What Are Uterine Fibroids? Understanding the Basics
Uterine fibroids, non-cancerous growths in the uterus, can raise concerns during pregnancy due to potential complications and misconceptions. Let’s delve into the relationship between uterine fibroids and pregnancy, addressing common myths and exploring treatment options to ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.
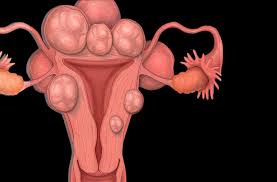
Pregnancy is a beautiful and miraculous time in a woman’s life, but it can also be accompanied by many concerns and questions. One of these concerns can be uterine fibroids, which are benign tumors that develop in the uterus.
What are Uterine Fibroids?
These also known as leiomyomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They are made up of muscle and fibrous tissue and can vary in size from tiny seedlings that can only be seen under a microscope to large masses that can distort the uterus. While fibroids are very common, with up to 80% of women developing them by the age of 50, many women may not even know they have them because they often do not cause any symptoms.
How do Uterine Fibroids Affect Pregnancy?
While many women with uterine fibroids go on to have normal, healthy pregnancies, fibroids can sometimes cause complications. The exact impact of fibroids on pregnancy depends on their size, location, and number. Here are some of the ways that fibroids can affect pregnancy:
- Difficulty Getting Pregnant: Large fibroids can sometimes interfere with the ability to conceive by blocking the fallopian tubes or causing infertility.
- Miscarriage: Fibroids can increase the risk of miscarriage, especially if they are located inside the uterine cavity.
- Preterm Labor: Fibroids can cause the uterus to contract prematurely, leading to preterm labor and delivery.
- Placental Abruption: In rare cases, fibroids can cause the placenta to detach from the uterine wall, which can lead to heavy bleeding and other complications.
- Cesarean Delivery: Depending on the location of the fibroids, a cesarean delivery may be necessary to avoid the risk of the fibroids obstructing the birth canal.
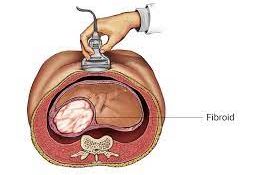
Treatment During Pregnancy?
If a woman has fibroids during pregnancy, her healthcare provider will closely monitor their growth and location to determine if any treatment is necessary. In most cases, fibroids will not require any treatment during pregnancy, but if they are causing complications, there are some options:
- Medications: If they are causing painful or heavy periods, medication can be given to manage symptoms during pregnancy.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary if fibroids are causing significant pain, bleeding, or other complications.
- Wait and See Approach: If fibroids are not causing any symptoms or complications, it may be best to wait until after delivery to consider treatment options.
In some cases, a cesarean delivery may be necessary. This decision will depend on the size, number, and location of the fibroids, as well as the position of the baby.
If it is located near the cervix or blocking the birth canal, a vaginal delivery may not be possible, and a cesarean delivery may be necessary to avoid complications such as obstructed labor, fetal distress, or excessive bleeding. Additionally, if a woman has multiple or very large fibroids, a cesarean delivery may be necessary to reduce the risk of uterine rupture during labor.
However, in many cases, a vaginal delivery is still possible, even with fibroids. The healthcare provider will carefully monitor the size and location during pregnancy and labor to determine the best delivery method for both the mother and the baby.
It’s important to note that each case is unique, and the decision to have a cesarean delivery will depend on individual circumstances. Women should discuss their options with their healthcare provider and develop a plan of care that is tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
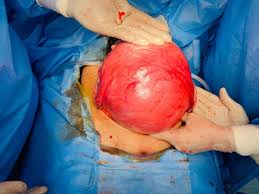
However, there are many myths and misconceptions surrounding pregnancy and fibroids that can cause unnecessary worry and confusion. We will now identify and address some of the most common myths related to pregnancy and uterine fibroids.
Myth #1: All women with fibroids will have complications during pregnancy.
Fact: While uterine fibroids can cause complications during pregnancy, the majority of women with fibroids will have normal, healthy pregnancies. Many women with fibroids may not even know they have them because they often do not cause any symptoms.
Myth #2: Fibroids will always grow during pregnancy.
Fact: While fibroids can grow during pregnancy due to increased hormone levels and blood flow to the uterus, they do not always grow. In fact, some fibroids may even shrink during pregnancy.
Myth #3: All fibroids need to be removed before pregnancy.
Fact: In most cases, fibroids do not need to be removed before pregnancy. Many women with fibroids go on to have normal, healthy pregnancies without any complications.
Myth #4: Women with fibroids cannot have a vaginal delivery.
Fact: While in some cases, a cesarean delivery may be necessary if a fibroid is blocking the birth canal or near the cervix, many women with fibroids are able to have a vaginal delivery.
Myth #5: Fibroids always cause infertility.
Fact: While large fibroids can sometimes interfere with the ability to conceive by blocking the fallopian tubes, many women with fibroids are still able to get pregnant and carry a baby to term.
Myth #6: Removing fibroids during pregnancy is always necessary.
Fact: In most cases, fibroids do not require any treatment during pregnancy. If fibroids are causing complications, such as preterm labor or heavy bleeding, then treatment may be necessary. However, surgery to remove fibroids during pregnancy is rare and generally only considered in severe cases.

In conclusion, while uterine fibroids can cause concerns during pregnancy, many of the myths surrounding pregnancy and fibroids are unfounded. Most women with fibroids will go on to have normal, healthy pregnancies without any complications. If you are pregnant and have fibroids, it is important to discuss any concerns or questions with your healthcare provider. They can help you understand your individual risks and develop a plan of care that is right for you and your baby.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.