The Importance of Consistent Sleep Habits for Better Health
Are you struggling to get a good night’s sleep? In today’s hectic world, mastering healthy sleep habits is more important than ever. This post will guide you through practical tips and strategies to improve your sleep quality, ensuring you wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated every morning. Let’s unlock the secrets to better sleep habits together!

Sleep is a fundamental aspect of our lives, crucial for maintaining optimal physical and mental health. However, in our fast-paced modern world, sleep often takes a backseat. Neglecting sleep can have far-reaching consequences on various aspects of our well-being. We will now explore the profound impact of sleep on overall health and provide practical tips for improving sleep habits to unlock the full potential of restorative sleep.
The Importance of Sleep:
Sleep is not just a time of rest and inactivity; it is a critical period during which the body and mind undergo essential processes for optimal functioning. During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates tissues, consolidates memories, and releases hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
Lack of sufficient sleep can lead to impaired cognitive function, decreased productivity, mood disturbances, weakened immune system, and an increased risk of chronic health conditions.
Sleep Habits, Deprivation and Health Risks:
Chronic sleep deprivation, which refers to consistently not getting enough sleep, can have serious consequences for overall health. It has been linked to an increased risk of obesity due to disruptions in appetite-regulating hormones, such as leptin and ghrelin. Sleep deprivation also disrupts glucose metabolism, potentially increasing the risk of developing diabetes. Furthermore, inadequate sleep has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. It can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and mood disorders are also closely linked to poor sleep quality and duration.
Leptin and ghrelin are two hormones involved in regulating appetite and body weight. Here’s a brief explanation of each hormone:
Leptin:
Leptin is often referred to as the “satiety hormone” because it signals to the brain when we’ve had enough to eat and helps regulate energy balance. It is primarily produced by adipose tissue (fat cells) and released into the bloodstream. Leptin acts on the hypothalamus in the brain, specifically targeting the appetite-regulating centers. When leptin levels rise, it signals to the brain that we are full and can reduce our appetite, thereby helping to control food intake and prevent overeating. In individuals with obesity, there is often a resistance to leptin, which means the brain does not respond adequately to the hormone’s signals, leading to a disrupted appetite regulation mechanism.
Ghrelin:
Ghrelin, known as the “hunger hormone,” is produced mainly by cells in the stomach and released into the bloodstream. Ghrelin levels typically increase before meals and decrease after eating. It stimulates appetite and promotes food intake. Ghrelin acts on the hypothalamus and other brain regions to increase hunger and enhance the reward value of food. Additionally, ghrelin can influence metabolism, fat storage, and the release of growth hormone. It plays a significant role in regulating short-term feeding behavior and meal initiation.
The balance between leptin and ghrelin is crucial for maintaining a healthy appetite and body weight. When this balance is disrupted, it can lead to overeating, weight gain, and difficulties in managing body weight. Factors such as sleep deprivation, stress, and certain medical conditions can impact the regulation of leptin and ghrelin levels, potentially affecting appetite control and contributing to weight-related issues.
Understanding Sleep Cycles:
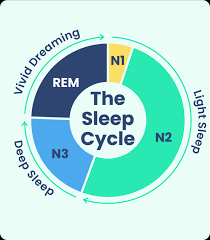
Sleep is a complex process that consists of different stages and cycles. There are two main categories of sleep: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep is further divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3, with N3 being the deepest and most restorative stage. REM sleep is the stage where vivid dreaming occurs. A complete sleep cycle consists of transitioning through these stages multiple times throughout the night. Each cycle typically lasts around 90 to 120 minutes.
The Impact of Sleep on Overall Health:
Physical Health:
Adequate sleep plays a vital role in supporting physical health. During sleep, the body repairs tissues, releases growth hormones, and restores energy levels. Consistent sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and compromised immune function.
Mental Well-being:
Quality sleep is crucial for mental well-being and cognitive function. It enhances concentration, memory retention, and problem-solving abilities. Chronic sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety, as well as decreased overall mental performance.
Immune Function:
Sleep and the immune system are closely intertwined. Sufficient sleep strengthens the immune system, enabling it to better defend against infections and diseases. Inadequate sleep can weaken immune function, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses and experiencing longer recovery times.
Hormonal Balance:
Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating hormone production and maintaining hormonal balance. Disrupted sleep patterns can impact the release of hormones that control appetite, leading to imbalances that contribute to weight gain and an increased risk of metabolic disorders.
Emotional Resilience:
Restful sleep is essential for emotional regulation and resilience. It helps improve mood, reduce stress, and enhance emotional stability. Conversely, chronic sleep deprivation can exacerbate feelings of irritability, anxiety, and emotional reactivity.
Tips for Improving Sleep Habits:
Stick to a Consistent Sleep Schedule:
Establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Consistency helps regulate your body’s internal clock, promoting better sleep quality.
Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine:
Develop a soothing routine before bed to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This may include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, practicing relaxation techniques, or listening to calming music.
Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment:
Optimize your sleep environment by making it cool, quiet, and dark. Use earplugs, eye shades, or white noise machines to block out disturbances. Invest in a comfortable mattress, pillows, and breathable bedding to ensure optimal comfort.

Limit Exposure to Electronics Before Bed:
The blue light emitted by electronic devices can disrupt sleep patterns. Minimize exposure to screens, such as smartphones, tablets, and computers, at least an hour before bedtime. Consider using blue light filters or wearing blue light-blocking glasses if screen use is unavoidable.
Avoid Stimulants and Heavy Meals:
Refrain from consuming stimulants like caffeine and nicotine in the afternoon and evening, as they can interfere with falling asleep. Additionally, avoid heavy meals close to bedtime, as digestion can disrupt sleep.
Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity promotes better sleep. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. However, avoid vigorous exercise too close to bedtime, as it may increase alertness and make it harder to fall asleep.
Manage Stress:
Stress and anxiety can interfere with sleep. Explore stress management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or journaling, to help calm the mind before sleep.
Seeking Professional Help:
Acknowledge that persistent sleep issues may require professional help. Encourage readers to consult with a healthcare professional if they consistently struggle with sleep despite implementing healthy habits. A healthcare professional can identify underlying sleep disorders or provide personalized guidance and treatment options.

By understanding the importance of sleep and implementing healthy sleep habits, you can unlock the power of sleep and reap its numerous benefits. Prioritize your sleep, create a sleep-friendly environment, establish a consistent routine, and manage stress effectively. Remember, quality sleep is not a luxury; it is a vital component of overall health and well-being.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.