Heat Loss Prevention: Essential Tips for New Parents
Welcome to our guide on preventing heat loss in your bundle of joy. As parents, ensuring your baby’s warmth is paramount. Join us as we delve into the crucial aspects of newborn heat regulation, exploring effective measures to keep your little one snug and cozy.

Dear Mothers, as a parent, ensuring the well-being and comfort of your baby is always a top priority. One crucial aspect to consider is preventing heat loss in your little one. Babies, especially newborns, are highly susceptible to heat loss, making it crucial for us to understand the reasons behind this vulnerability and the effective measures we can take to prevent it.
Understanding How Babies Lose Heat:
When it comes to heat loss, babies have a distinct disadvantage compared to adults. Their tiny bodies have a higher surface area-to-mass ratio, which makes it easier for heat to escape. Additionally, newborns are unable to regulate their body temperature as efficiently as older children and adults due to an underdeveloped thermoregulatory system. This makes them highly susceptible to both external and internal factors that can cause heat loss.
Why do babies lose heat?
Before we dive into preventive measures, let’s understand why babies are more prone to heat loss than adults. There are a few key factors at play:
-
Size and surface area: Babies have a larger surface area-to-body weight ratio, meaning they have more skin exposed to the environment. This makes them more vulnerable to heat loss through radiation, convection, and conduction.
-
Immature thermoregulatory system: A newborn’s ability to regulate body temperature is not fully developed. They have difficulty generating and retaining heat on their own, requiring external assistance to maintain a comfortable body temperature.
-
Limited subcutaneous fat: Babies have less insulation due to their limited subcutaneous fat layer, which acts as a natural barrier against heat loss.
Let’s delve into the various ways babies lose heat:
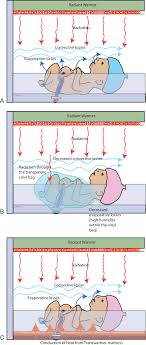
1. Conduction: Heat can be lost through direct contact with a cold surface, such as a chilly changing table or an improperly heated crib mattress.
2. Convection: Air movement around the baby can carry away heat. Drafts or cold air from open windows or fans can contribute to this type of heat loss.
3. Radiation: Heat loss through radiation occurs when the baby is exposed to cold objects or surfaces nearby, such as cold walls or windows.
4. Evaporation: Moisture on the baby’s skin, such as sweat or wet clothing, can evaporate and cause heat loss. This is particularly relevant after bath time or during hot weather.
The consequences of heat loss in babies

- Hypothermia: One of the most immediate and severe consequences of heat loss in babies is hypothermia. Hypothermia occurs when the body loses heat faster than it can generate, resulting in a drop in core body temperature. Newborns and young infants are particularly vulnerable to hypothermia due to their limited ability to generate heat and regulate body temperature. Prolonged exposure to cold environments, inadequate clothing, or insufficient warming techniques can increase the risk of hypothermia. This condition can lead to lethargy, poor feeding, breathing difficulties, and in severe cases, even life-threatening complications.
- Weakened Immune System: Heat loss in babies can compromise their immune system’s functioning, making them more susceptible to illnesses. When their body temperature drops, the immune system may become less effective at fighting off infections and viruses. This vulnerability can increase the risk of respiratory infections, colds, flu, and other illnesses. It’s crucial to maintain a warm environment for babies to support their immune system and reduce the likelihood of falling ill.
- Discomfort and Restlessness: When babies lose heat, they can experience discomfort and restlessness. Just like adults, they prefer a cozy and warm environment that allows them to feel secure and content. Cold temperatures can cause discomfort, leading to fussiness, crying, and disrupted sleep patterns. Ensuring that babies are adequately dressed and surrounded by a warm environment promotes their comfort and promotes better sleep and overall well-being.
- Difficulty in Weight Gain: Heat loss can impact a baby’s ability to gain weight optimally. When their body expends energy to generate heat, it may divert resources away from growth and development. Inadequate weight gain can be a concern, particularly for premature infants or babies with underlying health conditions. Maintaining a warm environment helps conserve energy and supports healthy weight gain in babies.
- Respiratory Distress: Cold temperatures can cause respiratory distress in babies, especially in those with pre-existing respiratory conditions. The drop in body temperature can constrict blood vessels, making it harder for the lungs to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently. This can lead to breathing difficulties, wheezing, and increased vulnerability to respiratory infections. Keeping babies warm reduces the strain on their respiratory system and supports healthy breathing.
- Increased Risk of Infections: Heat loss in babies can compromise their ability to fight off infections. Cold temperatures can suppress the immune system, making babies more vulnerable to bacterial and viral infections. Additionally, when babies are exposed to cold environments, their body’s defense mechanisms may focus on generating heat rather than combating pathogens, leaving them susceptible to various illnesses.
- Digestive Issues: Prolonged exposure to cold temperatures can affect a baby’s digestion. Cold can cause the muscles in the digestive system to contract, leading to discomfort, colic, and digestive disturbances. Proper warmth helps promote optimal digestion and absorption of nutrients, ensuring healthy growth and development.
- Impact on Brain Development: Maintaining a stable body temperature is crucial for optimal brain development in babies. Heat loss can divert energy away from brain functions, potentially affecting cognitive development. Adequate warmth ensures that the baby’s body can allocate energy and resources appropriately, supporting healthy brain development and cognitive abilities.
- Circulatory Problems: Cold temperatures can negatively impact the baby’s circulation, affecting blood flow to vital organs and extremities. When the body loses heat, blood vessels may constrict to conserve warmth, potentially leading to poor circulation. This can result in cold hands and feet, and in extreme cases, it may even affect the baby’s overall cardiovascular health.

