Dispelling Stroke Myths: Facts, Prevention, & Quick Action Tips
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of strokes, a critical medical condition that demands attention and understanding. Despite its prevalence, numerous myths surround strokes, leading to misconceptions and potential delays in treatment. In this article, we aim to debunk these misconceptions, providing vital information on the facts, prevention strategies, and swift actions crucial during a stroke. Join us on a journey to unravel the truth about strokes and empower yourself with knowledge to safeguard your health and the well-being of those around you.
Stroke is a serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, either due to a blockage or a burst blood vessel. Despite being a common condition, there are many myths that can lead to confusion and misinformation.
Myth 1: Strokes only affects the elderly
While it is more common in older adults, it can affect people of any age, including children. In fact, strokes are becoming increasingly common in younger adults due to risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. It is important to recognize the signs and seek medical attention immediately, regardless of age.
Myth 2: Strokes cannot be prevented
This is a common misconception that can be dangerous. While some risk factors, such as age and family history, cannot be changed, there are many lifestyle changes that can reduce your risk of having a stroke. These include maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes. By making these changes, you can significantly reduce your risk for strokes.
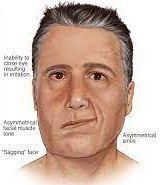
Myth 3: A Stroke always causes paralysis
While paralysis is a common complication, not all strokes lead to paralysis. The symptoms can vary depending on the part of the brain affected and the severity of the stroke. Other symptoms of strokes may include difficulty speaking or understanding speech, vision problems, and loss of coordination. It is important to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention immediately, as prompt treatment can greatly improve outcomes.
Myth 4: There is nothing you can do if someone is having a stroke
This is a dangerous myth that can lead to delayed treatment and poor outcomes. If you suspect someone is having a stroke, it is important to act quickly. Call emergency services immediately and note the time when the symptoms first appeared, as this information can be critical for treatment decisions. While waiting for help to arrive, keep the person calm and comfortable, and do not give them anything to eat or drink.
In conclusion, strokes are serious medical conditions that can have devastating consequences if not recognized and treated promptly. By debunking these common myths, we hope to raise awareness about strokes and encourage people to take steps to reduce their risk. Remember, if you suspect someone is having a stroke, act quickly and seek medical attention immediately.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this content is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or healthcare decisions.

