Dairy Consumption Benefits – Support Bone Health and More
Dairy consumption has long been a topic of discussion in the realm of nutrition and health. As a significant source of calcium and other essential nutrients, understanding the benefits and potential considerations for consuming dairy is crucial for informed dietary choices.

Dairy products have been a dietary staple for centuries, providing a rich source of nutrients and flavors. However, in recent times, debates have arisen regarding whether dairy is universally beneficial or whether it may have potential drawbacks. Some argue that dairy provides essential nutrients and promotes bone health, while others claim that it can lead to various health issues. Thus, in this post, we will take a closer look at the pros and cons of including dairy in your diet, allowing you to make informed choices based on your individual health needs and preferences.
The Nutritional Value of Dairy:

Dairy products are known for their rich nutrient profile. They are an excellent source of calcium, which is crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Additionally, dairy contains high-quality protein, essential vitamins such as vitamin D and B12, and minerals like phosphorus and potassium. These nutrients play a vital role in supporting overall health and well-being.
Calcium, in particular, is a mineral that is essential for bone development and maintenance. It is widely recognized that dairy products are one of the best dietary sources of calcium. Consuming adequate amounts of calcium during childhood and adolescence is crucial for achieving peak bone mass, which can help prevent osteoporosis later in life. Therefore, including dairy in the diet can be beneficial for individuals of all ages, especially those at risk of calcium deficiency.
The Pros of Dairy Consumption
1. Dairy products are well-known for their high calcium content, essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth.
2. Dairy is a good source of high-quality protein, aiding in muscle development and overall bodily functions.
3. Dairy provides essential nutrients like vitamin D, vitamin B12, phosphorus, and potassium, which contribute to various bodily functions.
4. Yogurt contains probiotics, beneficial bacteria that support gut health and digestion.
5. Some studies suggest that consuming low-fat dairy products may assist in weight management due to their protein content and potential impact on satiety.
Dairy and Bone Health:

The relationship between dairy consumption and bone health has been extensively studied. Numerous studies have consistently shown that individuals who consume dairy products regularly have higher bone mineral density, and a reduced risk of fractures compared to those who consume less or no dairy. This is primarily attributed to the calcium content in dairy, which plays a crucial role in bone formation and maintenance.
Furthermore, dairy products contain other nutrients like phosphorus, magnesium, and protein that work synergistically with calcium to promote bone health. These nutrients contribute to the overall strength and density of bones, reducing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. Therefore, incorporating dairy into a balanced diet can be an effective strategy for maintaining optimal bone health.
The Cons of Dairy Consumption:
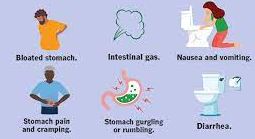
1. Lactose Intolerance: While dairy products offer several nutritional benefits, it is essential to consider potential health concerns associated with their consumption. One of the main concerns is lactose intolerance, which affects a significant portion of the population. Lactose intolerance occurs when the body lacks the enzyme lactase, which is needed to digest lactose, the sugar found in milk and other dairy products. This can lead to digestive discomfort and other symptoms. such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
However, it is worth noting that lactose-free dairy products are widely available, making it possible for individuals with lactose intolerance to still enjoy the benefits of dairy without experiencing digestive issues. Additionally, fermented dairy products like yogurt and certain types of cheese have lower lactose content and may be better tolerated by individuals with lactose intolerance.
2. Allergies: Some people are allergic to milk proteins, which can cause a range of allergic reactions.
3. Saturated Fat: Full-fat dairy products can be high in saturated fat, which, when consumed excessively, may contribute to heart disease risk.
4. Hormones and Antibiotics: Some conventional dairy products may contain traces of hormones and antibiotics used in livestock farming, though regulations vary.
5. Environmental Concerns: Dairy production can have significant environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions and land use.
6. Ethical Considerations: Concerns about animal welfare in the dairy industry can lead some individuals to avoid dairy products for ethical reasons.
Individual Variations and Moderation:
It is important to recognize that individual responses to dairy consumption can vary. While some people may tolerate and benefit from dairy, others may experience adverse effects. For instance, some individuals may be allergic to milk proteins, leading to allergic reactions such as hives or digestive problems. In such cases, avoiding dairy products is necessary.
Moreover, excessive consumption of dairy can contribute to an increased intake of saturated fats, which has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, moderation is key when it comes to consuming dairy. Including moderate amounts of dairy in a balanced diet can provide the desired nutritional benefits without exceeding recommended daily intake levels.
Making Informed Choices:
1. Individual Tolerance: If you are not lactose intolerant or allergic, moderate dairy consumption can provide valuable nutrients.
2. Alternatives: If you’re avoiding dairy, consider alternatives like fortified plant-based milk (almond, soy, oat), yogurt, and cheese.
3. Choose Wisely: Opt for low-fat or non-fat dairy options to reduce saturated fat intake.
4. Organic and Sustainable: Choose organic or sustainably produced dairy products to mitigate concerns about hormones and antibiotics.
5. Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body reacts to dairy consumption. If you experience discomfort, consider alternatives or consult a healthcare professional.
Dairy products can be a valuable part of a healthy diet due to their rich nutrient profile and positive impact on bone health. The calcium, protein, and other essential nutrients found in dairy contribute to overall well-being. The suitability of dairy consumption depends on your individual health status, preferences, and ethical considerations. Dairy can be a valuable source of essential nutrients, but it’s important to be aware of potential drawbacks such as lactose intolerance, allergies, and environmental concerns. Choose wisely, listen to your body, and consider alternatives if needed. As with any dietary decision, consulting a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.