Sleep Apnea Symptoms: What to Look for and When to Seek Help
If you or your partner experience loud and frequent snoring, gasping for breath during sleep, or pauses in breathing, these could be potential warning signs of sleep apnea. Understanding these indicators is crucial for recognizing this serious sleep disorder. Discover more about the symptoms, their impact on your health, and when it’s essential to consult a doctor for proper evaluation and guidance.
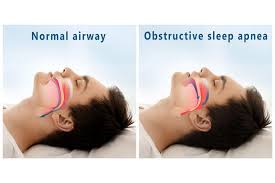
Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder that can cause a person to stop breathing repeatedly during sleep. Snoring can be a symptom, but not everyone who snores has sleep apnea.
Causes of Sleep Apnea:
This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, with the two main types being obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). OSA occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively, leading to a temporary blockage of the airway. CSA, on the other hand, results from a failure of the brain to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Other contributing factors include excess weight, obesity, smoking, alcohol use, and genetics. Identifying the specific cause is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing the condition. Obesity and excess weight are significant contributors, as the additional fat deposits around the neck can obstruct the airway. Age, gender, and family history also play a role, with males, older individuals, and those with a family history of sleep apnea being at higher risk. Lifestyle factors such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can exacerbate the condition. Understanding these risk factors is essential for both prevention and early detection.
Here are Eight Warning Signs to Look For:
- Loud and frequent snoring: Snoring is common, but if it is loud and frequent, it could be a sign of sleep apnea.
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Pauses in breathing during sleep, even for just a few seconds
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Morning headaches: Waking up with headaches
- Irritability or mood changes
- Restless sleep or insomnia: Having trouble falling or staying asleep
- Difficulty concentrating or forgetfulness
Prevention:
While some risk factors for sleep apnea, such as age and genetics, are beyond one’s control, certain lifestyle modifications can help prevent or reduce the severity of the condition. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can significantly decrease the risk. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake, especially close to bedtime, can also be beneficial. Good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and sleeping on one’s side, may contribute to prevention.
Effective management often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and, in some cases, surgical procedures. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is a common and highly effective treatment, involving the use of a device that delivers a continuous stream of air to keep the airway open. Lifestyle changes, including weight loss, smoking cessation, and reducing alcohol intake, can significantly improve symptoms. For more severe cases or when conservative measures fail, surgical options may be considered. Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare professionals are essential components of successful management.
If you or your partner have any of these symptoms, it is important to speak with a doctor to determine if sleep apnea is the cause. Sleep apnea can have serious health consequences if left untreated.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.