Preventing Malnutrition: Tips for a Balanced and Healthy Diet
In the battle against malnutrition, knowledge is our most potent weapon. Despite abundant resources, millions worldwide still suffer from inadequate nutrition, a problem that transcends borders and socioeconomic status. We will now delve into effective strategies aimed at preventing malnutrition, emphasizing education, collaboration, and sustainable solutions to ensure optimal nutrition for all.

In a world abundant with resources and scientific advancements, it is disheartening to acknowledge that malnutrition remains a critical global challenge affecting millions of lives. While it may seem like a distant issue, malnutrition is a pervasive problem that affects both developed and developing countries alike. This post aims to shed light on the gravity of malnutrition and explore effective strategies for its prevention, emphasizing the importance of nutrition in creating a healthier and brighter future for all.
Understanding Malnutrition:
Malnutrition is more than just a lack of food; it encompasses a range of conditions resulting from inadequate intake, poor absorption, or excessive loss of essential nutrients. It affects people of all ages, from infants and young children to adolescents, adults, and the elderly. Malnutrition manifests in two forms: undernutrition and overnutrition.
a) Undernutrition: This occurs when individuals do not receive adequate nutrients to meet their daily requirements, leading to stunted growth, weakened immune systems, and cognitive impairments. Undernutrition is particularly devastating for children, affecting their physical and mental development.
b) Overnutrition: Contrary to popular belief, malnutrition is not solely synonymous with hunger. Overnutrition, often associated with an unhealthy diet, occurs when individuals consume excessive calories but lack essential nutrients. This can lead to obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and other diet-related chronic illnesses.
The Global Burden of Malnutrition:
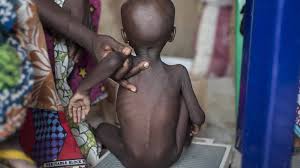
Malnutrition is a global crisis with far-reaching consequences. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly one in three people worldwide suffer from malnutrition in some form. These numbers are staggering, given that adequate nutrition is a basic human right and an essential component of sustainable development.
In developing countries, malnutrition remains a significant public health concern due to poverty, limited access to nutritious food, inadequate sanitation, and lack of healthcare infrastructure. However, even in wealthier nations, where food is abundant, unhealthy dietary habits, sedentary lifestyles, and social inequalities contribute to the prevalence of malnutrition.
Prevention Strategies: Empowering Change through Nutrition:

The fight against malnutrition requires a multi-faceted approach, combining individual actions, policy changes, and collective efforts. Here are some effective strategies to prevent malnutrition and promote optimal nutrition for all:
a) Promoting Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of nutrition and its impact on health is crucial. Empowering individuals with knowledge enables them to make informed decisions regarding their diet, ensuring a more balanced and nourishing lifestyle. Increasing knowledge about nutrition and its significance is essential to combat malnutrition. This can be achieved through educational campaigns, workshops, and community outreach programs. For instance, a local health organization can organize nutrition workshops in schools, teaching children about balanced diets, food groups, and the importance of consuming fruits and vegetables.
b) Strengthening Food Systems: Creating sustainable and resilient food systems that provide equitable access to diverse, nutritious, and affordable food is vital. This involves supporting local agriculture, improving storage and transportation infrastructure, and reducing food waste. Supporting local agriculture by providing farmers with resources, training, and access to markets also helps to ensure a diverse and nutritious food supply. Additionally, improving storage and transportation infrastructure reduces food spoilage and enables the distribution of fresh produce to remote areas. An example of this is the establishment of farmer cooperatives that collectively negotiate fair prices and distribute their produce efficiently.
c) Addressing Socioeconomic Inequalities: Poverty and inequality are key drivers of malnutrition. Tackling these issues requires comprehensive social policies that promote income equality, access to education, and healthcare services. Providing social safety nets and nutritional support programs for vulnerable populations can make a significant difference. Governments can implement policies that address poverty and inequality, such as increasing the minimum wage and providing social safety nets. Nutritional support programs, like subsidized or free school meals for low-income families, also help alleviate the burden of malnutrition. For example, Brazil’s Bolsa Família program provides financial assistance to low-income families, including nutritional support for pregnant women and children.
d) Empowering Women and Girls: Gender inequality exacerbates malnutrition rates, particularly among women and girls. Gender equality is vital in the fight against malnutrition. Empowering women and girls through education and economic opportunities enhances their decision-making power regarding nutrition within households. Initiatives can include vocational training programs, microfinance initiatives, and campaigns promoting women’s rights. For instance, in Rwanda, the Women for Women International program provides women with job skills, nutritional training, and education, enabling them to support themselves and their families.
e) Collaborating with Stakeholders: Governments, NGOs, healthcare professionals, and the private sector must collaborate to develop and implement effective nutrition policies and interventions. Partnerships can drive innovation, secure funding, and amplify the impact of initiatives aimed at combating malnutrition. By pooling resources, expertise, and networks, stakeholders can create comprehensive programs to address malnutrition. For example, the Scaling Up Nutrition (SUN) Movement brings together governments, civil society, and businesses to coordinate efforts and implement evidence-based interventions to improve nutrition in multiple countries.

Malnutrition remains a global challenge that demands immediate attention and action. By understanding the causes, consequences, and prevention strategies associated with malnutrition, we can work together to create a world where every individual has access to nutritious food. The prevention strategies above, combined with the commitment and active involvement of individuals and organizations, can contribute to the eradication of malnutrition and the creation of a healthier future for all.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.