- Sleep Disruptions: Babies who experience heat loss may have difficulty settling into restful sleep. Cold temperatures can disrupt their sleep patterns, causing frequent awakenings and restlessness. By maintaining a warm environment, you can help promote better sleep for your baby, contributing to their overall well-being and development.
- Impaired Thermoregulation: When babies consistently experience heat loss, it can disrupt their developing thermoregulatory system. The body’s ability to regulate temperature effectively may be compromised, leading to difficulties in adapting to temperature changes in the future. This can make them more susceptible to heat-related or cold-related illnesses as they grow older.
- Potential Long-Term Health Issues: In severe cases, prolonged or recurrent heat loss in babies can have long-term health implications. Chronic exposure to cold temperatures and inadequate warmth may increase the risk of respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and compromised immune function. It is crucial to address heat loss promptly and provide appropriate warmth to minimize the potential long-term health effects.
Preventing Heat Loss: Your Guide to a Warm and Cozy Baby:

1. Dressing your baby appropriately: Choose clothing that allows easy adjustment to regulate your baby’s temperature.
-
- Layering: Dress your baby in multiple thin layers rather than one thick garment. This allows you to adjust their clothing according to the temperature.
- Hat and booties: Ensure your baby wears a hat and soft booties to prevent heat loss through the head and feet.
- Swaddling: Swaddling can help regulate your baby’s body temperature by keeping them snug and secure. Opt for lightweight, breathable blankets. Swaddling is an age-old technique that mimics the coziness of the womb. Wrapping your baby snugly in a light blanket helps regulate their body temperature and can provide them with a sense of security.
2. Room temperature control:
-
- Maintain a warm environment: Set the room temperature between 68°F and 72°F (20°C and 22°C). Use a room thermometer to monitor the temperature accurately.
3. Avoid exposing your baby to cold drafts: Be cautious of open windows, fans, or air conditioning vents that may cause drafts. Shield your baby from direct exposure to these sources of cold air. Ensure windows and doors are properly sealed to prevent cold drafts from entering the room. Use door draft stoppers, seal windows, and avoid placing the crib near air conditioning vents or open windows. 
4. Proper bedding and sleep arrangements:
-
- Use appropriate bedding: Choose lightweight, breathable materials for your baby’s crib or bassinet. Avoid heavy blankets or comforters.
- Avoid overheating: Be mindful of overdressing or over bundling your baby during sleep. Overheating can increase the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
- Choose a firm mattress that fits snugly in the crib and cover it with a fitted sheet. Avoid loose or excessive bedding, which can lead to suffocation hazards. Use a swaddle or sleep sack to keep your baby warm and secure without the need for loose blankets.
5. Pre-warm the crib or bassinet: Before placing your baby in their sleeping space, warm it up by using a hot water bottle or a microwavable heating pad. Remember to remove these items before placing your baby in the crib.

6. Keep your baby’s head covered: Since a significant amount of body heat is lost through the head, ensure your baby wears a comfortable hat or cap when going outside or in cooler indoor settings.
7. Protect against evaporative heat loss: During bath time, make sure the water temperature is comfortable and wrap your baby in a warm towel immediately after. Pat dry gently to minimize evaporation from the skin’s surface.
8. Embrace the power of skin-to-skin contact:

Holding your baby against your bare chest provides warmth and promotes bonding. Skin-to-skin contact is especially beneficial for premature babies or those experiencing difficulty regulating their body temperature.
9. Stay attentive to your baby’s cues:
-
- Touch and check for warmth: Feel your baby’s hands, feet, and back to ensure they are warm to the touch. Cold extremities may indicate heat loss.
- Observe baby’s behavior: If your baby appears unusually fussy, cries excessively, or exhibits signs of discomfort, they might be feeling cold.
-
Regular Diaper Checks: Wet diapers can quickly cool your baby’s skin. Regularly check and change your baby’s diapers to ensure they stay dry and comfortable.
10. Warm up your baby’s clothing:
Before dressing your baby, warm their clothes, particularly during colder months. You can place them near a heater or use a towel warmer. Remember to check the temperature to ensure it’s safe for your baby’s delicate skin.
11. Use insulated bottles and food containers:

If you’re feeding your baby with a bottle or providing solid food, choose insulated containers to help maintain the desired temperature. This is especially important for warm formula or breast milk, as reheating can lead to nutrient loss.
12. Opt for babywearing:
Baby carriers or slings offer both convenience and warmth. The close contact between you and your baby helps regulate their body temperature while providing the added benefit of bonding.
13. Create a warm environment during outdoor activities:

If you’re venturing outside with your baby in chilly weather, consider using a stroller or carrier with a weather shield or canopy to shield them from wind and cold air. Additionally, dress your baby in appropriate outdoor gear such as a warm hat, mittens, and booties.
14. Monitor signs of overheating:
While preventing heat loss is crucial, it’s equally important to avoid overheating your baby. Keep an eye out for signs such as excessive sweating, flushed skin, or rapid breathing. Adjust the layers accordingly to maintain a comfortable temperature for your little one.

Mothers, the consequences of heat loss in babies should not be underestimated. By understanding how babies lose heat and implementing these preventive measures, you can create a warm and nurturing environment for your little one. By dressing your baby in appropriate layers, maintaining a warm indoor space, and protecting against drafts, you can help ensure their comfort and well-being. Remember, your attentiveness to their temperature needs and consistent monitoring will go a long way in keeping your bundle of joy cozy and content. Cherish these precious moments, knowing that you are providing them with the warmth and care they need.
Remember, while it’s important to prevent heat loss, it’s equally crucial to avoid overheating your baby. Keep a balance between warmth and comfort and always consult with your pediatrician if you have concerns about your baby’s body temperature regulation.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.