounding clots is paramount. Delve into this comprehensive guide to grasp the fundamentals and implications of clots in our health.
Blood clots, while necessary for healing injuries, can become life-threatening if they form abnormally. Thus, understanding the fundamentals about them is crucial for every patient.
What Are Blood Clots?
Also known as thrombi, they are gel-like, semi-solid masses that are formed in your blood vessels, when blood components (platelets and fibrin) clump together in response to injury or certain medical conditions. While clots are essential for stopping bleeding after an injury, they can become problematic when they form inside your blood vessels without a clear reason. They are a natural part of your body’s defense mechanism to stop bleeding when you’re injured. However, they can become problematic when they form inappropriately inside blood vessels.
Formation of Blood Clots:
Clots are formed through a process known as coagulation. This occurs in response to injury or when your body detects that bleeding needs to be stopped. The clotting process begins when blood vessels sustain damage, either from injury or underlying medical conditions. In response to the injury, platelets adhere to the damaged site and release chemicals that stimulate further clotting. Fibrin then forms a network, consolidating the platelets and sealing the wound. Clots originate from a complex process involving various blood components: 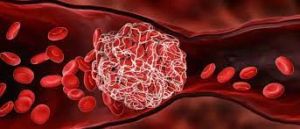
- Platelets: These small cell fragments are essential for clot formation. When blood vessels are damaged, platelets rush to the site to initiate clotting.
- Fibrin: A protein that forms a mesh-like structure, trapping blood cells to create a stable clot.
- Injury or Inflammation: When an injury occurs, platelets rush to the scene, adhere to the damaged vessel walls, and release chemicals that activate other platelets and initiate the coagulation process. Fibrin forms a mesh to trap blood cells and create a clot.
- Clotting Cascade: Chemical signals prompt the release of clotting factors, which activate a series of reactions. This cascade ultimately leads to the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin, creating a mesh that traps blood cells and forms the clot.
Common Types of Clots:
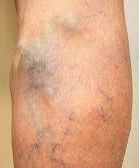
1. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): These clots form in deep veins, typically in the legs. DVT can be painful and potentially life-threatening if a piece breaks off and travels to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
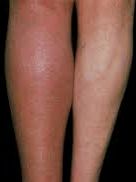
2. Pulmonary Embolism (PE): PE occurs when a clot, usually from a DVT, travels to the lungs, obstructing blood flow. Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and a rapid heart rate.
3. Arterial Clots: These clots develop in arteries and can lead to heart attacks or strokes, often caused by conditions like atherosclerosis where plaque builds up in the arteries.
Causes of Clots:
They can result from various factors:
– Inactivity: Prolonged sitting or immobility, such as during long flights or bed rest after surgery, increases clot risk.
– Medical Conditions: Conditions like atrial fibrillation, cancer, and thrombophilia can raise the likelihood of clot formation.
– Medications: Certain drugs, including birth control pills and hormone therapy, may increase clot risk.
– Injury: Trauma or surgeries can damage blood vessels, leading to clot formation.
Myths About Clots:
- Myth: Only the elderly get clots. Fact: Clots can affect people of all ages, including children and young adults.
- Myth: They are always associated with pain. Fact: While pain is a common symptom, some clots can form without noticeable symptoms.
- Myth: Blood thinners completely dissolve clots. Fact: Blood thinners help prevent further clot growth and reduce the risk of new clots, but they may not dissolve existing clots.
Dos for Clot Prevention, Management, and Treatment:
– Stay Active: Regular physical activity improves blood circulation and lowers clot risk.
– Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration prevents blood from thickening.
– Follow Medical Advice: Adhere to your doctor’s recommendations if you have conditions increasing clot risk.
– Know Family History: Inform your healthcare provider if there’s a family history of clots.
– Watch for Symptoms: Be vigilant for clot-related symptoms and seek prompt medical attention.
Don’ts: For Clot Prevention, Management, and Treatment:

– Don’t Ignore Symptoms: If you suspect a clot, don’t delay seeking medical help.
– Don’t Smoke: Smoking increases clot risk and should be avoided.
– Don’t Skip Medications: If prescribed blood thinners, take them as directed.
– Don’t Neglect Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce clot risk.
– Don’t Assume Immunity: Anyone can develop clots, even without apparent risk factors.
Prevention of Blood Clots: This involves proactive measures aimed at reducing risk factors:
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity, even light exercise like walking, helps keep blood flowing smoothly through your veins.
- Hydrate: Maintain proper hydration to prevent blood from thickening.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit saturated fats and cholesterol to keep your arteries clear.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases clot risk. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective steps you can take to reduce this risk.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: If you have underlying medical conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively.
- Medications: If prescribed, take blood thinners or other medications as directed by your doctor.
- Compression Stockings: These may be recommended to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) during extended periods of inactivity or following surgery. In some cases, wearing compression stockings can help prevent blood from pooling in the legs and reduce the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Treatment for Blood Clots: varies depending on their type, location, and severity:
- Anticoagulant Medications: Often referred to as blood thinners, these drugs slow down the body’s ability to form clots. Common anticoagulants include warfarin, heparin, and newer agents like apixaban and rivaroxaban. They are crucial for preventing the clot from growing larger and reducing the risk of new clots forming.
- Thrombolytic Therapy: In cases of severe clotting, especially when life-threatening situations like pulmonary embolism occur, thrombolytic agents may be used. These medications dissolve the clot quickly but are reserved for critical situations.
- Surgery: In some instances, especially with large clots that pose immediate danger, surgery may be necessary to physically remove the clot. This procedure is called thrombectomy.
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter: In cases where anticoagulants are contraindicated, a filter may be placed in the vena cava (the large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the heart) to prevent clots from reaching the lungs.
Understanding blood clots, from their formation and types to treatment and prevention, is essential for safeguarding your health. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to medical advice, and staying informed, you can significantly reduce the risk of clots and their potentially serious consequences. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and care.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.