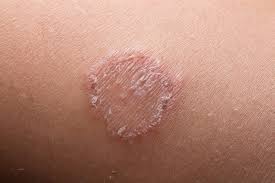
Effective Ringworm Treatment: How to Get Rid of It Quickly
Ringworm, a prevalent fungal infection caused by dermatophytes, affects the skin, nails, and scalp. Despite its misleading name, it’s crucial to understand that there are no worms involved in this condition. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and effective treatments for ringworm, shedding light on how to prevent and manage this contagious skin ailment.
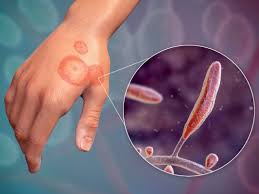
Ringworm is a common fungal infection that affects the skin, nails, and scalp. Despite its misleading name, ringworm is not caused by a worm but rather by various species of fungi. While it’s usually not serious, this contagious condition can cause discomfort and distress. It can be easily transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or animal, as well as by sharing personal items such as towels or clothing. In this post, we will explore what ringworm is, how it spreads, how to prevent infection, and the various treatment options available to manage this condition effectively.
What is Ringworm?
Contrary to its name, ringworm is not caused by a worm but rather a group of fungi known as dermatophytes. These fungi thrive on dead tissues like skin, hair, and nails, leading to the characteristic circular or ring-shaped rash that gives the infection its name. Ringworm can occur on various parts of the body, including the scalp (tinea capitis), body (tinea corporis), groin area (tinea cruris or jock itch), feet (tinea pedis or athlete’s foot), and nails (tinea unguium).
How Does Ringworm Spread?
Ringworm is highly contagious and can spread from person to person or through contact with contaminated objects and surfaces. Common ways of transmission include:
– Direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or animal.
– Sharing personal items such as clothing, towels, or hairbrushes with an infected individual.
– Coming into contact with contaminated surfaces in public places like locker rooms and swimming pools.
Causes and Symptoms
Ringworm is caused by a group of fungi known as dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm and moist environments, making certain areas of the body more susceptible to infection. Common sites for ringworm include the scalp, feet (athlete’s foot), groin (jock itch), and body. The infection typically presents as a red, circular rash with raised edges and a clear center, resembling a ring. However, the appearance may vary depending on the location and severity of the infection.

In addition to the characteristic rash, other symptoms of ringworm may include itching, burning, and scaling of the skin. If the scalp is affected, hair loss and small patches of baldness may occur. It is important to note that symptoms can take up to two weeks to appear after exposure to the fungus. If left untreated, ringworm can persist for several weeks or even months.
Prevention of Ringworm Infection
Preventing ringworm involves adopting certain hygienic practices and being mindful of potential sources of infection. Here are some tips to help reduce the risk of contracting ringworm:
1. Maintain good personal hygiene: Regularly wash your hands with soap and water, especially after touching animals or using public facilities such as gyms or swimming pools.
2. Keep your skin clean and dry: Fungi thrive in warm and moist environments, so it is important to keep your skin clean and dry, particularly in areas prone to sweating such as the feet and groin.
3. Avoid sharing personal items: Do not share towels, clothing, or other personal grooming items with individuals who have ringworm or unknown skin conditions to reduce the risk of transmission.
4. Wear protective footwear: When using public showers or walking in communal areas such as locker rooms or pool decks, wear sandals or flip-flops to reduce the risk of coming into contact with potentially contaminated surfaces and the fungus.
5. Treat pets for ringworm: If you have pets, ensure they receive regular veterinary check-ups and prompt treatment if they develop signs of ringworm. This will help prevent transmission to humans and other animals.
Treating Ringworm
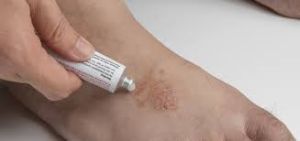
When it comes to treating ringworm, over-the-counter antifungal creams and ointments can be effective for mild cases. It’s essential to follow the instructions and continue using the medication even after the rash disappears to prevent a recurrence. These topical medications usually contain ingredients such as clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine, which work by inhibiting the growth of the fungi. It is important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and continue the treatment for the recommended duration, even if the symptoms subside.
In addition to medication, practicing good hygiene is essential in managing and preventing the spread of ringworm. Regularly wash and dry the affected area, and avoid sharing personal items such as towels, clothing, or hairbrushes. Keep the skin clean and dry, as fungi thrive in warm and moist environments. If you have pets, ensure they are regularly checked for signs of ringworm and promptly treated if necessary.
For more severe or persistent cases of ringworm, or those involving the scalp or nails, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional who may prescribe oral antifungal medications or stronger topical treatments to manage the infection effectively. These medications are typically reserved for infections that do not respond to topical treatments or involve the scalp or nails. It is crucial to complete the full course of oral medication as prescribed, even if the symptoms improve before the treatment is finished.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
While over-the-counter medications are the most common treatment, some natural remedies can complement traditional treatments:
– Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antifungal properties, dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil and apply it to the affected area.
– Garlic: Crush a garlic clove and apply the juice to the rash. Garlic has natural antifungal properties.
– Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel can soothe and promote healing of the affected skin.

Ringworm is a common fungal infection that affects various parts of the body of people of all ages and can be easily treated with proper care. By understanding how it spreads and implementing preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of infection. Although it is highly contagious, ringworm can be effectively treated with over the counter or prescription antifungal medications. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items, and taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of contracting ringworm. If you suspect you have ringworm or if the infection persists despite treatment, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis, prompt treatment and guidance, to avoid the spread of the infection to others. Remember, maintaining good hygiene and practicing preventive measures are essential in keeping yourself and others safe from this bothersome fungal infection.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.